In the realm of hydraulic fittings, understanding the differences and similarities between JIC and AN fittings is crucial for making informed decisions that can affect the performance and longevity of hydraulic systems. Despite their similar 37-degree flare design, these fittings cater to different standards and applications, leading to potential confusion among users. This post aims to demystify JIC and AN fittings, providing a clear and comprehensive comparison that highlights their unique attributes and commonalities.
JIC
JIC fittings, developed by the Joint Industry Council, have a rich history rooted in the need for standardized hydraulic connections across various industries. Established to create a unified set of standards for hydraulic fittings, the Joint Industry Council aimed to ensure compatibility, reliability, and safety in hydraulic systems. JIC fittings feature a 37-degree flare design, which provides a secure, leak-resistant connection suitable for a wide range of applications.
The primary standard governing JIC fittings is SAE J514, which outlines the specifications for flare fittings used in hydraulic systems. This standard ensures that JIC fittings meet specific criteria for dimensions, materials, and performance, making them a trusted choice in many industries. JIC fittings are commonly used in agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial machinery, and various other sectors where hydraulic systems are essential.
AN
AN fittings, originating from military specifications developed for the U.S. Army and Navy, are designed to meet rigorous performance and reliability standards. These fittings were initially created to ensure high-quality, reliable connections in military aircraft and vehicles, where failure could have catastrophic consequences. Over time, AN fittings have become synonymous with precision and durability, making them a preferred choice in demanding applications.
The standards governing AN fittings are MIL-F-5509 and SAE AS4875, which specify the design, materials, and performance requirements for flare fittings used in military and aerospace applications. AN fittings also feature a 37-degree flare design but are manufactured to tighter tolerances and higher quality standards than their industrial counterparts. These fittings are commonly used in aerospace, military, high-performance automotive applications, and other sectors where superior performance and reliability are paramount.

Both JIC and AN fittings are typically made from high-quality materials to ensure durability and reliability. The most common materials used include:
Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and strength, stainless steel is often used in applications requiring long-lasting, durable fittings.
Carbon Steel: This material is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and mechanical properties, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Brass: Used for its excellent machinability and resistance to corrosion, brass is often chosen for low-pressure applications and environments where chemical resistance is essential.
Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, aluminum is commonly used in aerospace and automotive applications where weight reduction is crucial.
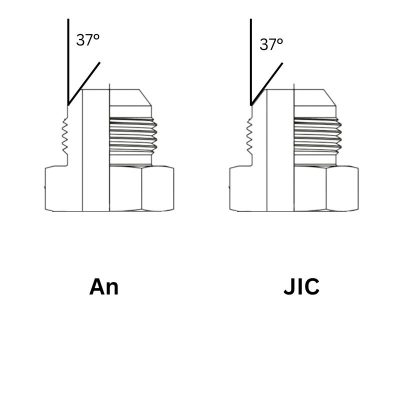
JIC and AN fittings share a 37-degree flare design, which provides a reliable, leak-resistant connection by compressing the flare against a mating seat. However, there are differences in their design specifications and threading:
Thread Types: JIC fittings typically use SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) threads, specifically SAE J514, which standardizes the dimensions and tolerances for these fittings. AN fittings, on the other hand, adhere to military specifications, such as MIL-F-5509 and SAE AS4875, ensuring higher precision and tighter tolerances.
Dimensions: While both fittings use a 37-degree flare, the dimensions of the threads and the fittings themselves may vary slightly. AN fittings are manufactured with more stringent tolerances, ensuring a more precise fit and reducing the risk of leaks or failure in high-stress environments.
The pressure ratings and performance standards for JIC and AN fittings are critical factors in their selection and use:
JIC Fittings: Typically rated for moderate to high-pressure applications, JIC fittings can handle pressures up to 10,000 PSI, depending on the size and material. The SAE J514 standard specifies the performance requirements, ensuring that JIC fittings provide reliable performance in various industrial applications.
AN Fittings: Designed for high-performance and high-pressure environments, AN fittings often exceed the pressure ratings of JIC fittings. These fittings can handle pressures up to 20,000 PSI or more, depending on the size, material, and application. The MIL-F-5509 and SAE AS4875 standards ensure that AN fittings meet the rigorous performance requirements necessary for military and aerospace applications.
Comparison of Angles
Both JIC and AN fittings utilize a 37-degree flare design. This specific angle is chosen because it provides an optimal balance between sealing efficiency and mechanical strength. The 37-degree flare allows the fitting to create a secure, leak-resistant seal when tightened against a mating surface. This design is effective in preventing leaks and ensuring reliable fluid transfer, which is crucial for the performance of hydraulic systems.
Despite sharing the same flare angle, JIC and AN fittings are not identical in other aspects of their design and construction. The shared 37-degree flare is a key point of similarity, but several differences set these fittings apart.
Differences in Thread Dimensions and Tolerance
While the 37-degree flare angle is consistent, the thread dimensions and tolerances between JIC and AN fittings differ significantly:
Thread Dimensions: JIC fittings adhere to SAE J514 standards, which specify the dimensions and tolerances for these fittings. The threads on JIC fittings are typically coarser and may have slightly different pitch and diameter compared to AN fittings. This difference can affect the ease of installation and the level of precision in the connection.
Tolerances: AN fittings, designed to meet military specifications (such as MIL-F-5509 and SAE AS4875), have much tighter tolerances than JIC fittings. These tighter tolerances ensure a higher degree of precision and reliability, which is essential in high-stress environments like aerospace and military applications. The stricter manufacturing standards for AN fittings result in a more consistent and dependable connection.

Common Industries Using JIC Fittings
JIC fittings are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Some common industries and applications include:
Agriculture: JIC fittings are commonly used in agricultural machinery, such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems. Their robust design and ease of use make them ideal for the demanding conditions of agricultural operations.
Construction: In the construction industry, JIC fittings are found in equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. Their ability to withstand high pressures and vibrations makes them suitable for heavy-duty construction machinery.
Industrial Machinery: JIC fittings are used in various types of industrial machinery, including manufacturing equipment, hydraulic presses, and material handling systems. Their reliability and availability make them a popular choice for industrial applications.
Common Industries Using AN Fittings
AN fittings are primarily used in applications that require the highest levels of performance and reliability. Some common industries and applications include:
Aviation: AN fittings were originally developed for military aviation and are now widely used in both military and civilian aircraft. Their high precision and durability ensure reliable performance in the critical systems of airplanes and helicopters.
Military: AN fittings are extensively used in military vehicles, including tanks, armored personnel carriers, and other ground vehicles. The stringent standards for these fittings ensure they can withstand the harsh conditions of military operations.
High-Performance Automotive: In the automotive industry, AN fittings are used in high-performance and racing vehicles. Their superior performance and reliability make them ideal for fuel, oil, and hydraulic systems in racing cars and other high-stress automotive applications.
The question of interchangeability between JIC and AN fittings is a common one, given their similar 37-degree flare design. While it is possible to connect JIC and AN fittings due to this shared feature, several important considerations must be taken into account:
Thread Compatibility: The thread dimensions and tolerances differ between JIC and AN fittings. While they may physically connect, the difference in tolerances can affect the sealing efficiency and reliability of the connection. AN fittings’ tighter tolerances ensure a more precise fit, whereas JIC fittings may not provide the same level of precision.
Performance Requirements: The choice between JIC and AN fittings should be based on the specific performance requirements of the application. In high-stress environments where reliability and precision are critical, AN fittings are the preferred choice. In less demanding applications, JIC fittings may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
When considering using JIC and AN fittings together, several potential issues and best practices should be addressed:
Leakage Risks: The difference in thread tolerances can lead to leakage if not properly managed. It is essential to ensure that the fittings are tightened correctly and inspected for any signs of leakage.
Pressure Ratings: Ensure that the pressure ratings of the fittings match the requirements of the application. Using fittings with lower pressure ratings in high-pressure systems can lead to failures and safety hazards.
Application Requirements
When selecting between JIC and AN fittings, understanding the specific requirements of your application is crucial. Key factors to consider include:
Pressure: The pressure rating of the fitting must match or exceed the system’s operating pressure. JIC fittings typically handle pressures up to 10,000 PSI, while AN fittings can withstand pressures up to 20,000 PSI or more. Ensure that the chosen fitting can safely accommodate the maximum pressure of your hydraulic system to prevent leaks and failures.
Temperature: The operating temperature range of the hydraulic system also plays a critical role in fitting selection. Both JIC and AN fittings are available in materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and aluminum, each offering different temperature tolerances. Select a material that can maintain integrity under the expected temperature conditions of your application.
Fluid Type: The compatibility of the fitting material with the hydraulic fluid used is essential to prevent corrosion and degradation. For example, stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and is suitable for a wide range of fluids, while brass is ideal for applications involving water or non-corrosive fluids. Ensure that the material chosen for the fittings is compatible with the hydraulic fluid to maintain system performance and longevity.
Adherence to industry standards and regulatory compliance is another critical factor in selecting the appropriate fitting. These standards ensure that the fittings meet specific safety, performance, and quality requirements:
JIC Standards: Governed by SAE J514, JIC fittings are widely accepted in industrial applications and ensure a certain level of performance and reliability. These standards specify dimensions, materials, and performance criteria, providing a benchmark for quality and compatibility.
AN Standards: AN fittings comply with military standards, such as MIL-F-5509 and SAE AS4875, which demand higher precision and tighter tolerances. These fittings are often required in aerospace and military applications where performance and reliability are paramount. Compliance with these standards ensures that the fittings can withstand the rigorous demands of these industries.
Cost considerations and the availability of fittings are also important practical factors:
Budget: JIC fittings are generally more cost-effective than AN fittings due to their broader use and lower manufacturing precision requirements. If the application does not demand the high precision and tight tolerances of AN fittings, JIC fittings can offer a more economical solution without compromising performance.
Availability: The widespread use of JIC fittings means they are readily available from various suppliers, making them easier to source and replace. AN fittings, while available, may be less common and potentially more expensive due to their specialized use and higher manufacturing standards.
One of the most prevalent myths about JIC and AN fittings is that they are fully interchangeable due to their shared 37-degree flare design. While it is true that both types of fittings use the same flare angle, this does not mean they can be used interchangeably without potential issues. The differences in thread dimensions and tolerances between JIC and AN fittings mean that although they may physically connect, they might not provide the same level of performance, reliability, or safety.
Another common misconception is that JIC fittings are inferior to AN fittings. While AN fittings are manufactured to meet more stringent military specifications, this does not inherently make JIC fittings inferior. JIC fittings are designed to meet the needs of a wide range of industrial applications and are cost-effective and versatile. Their performance is adequate for many uses, and they offer a reliable and economical solution for many hydraulic systems.
In summary, while JIC and AN fittings share a 37-degree flare design, they differ in thread dimensions, tolerances, and application suitability. JIC fittings are versatile and cost-effective for general industrial use, while AN fittings offer higher precision and reliability for demanding applications like aerospace and military. Making informed decisions when selecting fittings is crucial for ensuring system performance and safety. Consult with professionals to determine the best fitting for your specific needs.
The main difference lies in their thread dimensions and tolerances. JIC fittings adhere to SAE J514 standards, while AN fittings follow military specifications (MIL-F-5509 and SAE AS4875), ensuring tighter tolerances and higher precision.
While they can physically connect due to the same 37-degree flare design, differences in thread tolerances can affect sealing integrity and reliability. It’s best to use them as per their intended applications.
JIC fittings are commonly used in agriculture, construction, and industrial machinery due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and availability.
AN fittings are preferred because they are manufactured to meet stringent military standards, offering higher precision, reliability, and the ability to withstand extreme conditions and high pressures.
Both fittings are made from materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and aluminum, chosen based on the application’s requirements for corrosion resistance, strength, and temperature tolerance.
Consider factors like pressure, temperature, fluid type, industry standards, and budget. Consulting with industry professionals can help ensure you select the most suitable fitting for your specific application.