Core selection is not just a technical detail but a critical factor influencing the overall efficiency, longevity, and reliability of hydraulic systems. The right core can enhance the lifespan of a hose, reduce maintenance costs, and improve performance in high-pressure or high-flexibility applications.
Understanding Hydraulic Hoses and Their Core Components
Hydraulic Hose Basics
A hydraulic hose is a critical component in hydraulic systems, designed to convey pressurized fluid between various parts of the system, such as pumps, valves, actuators, and cylinders. Hydraulic hoses are used in numerous industries, including construction, automotive, agriculture, and manufacturing, where high-pressure fluid power is needed to operate machinery and equipment. The primary function of a hydraulic hose is to transfer hydraulic fluid under high pressure, and this fluid can be oil, water, or other liquids depending on the application.
What makes hydraulic hoses indispensable is their ability to carry fluid at very high pressures, typically ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 psi, depending on the application. The key to maintaining such high pressures without leakage or failure is the design and construction of the hose, specifically the core and the layers surrounding it. The core material of a hydraulic hose plays a significant role in determining its pressure tolerance, flexibility, durability, and overall lifespan.
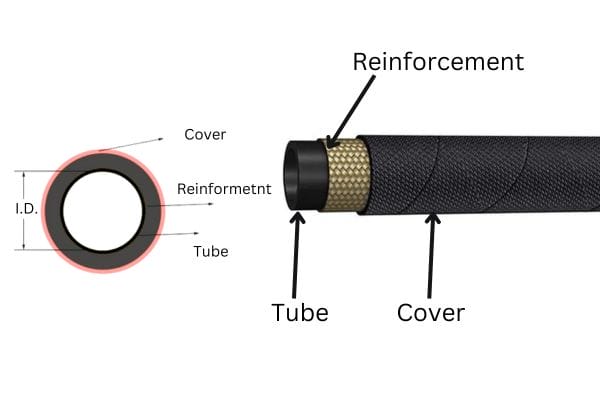
Core Structure in Hydraulic Hoses
The core of a hydraulic hose is the central component that directly interacts with the fluid being transferred. It serves as the primary structural element that withstands the pressure and maintains the internal flow of fluid. The core is typically made from materials that can handle internal pressure while resisting wear and tear over time.
In addition to pressure tolerance, the core of a hydraulic hose must also be flexible enough to allow for the hose’s movement without breaking or kinking. This balance between strength and flexibility is one of the key considerations in designing hydraulic hoses. The core works in conjunction with additional layers, such as reinforcement (made from steel or synthetic fibers) and outer covers (designed for abrasion resistance and environmental protection).
The core also plays a crucial role in determining the hose’s ability to handle high and low temperatures, as well as its chemical resistance. If the core material is too rigid, the hose may be unable to flex or bend without cracking, which could lead to failure. Conversely, if the core is too soft, the hose may not be able to withstand the pressure of the fluid, resulting in leakage or bursting.
Types of Core Materials
There are two primary types of core materials used in hydraulic hoses: softcore and rigid core. Each material offers distinct advantages and is selected based on the specific demands of the hydraulic system.
Soft Core:
Soft core materials are typically made from synthetic rubber or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). These materials are flexible, lightweight, and resistant to kinking, making them ideal for applications where the hose needs to bend or flex frequently, such as in machinery with moving parts. The flexibility of a soft core allows hydraulic hoses to navigate tight spaces and curve around obstacles without compromising the flow of fluid. However, soft core hoses are generally less resistant to high-pressure environments compared to their rigid counterparts.
Rigid Core:
Rigid core hoses are constructed with materials like steel, stainless steel, or composite materials. These materials provide greater strength and durability, allowing the hose to withstand higher pressure and more demanding environments. Rigid core hoses are typically used in static applications, such as in fixed industrial systems or where the hose must remain straight and resist mechanical stresses. While they offer superior pressure resistance, their lack of flexibility can limit their use in dynamic applications where bending and flexibility are required.
What is a Soft Core in Hydraulic Hoses?
Definition and Description
A soft core in hydraulic hoses refers to a central material that is flexible and adaptable, typically made from synthetic rubber, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), or other flexible polymer compounds. Unlike rigid cores, which are built from materials such as metal or reinforced composites, soft cores prioritize flexibility and ease of handling. The material’s elasticity and capacity to bend without cracking or breaking make softcore hoses ideal for applications that require frequent movement or tight installation spaces.
The soft core is the innermost layer of the hydraulic hose, through which the hydraulic fluid flows. It is encased by one or more layers of reinforcement (such as braided steel or synthetic fibers) and an outer cover that protects against external elements like heat, abrasion, and chemicals. While soft core hoses are designed to handle high-pressure fluid systems, their main feature is the ability to flex and move without significant degradation of the hose structure.
The primary distinction between a soft core and a rigid core is in their flexibility. Soft core hoses are designed for dynamic systems where movement is a factor. In contrast, rigid core hoses are designed to maintain a fixed shape under pressure, making them better suited for static applications.
Advantages of Soft Core
The key benefits of soft core hydraulic hoses are tied to their flexibility, lightness, and ability to operate in dynamic environments. These advantages make soft core hoses an attractive choice for various industrial applications. Here’s a closer look at the major benefits:
Flexibility
The most notable advantage of soft core hydraulic hoses is their exceptional flexibility. Unlike rigid core hoses, which can be difficult to manipulate in confined spaces, soft core hoses can easily bend, twist, and curve without breaking. This flexibility allows for easier installation, especially in complex systems with limited access or tight corners. Additionally, soft core hoses can move with the equipment they are connected to, reducing the risk of damage due to bending or stretching.
Lightweight
Soft core hoses tend to be significantly lighter than their rigid counterparts, primarily due to the use of synthetic materials such as rubber and TPE. This reduced weight not only makes them easier to handle during installation and maintenance but also reduces the overall weight load on the hydraulic system. This feature is particularly important in mobile and heavy-duty equipment, such as construction machinery, where minimizing weight can enhance performance and fuel efficiency.
Resistance to Kinking
Another major advantage of soft core hydraulic hoses is their resistance to kinking. A kink in a hydraulic hose can cause serious issues in fluid flow, potentially leading to system malfunctions or even complete failure. The flexible nature of soft core hoses allows them to absorb bends and twists without compromising the internal flow of fluid. This makes them especially suitable for systems where hoses are subjected to frequent movement or positioning, such as in construction, agricultural, and automotive applications.
Suitable for Dynamic Applications
Soft core hoses are ideal for dynamic hydraulic systems, where the hoses must move, flex, or be repositioned during normal operation. For instance, construction machines like cranes, excavators, and bulldozers often use soft core hoses because of their ability to withstand bending, stretching, and vibration without failure. Similarly, agricultural machinery that operates in varied terrains benefits from soft core hoses, as these hoses can flex with the movement of the vehicle and the shifts in terrain.

Applications of Soft Core Hoses
Due to their flexibility, lightweight nature, and ability to resist kinking, soft core hoses are used across a wide variety of industries. Some of the key applications include:
Construction
In construction, heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes rely on soft core hoses for hydraulic power. The hoses in these machines must endure constant movement and exposure to harsh environments, making the flexibility of a soft core essential. Additionally, construction equipment often operates in tight or irregular spaces, where rigid hoses would be impractical.
Agriculture
Agricultural equipment, including tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems, frequently uses soft core hydraulic hoses. These machines often need to navigate rough, uneven terrain and deal with frequent adjustments, meaning flexibility and resistance to kinking are paramount. Soft core hoses allow farmers to operate equipment efficiently while minimizing the risk of hose failure in dynamic conditions.
Automotive and Transport
Soft core hoses are also used in automotive and transport systems, particularly in mobile hydraulic systems. They can be found in vehicles such as trucks, trailers, and buses, where flexible hoses are needed to manage hydraulic systems that may require frequent adjustments or exposure to movement.
Limitations of Soft Core Hoses
While soft core hoses offer numerous benefits, they are not without limitations. Understanding these limitations is crucial when selecting the right hose for a specific application:
Lower Pressure Ratings
One of the primary drawbacks of soft core hydraulic hoses is their lower pressure tolerance when compared to rigid core hoses. Due to the flexible nature of the core material, soft core hoses typically have lower pressure ratings, which means they may not be suitable for high-pressure hydraulic systems or applications where very high fluid pressure is required. While soft core hoses can handle moderate to high pressures, they may not be able to withstand extreme pressures found in industries like aerospace or high-performance industrial machinery.
Reduced Durability in High-Stress Environments
Soft core hoses tend to be less durable in environments where high temperatures, extreme abrasion, or chemical exposure are prevalent. While some soft core hoses come with protective covers to improve resistance to these factors, they are still more susceptible to wear and tear compared to rigid core hoses. In high-stress environments, soft core hoses may degrade faster, requiring more frequent maintenance and replacement.
Limited Use in Static Applications
Soft core hoses are best suited for dynamic, flexible applications. In static applications where the hose needs to remain fixed and resist movement, a rigid core hose is often more appropriate due to its superior structural integrity and pressure-bearing capabilities.
What is a Rigid Core in Hydraulic Hoses?
Definition and Description
A rigid core in hydraulic hoses refers to the central structural component made from materials that provide exceptional strength and stiffness, typically metal (such as steel or stainless steel) or composite materials. Unlike soft core hoses, which are designed for flexibility, rigid core hoses are engineered to maintain a fixed shape and resist deformation under high pressure. These hoses are ideal for applications that require structural stability and the ability to handle extreme conditions without losing their form.
The construction of a rigid core hydraulic hose involves a tough inner core, often reinforced with multiple layers to enhance its ability to withstand high pressures and environmental stress. The core is usually covered by several layers of reinforcement—such as braided steel wire, spiral wire, or synthetic fibers—that provide additional strength and resistance to mechanical damage. Finally, an outer protective cover shields the hose from abrasion, chemicals, UV light, and other environmental factors. This multi-layer design ensures that the hose can carry fluids under high pressure while remaining structurally intact.
Unlike soft core hoses, which excel in dynamic, flexible applications, rigid core hoses are better suited to static installations where movement is limited or not required.
Advantages of Rigid Core
The rigid core hydraulic hose offers several key benefits that make it the ideal choice for high-pressure, static applications. Here are the primary advantages:
Higher Pressure Tolerance
One of the most significant advantages of rigid core hoses is their ability to withstand much higher pressures compared to soft core hoses. The rigid materials used in the core provide increased structural integrity, which allows the hose to carry fluids under higher internal pressures without risk of deformation or failure. This makes rigid core hoses essential for systems that operate in environments where fluid pressure exceeds the limits that a soft core hose could safely handle. For example, they are commonly used in industrial applications and heavy-duty machinery that require fluid pressures of 5,000 psi or higher.
Durability in Harsh Environments
Rigid core hoses are known for their superior durability, especially in harsh environments. Their construction is designed to resist extreme conditions such as high temperatures, exposure to chemicals, abrasion, and mechanical stress. Rigid core hoses can be used in industries such as oil and gas, mining, and heavy machinery, where hoses are subjected to continuous wear and tear from abrasive materials, harsh weather conditions, and exposure to chemicals. The rigid core’s ability to maintain its structure over time, even under severe stress, contributes significantly to the hose’s lifespan.
Greater Structural Integrity
The rigid core provides enhanced structural integrity, meaning these hoses are less likely to collapse, expand, or deform when exposed to high pressure. The rigid material prevents the hose from becoming deformed under heavy loads, ensuring the fluid flow is consistent and uninterrupted. This characteristic makes rigid core hoses ideal for hydraulic systems where maintaining the integrity of the hose is critical for smooth operations, such as in large industrial machines and fixed hydraulic systems.
Better Suited for Static Applications
Rigid core hoses excel in static applications, where flexibility is not a primary concern. For example, in fixed installations such as those found in factories, power plants, or oil rigs, rigid core hoses can be laid out in a permanent configuration. They remain stable and reliable without the need for movement or repositioning. Rigid core hoses are typically used in high-pressure lines that require minimal flexing, providing an excellent solution where flexibility would add unnecessary complexity or risk to the system.

Applications of Rigid Core Hoses
Rigid core hydraulic hoses are used in a wide range of industrial and high-pressure systems where the demands for durability and pressure resistance outweigh the need for flexibility. Some of the common applications of rigid core hoses include:
Industrial Machinery
Rigid core hoses are widely used in heavy-duty industrial machinery where high-pressure hydraulic systems are required. These include hydraulic presses, injection molding machines, and large construction equipment. In these systems, hoses must be able to handle constant high pressure without collapsing or degrading, making the rigidity of the core crucial. The use of rigid core hoses ensures long-lasting, reliable performance even in the most demanding conditions.
Oil & Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, hydraulic systems are exposed to extreme pressure and hazardous environments. Rigid core hoses are used to transfer fluids in offshore drilling rigs, refineries, and pipelines. These hoses can handle the high-pressure fluid transfer required for drilling operations while withstanding the corrosive nature of the chemicals and the harsh conditions at sea. Rigid core hoses are critical for ensuring that hydraulic systems in oil rigs continue to operate efficiently and safely under high-pressure conditions.
Mining
Mining operations use rigid core hydraulic hoses in the machines responsible for drilling, excavating, and transporting materials. These hoses are exposed to heavy-duty conditions, including extreme pressure and constant abrasion from dirt, rock, and other abrasive materials. The robust nature of the rigid core hose ensures it remains intact and functional even in the harshest of environments, providing consistent fluid transfer for mining equipment.
Limitations of Rigid Core Hoses
While rigid core hydraulic hoses offer several advantages, they also come with some limitations that need to be considered when choosing the right hose for an application:
Less Flexibility
The main limitation of rigid core hoses is their lack of flexibility. Unlike soft core hoses, which can bend and flex to accommodate movement, rigid core hoses are designed to remain straight and resist bending. This lack of flexibility can make installation more challenging in environments where hoses need to be routed through tight spaces or around obstacles. Additionally, rigid hoses are less suitable for dynamic systems that require frequent movement, as they can be prone to cracking or breaking when subjected to constant flexing.
Prone to Bending Under Stress
While rigid core hoses are durable, they can become susceptible to bending or damage under extreme mechanical stress. When subjected to bending forces beyond their design capacity, rigid core hoses may lose their structural integrity, leading to cracks or ruptures. This can be a particular concern in systems where the hose must be installed in areas subject to vibration or physical movement, as the rigid nature of the hose could lead to premature failure.
Conclusion
Choosing between a soft core and a rigid core hose depends on the specific needs of your hydraulic system. If your application involves constant movement, flexibility, and resistance to kinking, soft core hoses are likely the best option. For personalized advice on selecting the right core for your hydraulic hoses, consider reaching out to Topa.
FAQ
What is the difference between soft vs rigid core hydraulic hoses?
Soft core hoses are flexible and ideal for dynamic applications where frequent movement is required. Rigid core hoses are more rigid, providing higher pressure tolerance and durability, making them suitable for static or high-pressure systems.
When should I use a soft core hydraulic hose?
Soft core hoses are best used in applications that involve frequent movement, tight spaces, or bending, such as in construction, agriculture, and automotive industries.
What are the benefits of a rigid core hydraulic hose?
Rigid core hoses offer higher pressure resistance, greater durability in harsh environments, and better structural integrity, making them ideal for high-pressure, static applications like industrial machinery or oil and gas systems.
Can soft core hoses handle high pressure?
Soft core hoses can handle moderate to high pressures but are not suitable for extremely high-pressure systems. Rigid core hoses are preferred for applications requiring very high pressure.
Are rigid core hoses flexible?
No, rigid core hoses are not flexible. They are designed for static installations and are less suitable for dynamic systems that require bending or frequent movement.
How do I choose between soft core and rigid core for my hydraulic system?
Choose soft core hoses for flexibility and movement in low to medium-pressure systems, and rigid core hoses for high-pressure systems where structural integrity and durability are more critical. Always consider the specific demands of your application.





