Will JIC Fittings Work with AN Fittings?
Introduction
JIC (Joint Industry Council) and AN (Army-Navy) fittings are both popular in various industries due to their reliable performance in high-pressure and high-vibration environments. Understanding their compatibility is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety in hydraulic systems. This post explores whether JIC fittings can be used with AN fittings, highlighting their differences and similarities, and providing practical guidelines for their use.
Will JIC Fittings Work with AN Fittings?
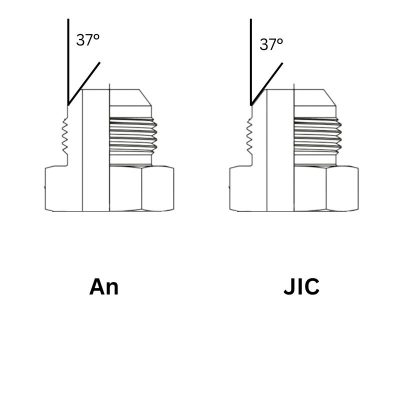
JIC and AN fittings have similar 37-degree flares, allowing them to physically connect. However, due to different thread tolerances and standards, they are not ideally interchangeable. Using JIC fittings in place of AN fittings can lead to leaks and equipment failure while using AN fittings instead of JIC might be unnecessarily costly. The choice depends on the application’s requirements, with AN fittings preferred for high-precision, high-vibration environments and JIC fittings suitable for general hydraulic systems.
Understanding JIC and AN Fittings
What Are JIC Fittings?
JIC hydraulic fittings are a type of flare fitting standardized under SAE J514. These fittings are known for their 37-degree flare seating surface, which creates a tight and leak-proof seal when connected. Commonly used in hydraulic applications, JIC fittings are prized for their robustness, ease of assembly, and adaptability across a range of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
JIC fittings come in various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and brass, each chosen based on the specific requirements of the application. Their versatility and durability make them a preferred choice in environments where reliability and performance are critical.
What Are AN Fittings?
AN fittings were originally developed for military use and adhere to the stringent standards set by military specification MS33656. Like JIC fittings, AN fittings feature a 37-degree flare but are manufactured to much tighter tolerances. This precision ensures a secure fit and reliable performance in high-pressure and high-vibration applications. AN fittings are commonly used in aviation, aerospace, and high-performance automotive sectors, where exacting standards are a necessity.
The materials used for AN fittings typically include high-grade aluminum alloys and stainless steel, providing excellent strength and corrosion resistance. The rigorous manufacturing process ensures that AN fittings can handle extreme conditions, offering long-term reliability and safety. These fittings are designed to meet the highest standards of performance, making them indispensable in critical applications where failure is not an option.
Historical Background
The development of JIC and AN fittings can be traced back to different needs and standards. JIC fittings emerged from the industrial sector’s need for a standardized hydraulic connection that could be universally applied across various equipment and machinery. Over time, JIC fittings became a standard in industries requiring robust and reliable hydraulic connections.
AN fittings, on the other hand, were developed to meet the exacting demands of military and aerospace applications. The military required fittings that could withstand extreme conditions, including high pressure, vibration, and varying temperatures. The AN fitting was designed to provide a superior level of precision and reliability, meeting stringent military specifications.
As industries evolved, both JIC and AN fittings were adapted to meet specific needs, resulting in distinct differences in their specifications and uses. While JIC fittings offer versatility and ease of use for general applications, AN fittings provide unmatched precision and reliability for high-stakes environments.
Technical Specifications and Differences
Thread Tolerances and Standards
JIC fittings are manufactured in accordance with SAE standards, which allow for slight variations in thread tolerances. This flexibility is sufficient for many industrial applications but can lead to minor deviations in thread alignment. On the other hand, AN fittings adhere to stringent military specifications, resulting in highly precise and uniform threading. This level of precision is essential in applications where even the smallest deviations can lead to performance issues, such as in aviation or high-performance automotive systems. The tighter tolerances of AN fittings ensure a more secure and reliable connection, minimizing the risk of leaks and mechanical failures.
Material and Build Quality
JIC fittings are typically made from a range of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and brass. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the environmental conditions the fitting will encounter. Carbon steel is commonly used for its strength and affordability, stainless steel for its corrosion resistance and durability, and brass for its excellent machinability and resistance to corrosion.
In contrast, AN fittings are often made from high-grade aluminum alloys or stainless steel. Aluminum alloys are favored in applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in aerospace and racing, while stainless steel is used for its exceptional strength and resistance to extreme conditions. The high-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes used for AN fittings ensure they can withstand the rigorous demands of high-performance environments, providing long-lasting reliability and safety.
Pressure Ratings and Temperature Limits
The pressure ratings and temperature limits of JIC and AN fittings differ significantly due to their intended applications and manufacturing standards. JIC fittings generally have lower pressure ratings, making them suitable for less demanding applications. They are designed to handle a range of pressures, but their ratings typically do not match the higher thresholds required for critical applications.
AN fittings are engineered to endure higher pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for use in high-stakes environments where failure is not an option. The stringent manufacturing standards and superior material quality of AN fittings allow them to perform reliably under extreme conditions, ensuring the integrity of the hydraulic or fluid transfer systems they are used in.
Design and Shape Variations
While both JIC and AN fittings feature a 37-degree flare, the design and shape of AN fittings are often more refined. AN fittings typically have smoother surfaces and more precise angles, which contribute to their enhanced performance and reliability. These subtle design differences result from the tighter manufacturing tolerances and higher standards to which AN fittings are held. The refined design of AN fittings ensures a more secure and leak-proof connection, even in the most demanding applications.
In contrast, JIC fittings, while still effective, may have slightly less precise dimensions due to the broader manufacturing tolerances allowed by SAE standards. These differences, though minor, can impact the overall performance and reliability of the fittings in specific applications. Therefore, understanding the design and shape variations between JIC and AN fittings is crucial for selecting the appropriate fitting for the intended use, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Compatibility and Interchangeability
Physical Compatibility
JIC and AN fittings can physically connect due to their identical 37-degree flare. However, the differences in thread tolerances mean that the fit might not be perfect, potentially leading to issues like leaks. It’s essential to ensure that the fittings are properly aligned and torqued to avoid any connection problems. A misaligned or improperly torqued fitting can compromise the seal, leading to leaks or system failure.
Functional Compatibility
Using JIC fittings where AN fittings are required can result in suboptimal performance, including leaks and equipment failure. This is due to the looser thread tolerances of JIC fittings, which may not provide the precise fit needed in high-performance applications. Conversely, using AN fittings in place of JIC is generally acceptable but may not be cost-effective due to the higher price of AN fittings. While AN fittings will usually perform well in place of JIC, the increased cost might not justify their use in less critical applications. It’s crucial to match the fitting type to the application’s specific requirements to avoid functional issues.
How to Choose Suitable JIC and AN Fittings
Understand Application Requirements
Operating Conditions: Determine the operating pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions your fittings will face. High-pressure environments, extreme temperatures, and specific environmental factors (like exposure to corrosive substances) will influence your choice.
Application Criticality: Assess how critical the application is. For instance, aerospace and high-performance automotive systems require fittings with high precision and reliability, while general industrial machinery may not need such stringent specifications.
Material Selection
JIC Fittings: Choose materials like carbon steel for its strength and cost-effectiveness, stainless steel for its corrosion resistance and durability, or brass for excellent machinability and moderate corrosion resistance. The material choice should match the environmental conditions and mechanical demands of the application.
AN Fittings: High-grade aluminum alloys are suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and motorsport. Stainless steel is chosen for its superior strength and resistance to harsh environments, ensuring long-term reliability.
Performance Needs
JIC Fittings: Ideal for applications involving moderate pressure and vibration, JIC fittings offer versatility and ease of assembly, making them suitable for various industrial uses.
AN Fittings: AN fittings are designed for high-performance and high-precision applications where strict tolerance requirements are necessary. Their use in aerospace, racing, and other demanding fields underscores their reliability and precision.
Cost Considerations
JIC Fittings: More cost-effective and suitable for non-critical applications where performance demands are moderate. Their affordability makes them a practical choice for general hydraulic systems.
AN Fittings: Although more expensive, AN fittings justify their cost in critical applications where failure is not an option. Their higher initial investment is offset by their reliability and performance in demanding environments.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper Installation: Ensure that fittings are properly aligned and torqued during installation. Misalignment or incorrect torque can lead to leaks and system failures.
Regular Maintenance: Conduct regular inspections and maintenance to detect and address any issues early. Proper maintenance practices, such as checking for signs of wear and ensuring connections remain secure, can significantly extend the life of the fittings and maintain system performance.
Conclusion
JIC and AN fittings can physically connect due to their identical 37-degree flare, but their differing thread tolerances can lead to potential issues like leaks. AN fittings can replace JIC fittings in less critical applications, but it’s not cost-effective. If you have any needs, just contact Topa!
Topa's Custom JIC and AN Fitting Services
Custom Design and Manufacturing
At Topa, we specialize in providing customized JIC and AN fittings tailored to meet your specific requirements. Our expert team collaborates closely with clients to understand their unique needs, ensuring that each fitting we produce meets the highest standards of quality and precision.
Our customization process includes:
Detailed consultations to understand client requirements
Designing fittings to meet specific application needs
Utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques for precision
High-Quality Materials
We offer fittings made from a variety of high-quality materials, including:
Carbon Steel: Known for its strength and cost-effectiveness, ideal for general industrial applications.
Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability, suitable for harsh environments.
Brass: Provides good machinability and resistance to corrosion, perfect for moderate conditions.
High-Grade Aluminum Alloys: Lightweight and durable, essential for aerospace and performance applications.
Each material is selected based on the specific demands of your application, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.

Strict Adherence to Standards
Topa’s fittings are manufactured to meet stringent SAE and military standards, guaranteeing reliable performance even in the most demanding environments. This adherence to high standards ensures that our fittings:
Maintain consistent quality
Provide secure and leak-proof connections
Perform reliably under varying conditions
Versatile Applications
Our custom JIC and AN fittings are designed to serve a wide range of industries, including:
Automotive: Ensuring reliable fluid transfer in vehicles.
Aerospace: Providing high precision and durability in aircraft systems.
Industrial Machinery: Offering robust connections for heavy machinery.
High-Performance Applications: Ensuring optimal performance in racing and other high-stakes environments.
Competitive Pricing and Timely Delivery
At Topa, we understand the importance of cost and efficiency. Therefore, we offer:
Competitive pricing without compromising on quality
An extensive inventory to enable prompt delivery
Efficient supply chain management to ensure timely service
Our goal is to keep your operations running smoothly with high-quality fittings delivered on time.
Customer Support
We pride ourselves on exceptional customer support. Our dedicated team is always available to:
Assist with inquiries
Provide professional guidance on fitting selection
Offer after-sales support to ensure customer satisfaction
Our commitment to service ensures that you receive the right fittings for your needs, backed by reliable support.
Contact Us
For more information on our custom JIC and AN fitting services, please contact us through our website or via direct email communication. We are committed to providing top-notch products and exceptional service to our clients worldwide.
FAQ
JIC fittings follow SAE standards with moderate thread tolerances, while AN fittings adhere to stricter military specifications with tighter tolerances, offering higher precision.
They can physically connect due to their identical 37-degree flare, but differences in thread tolerances may cause leaks or performance issues. It’s generally not recommended to use them interchangeably.
JIC fittings are typically made from carbon steel, stainless steel, or brass. AN fittings are often made from high-grade aluminum alloys or stainless steel.
JIC fittings are used in automotive, industrial machinery, and general hydraulic applications. AN fittings are used in aerospace, high-performance automotive, and military applications.
Consider the operating pressure, temperature, environmental conditions, and criticality of the application. JIC fittings are suitable for moderate conditions, while AN fittings are ideal for high-performance environments.
JIC fittings are generally more cost-effective for non-critical applications, while AN fittings, though more expensive, provide reliability and performance in demanding environments.