In hydraulic systems, the correct selection of pipe threads is crucial for maintaining proper sealing, pressure management, and overall system integrity. Misunderstanding or misusing different thread types can lead to leakage, pressure loss, or even equipment failure, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. Each of these thread types—BSPP, BSPT, PF, and PT—has unique characteristics suited to specific applications.
Overview of Pipe Thread Standards
General Definition
Pipe threads are standardized helical structures that allow for the mechanical connection of pipes and fittings. Their primary role is to create a seal that prevents fluid leakage while ensuring secure connections between components in hydraulic systems. The threads facilitate easy assembly and disassembly, which is crucial for maintenance and repair. Properly designed and implemented pipe threads contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of hydraulic systems, ensuring that fluids are transported under the required pressure without leaks.
International Standards
Various international standards govern pipe threads to ensure compatibility and performance across different applications and regions. The most notable standards include:
ISO (International Organization for Standardization): This organization sets global standards, including ISO 7-1 for taper threads (similar to BSPT) and ISO 228-1 for parallel threads (similar to BSPP). These standards facilitate international trade and ensure consistency in product quality.
JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards): JIS outlines specific standards for Japanese threads, including JIS B0202 for PF threads and JIS B0203 for PT threads. These standards ensure that products manufactured in Japan meet quality and compatibility requirements for hydraulic applications.
BS (British Standards): The British Standards Institution (BSI) provides guidelines for BSP threads, with specifications such as BS EN 10226-1 for tapered threads and BS2779 for parallel threads. These standards ensure that fittings and pipes manufactured in the UK or imported from other countries adhere to established performance criteria.
These international standards promote interoperability among different manufacturers, reducing the risk of assembly errors and ensuring that components function correctly within hydraulic systems.
Importance of Choosing the Right Thread
Selecting the correct pipe thread type is vital for several reasons:
System Integrity: The right thread ensures a secure connection that can withstand operational pressures and prevent leaks. Incorrect thread types may lead to improper sealing, causing fluid loss and reducing system efficiency.
Safety: Hydraulic systems often operate under high pressure. A failure due to improper thread selection can lead to catastrophic results, including equipment damage, environmental hazards, and personal injury. Proper thread choice minimizes these risks.
Compatibility: Different regions and industries may utilize varying thread standards. Choosing the right thread type ensures compatibility with existing systems, facilitating repairs and upgrades without requiring extensive modifications.
Cost Efficiency: Using the appropriate thread type can lead to reduced maintenance costs and extended equipment life. Preventing leaks and ensuring secure connections means less downtime and fewer repairs, resulting in significant savings over time.
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) Thread
Definition
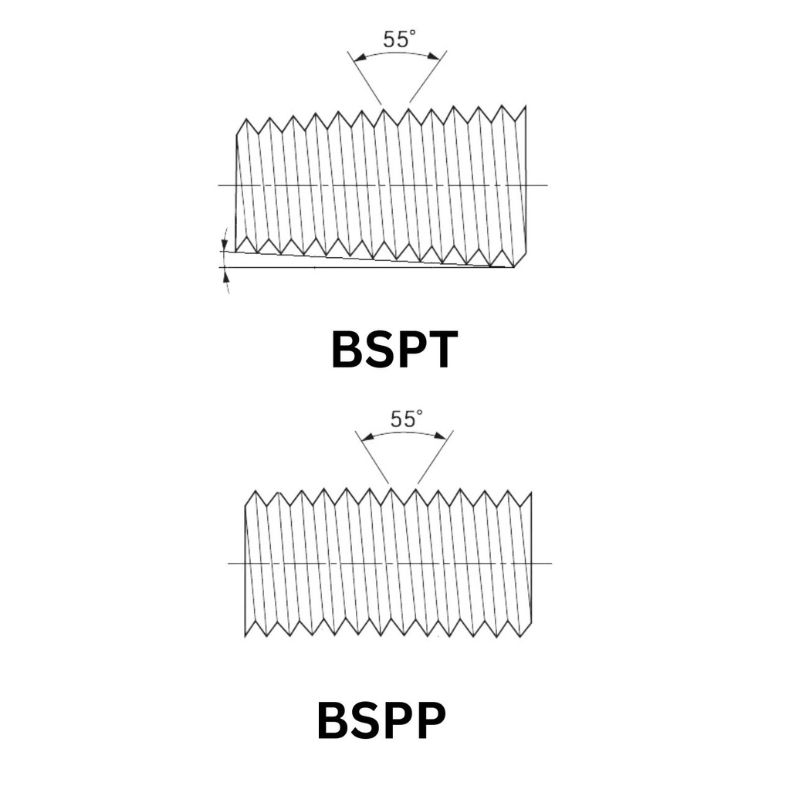
BSPP, or British Standard Pipe Parallel, is a type of pipe thread characterized by its parallel design. Unlike tapered threads, BSPP threads do not taper along their length; instead, they maintain a consistent diameter. This design is typically used with a sealing mechanism that involves a bonded washer or O-ring placed at the base of the fitting. The sealing occurs between the fitting and the mating surface, which helps prevent fluid leaks without relying on thread engagement alone.
Standards
BSPP threads conform to several important standards, ensuring consistency and compatibility across various applications:
ISO 228-1: This international standard specifies the requirements for parallel threads without a sealing surface, ensuring that fittings meet global compatibility.
DIN 259: A German standard that defines specifications for various pipe threads, including BSPP, further promoting international interoperability.
BS2779: The British Standard provides guidelines for BSP threads, ensuring they meet safety and quality standards in the UK and beyond.
Applications
BSPP threads are widely used in hydraulic systems across Europe, Asia, and other regions. Typical applications include:
Hydraulic Machinery: Commonly found in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial hydraulic systems.
Pneumatic Systems: Used in air and gas connections where a secure, leak-free joint is essential.
Water and Fluid Transport: Employed in plumbing and fluid transfer systems due to their reliability in preventing leaks.
Advantages
BSPP threads offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice in many applications:
Ease of Sealing: The use of bonded washers or O-rings allows for a secure seal without needing to apply excessive torque, reducing the risk of damaging components.
Widespread Availability: BSPP fittings and components are readily available in many markets, making sourcing replacements or upgrades straightforward.
Interchangeability: Due to standardization, BSPP threads can often be interchanged with other compatible thread types, increasing flexibility in design and repair.
Cost-Effectiveness: Their reliable sealing mechanism can lead to lower maintenance costs and extended service life of hydraulic systems.
Common Issues
Despite their advantages, there are potential issues associated with BSPP threads, particularly if not properly matched or sealed:
Incorrect Torque Application: Over-tightening can lead to damage or deformation of the fitting, while under-tightening may result in leaks.
Incompatibility with Tapered Threads: Mixing BSPP with BSPT or other tapered threads can cause sealing failures due to the lack of proper alignment and engagement.
Wear and Tear: Over time, the sealing elements (washers or O-rings) may wear out, leading to leaks if not regularly inspected and replaced.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures can compromise the integrity of the seals, necessitating careful material selection based on the application.
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) Thread
Definition
BSPP, or British Standard Pipe Parallel, is a type of pipe thread characterized by its parallel design. Unlike tapered threads, BSPP threads do not taper along their length; instead, they maintain a consistent diameter. This design is typically used with a sealing mechanism that involves a bonded washer or O-ring placed at the base of the fitting. The sealing occurs between the fitting and the mating surface, which helps prevent fluid leaks without relying on thread engagement alone.
Standards
BSPP threads conform to several important standards, ensuring consistency and compatibility across various applications:
ISO 228-1: This international standard specifies the requirements for parallel threads without a sealing surface, ensuring that fittings meet global compatibility.
DIN 259: A German standard that defines specifications for various pipe threads, including BSPP, further promoting international interoperability.
BS2779: The British Standard provides guidelines for BSP threads, ensuring they meet safety and quality standards in the UK and beyond.
Applications
BSPP threads are widely used in hydraulic systems across Europe, Asia, and other regions. Typical applications include:
Hydraulic Machinery: Commonly found in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial hydraulic systems.
Pneumatic Systems: Used in air and gas connections where a secure, leak-free joint is essential.
Water and Fluid Transport: Employed in plumbing and fluid transfer systems due to their reliability in preventing leaks.
Advantages
BSPP threads offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice in many applications:
Ease of Sealing: The use of bonded washers or O-rings allows for a secure seal without needing to apply excessive torque, reducing the risk of damaging components.
Widespread Availability: BSPP fittings and components are readily available in many markets, making sourcing replacements or upgrades straightforward.
Interchangeability: Due to standardization, BSPP threads can often be interchanged with other compatible thread types, increasing flexibility in design and repair.
Cost-Effectiveness: Their reliable sealing mechanism can lead to lower maintenance costs and extended service life of hydraulic systems.
Common Issues
Despite their advantages, there are potential issues associated with BSPP threads, particularly if not properly matched or sealed:
Incorrect Torque Application: Over-tightening can lead to damage or deformation of the fitting, while under-tightening may result in leaks.
Incompatibility with Tapered Threads: Mixing BSPP with BSPT or other tapered threads can cause sealing failures due to the lack of proper alignment and engagement.
Wear and Tear: Over time, the sealing elements (washers or O-rings) may wear out, leading to leaks if not regularly inspected and replaced.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures can compromise the integrity of the seals, necessitating careful material selection based on the application.
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) Thread
Definition
BSPT, or British Standard Pipe Taper, is characterized by its tapered design, which facilitates a tighter seal through metal-to-metal contact. As the threads are tapered, they become progressively narrower along their length, allowing for a secure fit as the fittings are tightened. This design promotes a strong, leak-resistant connection, making BSPT threads ideal for high-pressure applications.
Standards
BSPT threads are governed by several key standards, which ensure their reliability and compatibility:
ISO 7-1: This international standard specifies the requirements for tapered threads, including dimensions and performance criteria, ensuring consistency in global applications.
BS EN 10226-1: A European standard that outlines requirements for both parallel and tapered threads, further enhancing compatibility in hydraulic systems across Europe.
Applications
BSPT threads are commonly used in scenarios where secure, high-pressure sealing is essential. Typical applications include:
Hydraulic Systems: Widely employed in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and industrial applications requiring robust connections that can withstand high pressures.
Pneumatic Systems: Utilized in air compressor and pressure regulation systems where leak-proof fittings are critical.
Oil and Gas Industry: Used in pipelines and equipment that transport fluids under high pressure, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Advantages
BSPT threads offer several advantages that make them suitable for demanding applications:
Effectiveness in High-Pressure Systems: The tapered design allows for a tighter fit, providing enhanced sealing capabilities, which is vital for high-pressure applications.
Compatibility with Sealants: BSPT threads can be effectively used with various thread sealants, enhancing their leak-proof capabilities and allowing for adjustments during installation.
Durability: The metal-to-metal sealing of BSPT threads reduces the risk of leaks over time, contributing to long-term reliability in hydraulic systems.
Differences from BSPP
While BSPP and BSPT threads may seem similar, they have distinct differences that affect their applications and performance:
Thread Design: BSPP threads are parallel, meaning they maintain a consistent diameter, while BSPT threads are tapered, narrowing towards the end. This difference influences how each type seals against pressure.
Sealing Mechanism: BSPP relies on sealing washers or O-rings for a leak-proof joint, whereas BSPT achieves its seal primarily through the metal-to-metal contact created by the taper.
Installation Method: The installation of BSPP threads allows for more flexibility in alignment since the seal is not dependent on thread engagement, while BSPT requires careful alignment to ensure the taper fits securely and seals properly.
Applications: BSPT is more commonly used in high-pressure applications, while BSPP is typically favored for lower-pressure situations or where ease of assembly is prioritized.
PF Thread (Japanese Equivalent of BSPP)
Definition
PF, or Pipe Fastening thread, is the Japanese equivalent of the British Standard Pipe Parallel (BSPP) thread and is governed by the JIS B0202 standard. Like BSPP, PF threads feature a parallel design that relies on sealing methods such as O-rings or bonded washers. This design makes PF threads suitable for applications requiring secure connections without the need for tapering.
Compatibility
PF threads can be interchangeable with BSPP threads when the dimensions match, making it relatively easy to replace or adapt fittings across different systems. This compatibility is particularly beneficial in international projects or when sourcing components from various suppliers, as it allows for greater flexibility in design and assembly.
Applications
PF threads are predominantly used in Japan and Korea, particularly in hydraulic and industrial systems. Typical applications include:
Hydraulic Equipment: Commonly found in machinery used in manufacturing, construction, and agriculture, where reliable fluid transfer is crucial.
Pneumatic Systems: Utilized in air and gas connections that require secure, leak-proof fittings.
Industrial Automation: Employed in various automated systems where fluid control and reliability are essential.
Standards
The relevant standards governing PF threads include:
JIS B0202: This standard specifies the dimensions and requirements for PF threads, ensuring consistency in manufacturing and application within Japan.
KS B 0221: The Korean standard for PF threads, ensuring compatibility and quality for applications within Korea.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
Interchangeability: Their compatibility with BSPP threads allows for flexibility in sourcing and system design, facilitating easier upgrades and repairs.
Ease of Sealing: Like BSPP, PF threads can utilize bonded washers or O-rings, simplifying the sealing process and reducing the likelihood of leaks.
Widely Used in Asia: PF threads are common in Japanese and Korean markets, making them readily available and familiar to local manufacturers and technicians.
Cons:
Limited Global Recognition: While PF threads are well-known in Japan and Korea, they may not be as widely recognized in other regions, which can complicate sourcing components internationally.
Potential Sourcing Issues: In areas outside Japan and Korea, finding PF-compatible fittings may be challenging, leading to potential delays or higher costs.
Material Considerations: The effectiveness of sealing with PF threads may be influenced by environmental factors, such as temperature and chemical exposure, necessitating careful material selection based on the application.
PT Thread (Japanese Equivalent of BSPT)
Definition
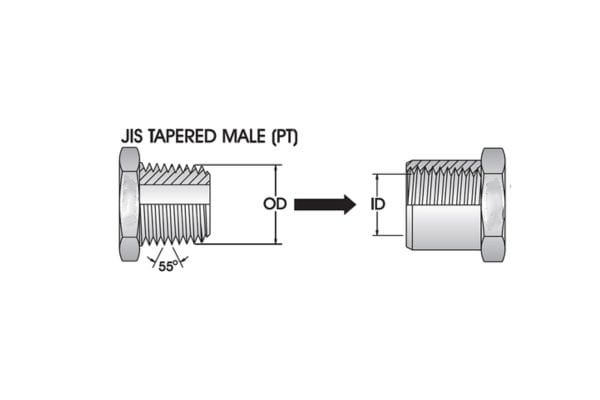
PT, or Pipe Taper, is Japan’s equivalent of the British Standard Pipe Taper (BSPT) thread, specified under the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS B0203. Like BSPT, PT threads feature a tapered design, which narrows along its length to facilitate sealing through metal-to-metal contact when tightened. This tapering creates a tight, leak-resistant fit, making PT threads suitable for high-pressure hydraulic applications.
Standards
PT threads are regulated by the following standards:
JIS B0203: This standard outlines the specifications for tapered pipe threads in Japan, ensuring consistency in manufacturing and application.
KS B 0222: The equivalent Korean standard for PT threads, ensuring that these components meet similar quality and compatibility requirements for use in Korea.
Applications
PT threads are extensively used in Japanese and Korean hydraulic systems, especially in scenarios where high-pressure seals are necessary. Common applications include:
Hydraulic Machinery: PT threads are commonly found in construction and agricultural equipment in Japan and Korea, where secure and leak-proof connections are vital for maintaining high-pressure hydraulic circuits.
Industrial Systems: They are also used in various industrial and manufacturing systems, including automation equipment, where high-pressure fluid transfer is essential for operation efficiency.
Pneumatic Equipment: PT threads are utilized in air compressors and pneumatic devices where robust, pressure-resistant connections are required.
Compatibility
PT threads are generally compatible with BSPT threads when the dimensions align, allowing for interchangeability in some cases. However, there are important considerations when using PT threads with BSPT fittings:
Thread Sealant: While PT threads can be used interchangeably with BSPT, using the appropriate thread sealant is crucial to ensure a leak-proof connection. This is particularly important because different sealants may be needed based on the application and pressure conditions.
Taper Angle: Although both PT and BSPT threads share a 1:16 taper ratio, it is essential to verify compatibility, especially when mixing components from different regions, to prevent leaks or fitting damage.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
High-Pressure Sealing: The taper design allows PT threads to provide a secure seal, suitable for high-pressure hydraulic systems, which is essential for reliability and safety.
Standardization: The existence of clear standards (JIS B0203 and KS B 0222) ensures consistency and quality, making PT threads a trusted choice in Japanese and Korean markets.
Interchangeability: The ability to interchange PT threads with BSPT threads offers flexibility in system design and maintenance, especially in international projects.
Limitations
Availability Outside Japan and Korea: Outside of these regions, PT threads are not as commonly available, potentially leading to sourcing difficulties and delays when replacing or upgrading components.
Sealing Considerations: Since PT threads rely on metal-to-metal sealing, achieving a proper seal may require specialized knowledge or tools, especially when using components from different standards or regions.
Adaptation Challenges: When using PT threads in regions where BSPT is more common, technicians must ensure that both the sealant and installation technique are compatible to avoid leaks and ensure system safety.
Best Practices for Selecting Pipe Threads
Assessing System Requirements
To determine the most suitable thread type for a hydraulic system, consider the following factors:
Pressure Ratings: Evaluate the maximum operating pressure of the system. For high-pressure applications, tapered threads like BSPT or PT are typically preferred due to their metal-to-metal sealing capability, which offers enhanced leak resistance. In contrast, parallel threads like BSPP or PF may be more suitable for lower-pressure scenarios.
Temperature Conditions: Assess the operating temperature range of the application. Some materials and sealing methods may not perform well under extreme temperatures. Ensure that the chosen thread type and sealing materials can withstand the specific thermal conditions.
Fluid Compatibility: Consider the type of fluid being transported through the system. Different fluids may require specific materials for the threads and seals to prevent degradation or failure.
Application Environment: Identify the environmental conditions, such as exposure to chemicals, moisture, or vibrations, which can affect thread performance and sealing integrity.
Compatibility Considerations
Ensuring compatibility among thread types is crucial, especially when working with international equipment and machinery:
Standardization Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the various thread standards (e.g., BSPP, BSPT, PF, PT) to avoid mismatches. When sourcing components, check specifications to confirm compatibility between different thread types.
Metric vs. Imperial: Be mindful of the measurement systems used in different regions. Mixing metric and imperial threads can lead to improper fittings and potential leaks.
International Sourcing: When procuring parts from different countries, verify that the components adhere to relevant standards and are designed to work together. This includes checking thread profiles and sealing requirements.
Proper Sealing Techniques
Effective sealing is essential for preventing leaks and ensuring system integrity. Here are some tips for sealing methods for each thread type:
BSPT/PT Threads:
Use Thread Sealants: Apply appropriate thread sealant to the male threads before assembly. This helps fill any gaps and ensures a tighter seal.
Tightening Technique: Carefully tighten the fitting until resistance is felt, ensuring a secure seal without over-torquing, which can damage the threads.
BSPP/PF Threads:
Bonded Washers or O-rings: Incorporate bonded washers or O-rings at the base of the fitting to enhance sealing. Ensure that the washer is compatible with the fluid being transported.
Proper Alignment: When assembling, ensure the fittings are properly aligned to avoid uneven pressure on the seal, which can lead to leaks.
Conclusion
To ensure the optimum performance of your hydraulic system, be sure to carefully review thread specifications. Verify compatibility, especially when sourcing components internationally. If you are unsure which thread type or sealing method is appropriate, seek professional advice or consult technical manuals to prevent errors that could lead to system failure. For further assistance, contact Topa and we will guide you through the process of selecting the most appropriate components for your needs.
FAQ
What is the difference between BSPP and BSPT threads?
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) threads are parallel and rely on a washer or O-ring for sealing, whereas BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) threads are tapered and sealed through metal-to-metal contact, often supplemented with thread sealants.
Can BSPP and BSPT threads be used interchangeably?
No, BSPP and BSPT threads are not directly interchangeable due to their differences in design (parallel vs. tapered). However, adapters are available to connect these different thread types if necessary.
What is a PF thread?
PF (Pipe Fastening) thread is the Japanese equivalent of BSPP. It is a parallel thread governed by JIS B0202 standards and is interchangeable with BSPP when dimensions match.
How does a PT thread compare to BSPT?
PT (Pipe Taper) thread is the Japanese equivalent of BSPT, following JIS B0203 standards. Both are tapered threads and can be used interchangeably, provided the dimensions match and proper sealing methods are applied.
Which thread type is best for high-pressure applications?
BSPT and PT threads are ideal for high-pressure applications as their tapered design allows for a secure metal-to-metal seal that can withstand high pressure.
Do I need thread sealant for BSPP threads?
No, BSPP threads typically use a bonded washer or O-ring for sealing and do not require thread sealant. Thread sealants are usually applied with BSPT or PT threads to enhance the metal-to-metal seal.