Taper threads are designed with a gradually decreasing diameter along the length of the fitting. This taper allows the male and female threads to compress tightly as they are screwed together, creating a strong, metal-to-metal seal. Unlike parallel threads, which rely on gaskets or O-rings for sealing, taper threads are self-sealing, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. Their ability to form a reliable, leak-proof seal without additional components is crucial for systems that handle fluids and gases under pressure, such as those found in industrial piping and hydraulic applications.
Understanding NPT and BSPT Taper Threads
What Are Taper Threads?
Taper threads are designed with a gradually decreasing diameter along the length of the thread, meaning the male and female parts of the fitting become progressively tighter as they are screwed together. This tapering allows for thread interference, where the threads compress against each other to form a strong mechanical seal. Taper threads are widely used in high-pressure applications, as the metal-to-metal contact provides a leak-proof connection without the need for additional sealing elements like gaskets or O-rings in many cases. This makes taper threads highly reliable in environments where pressure containment is critical, such as in gas or fluid systems.
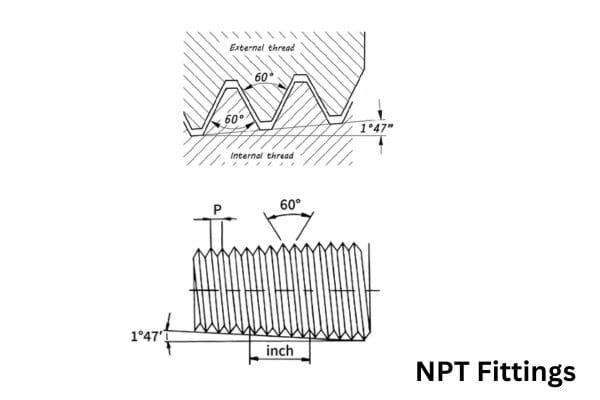
Overview of NPT (National Pipe Taper)
Definition:
NPT (National Pipe Taper) is the standard taper thread used in North America for threaded pipe fittings. NPT threads have a 60-degree thread angle and a taper of 1/16 inch per inch, which means the threads decrease in diameter by 1/16 of an inch for every inch of thread length. This tapering allows NPT threads to create a secure, self-sealing connection in piping systems by compressing the male and female parts tightly as they are screwed together.
How NPT Threads Seal:
NPT threads form a seal through metal-to-metal contact and thread interference. As the threads are tightened, the taper forces the threads to jam against each other, creating a strong mechanical bond that prevents leaks. The interference between the threads eliminates gaps, allowing NPT to be effective in high-pressure applications. To further ensure a leak-proof connection, thread sealants such as PTFE tape or pipe dope are often used to fill any microscopic gaps and enhance sealing performance.
Common Applications:
NPT threads are widely used in industrial piping systems, particularly in North America. Some of the most common applications for NPT include:
High-Pressure Hydraulic Systems: NPT threads are ideal for hydraulic systems where high pressure requires a strong, reliable seal.
Gas and Fluid Systems: NPT fittings are commonly used in natural gas pipelines, water lines, and compressed air systems.
Plumbing Systems: In commercial and residential plumbing, NPT threads are used to connect pipes that carry water, gas, or other fluids.
Overview of BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper)
Definition:
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) is the standard taper thread used primarily in Europe, Asia, and other parts of the world outside North America. BSPT threads have a 55-degree thread angle, which is slightly different from the 60-degree angle of NPT threads. The taper rate in BSPT threads is similar to that of NPT, but the thread profile and angle make BSPT threads incompatible with NPT fittings.
How BSPT Threads Seal:
Like NPT threads, BSPT threads create a seal through thread interference. As the BSPT threads are tightened, the male and female threads wedge together, forming a metal-to-metal seal. The compression of the taper creates a leak-proof connection, making BSPT threads suitable for high-pressure applications. Just as with NPT, sealants like PTFE tape or liquid sealants are often used to enhance sealing capabilities, especially in gas and fluid systems.
Common Applications:
BSPT threads are used in a variety of industries around the world, particularly in regions where British or international standards are followed. Common applications for BSPT include:
Gas and Oil Systems: BSPT is frequently used in the oil and gas industry for pipelines and drilling equipment, especially in Europe and Asia.
Plumbing Systems: In countries that use British standards, BSPT threads are common in plumbing systems, connecting pipes that transport water, gas, or compressed air.
Industrial Machinery: BSPT fittings are used in industrial equipment that handles high-pressure fluids or gases, ensuring a reliable, leak-proof seal under demanding conditions.
Key Differences Between NPT and BSPT
Thread Angle
NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads have a 60-degree thread angle, while BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) threads have a 55-degree thread angle. Although both are taper threads, this difference in angle is critical because it affects how the threads engage when tightened.
The difference in thread angle means that NPT and BSPT threads are incompatible with each other. When trying to screw an NPT fitting into a BSPT counterpart (or vice versa), the threads won’t align properly. This misalignment prevents a tight, uniform fit, leading to gaps in the connection. As a result, the threads won’t be able to create the metal-to-metal contact necessary for a proper seal, increasing the risk of leaks and system failures.
Pitch and Thread Design
Pitch Differences:
The thread pitch—the distance between threads—varies between NPT and BSPT fittings. NPT and BSPT threads have different pitch specifications, which means that the spacing between threads on the male and female fittings won’t match up if they are combined. This leads to improper thread engagement, further preventing the formation of a reliable seal.
Profile Differences:
The thread profile—the shape and depth of the threads—also differs between NPT and BSPT. NPT threads have a deeper, more rounded profile, while BSPT threads are slightly shallower with a different thread depth. These design differences mean that NPT and BSPT threads interact with their respective male and female fittings differently, creating distinct sealing mechanisms. NPT relies more on the tapered, wedging action to create a seal, while BSPT’s slightly different thread depth works to compress the threads together in a similar but regionally unique way.

Regional Standards
NPT is the dominant standard in North America, particularly in the U.S. and Canada. NPT fittings are used in most industries, including oil and gas, hydraulics, plumbing, and HVAC systems.
BSPT is more commonly used in Europe, Asia, and other international markets where British or ISO standards dominate. BSPT fittings are found in similar applications as NPT, including plumbing, gas pipelines, and industrial machinery.
It is crucial to know the regional standards used in your location, as this ensures that you are using compatible fittings and components. Failure to use the correct standard can lead to compatibility issues that compromise the integrity of the system, resulting in inefficiency or leaks.
Interchangeability
NPT and BSPT Threads Are Not Compatible:
Due to differences in thread angle, pitch, and profile, NPT and BSPT threads cannot be used together. Attempting to mix NPT and BSPT fittings can lead to poor sealing or leaks because the threads won’t engage properly. The mismatched threads will not form the required metal-to-metal contact, leading to gaps where fluid or gas can escape. In systems under high pressure, even minor leaks can be dangerous and lead to catastrophic failures.
Risks of Using Incompatible Threads:
In critical systems such as gas pipelines, hydraulic systems, or high-pressure fluid transport, using incompatible thread types can result in serious consequences, including leaks, pressure loss, or equipment damage. A poor seal caused by mismatched threads can cause a system to lose efficiency or, worse, fail under pressure. For industries that require leak-proof performance, such as the oil and gas or chemical industries, ensuring that NPT or BSPT fittings are used correctly is essential for maintaining system integrity and safety.
When to Use NPT Taper Threads
Ideal Applications for NPT Threads
Industrial Piping Systems:
NPT taper threads are widely favored in North America for industrial piping systems, especially in high-pressure and high-temperature environments such as factories, power plants, and chemical processing facilities. The robust self-sealing properties of NPT threads allow them to form a tight, leak-proof connection in demanding conditions. In these systems, the high pressure and elevated temperatures require connections that can withstand the stress and provide reliable performance over time. NPT’s tapered design helps create a secure seal, ensuring system integrity and preventing leaks in critical applications.
Gas and Fluid Transport:
NPT threads are commonly used in gas and fluid transport systems, including natural gas pipelines and HVAC systems. The tight seal formed by NPT threads makes them ideal for transporting gases and liquids under pressure, preventing leaks that could lead to safety hazards or system inefficiencies. In gas transport systems, the ability of NPT threads to withstand pressure variations and form a secure seal is essential for maintaining the efficiency and safety of the system. Similarly, in HVAC systems, where air and fluids need to be transported without leaks, NPT provides a reliable solution for fittings and connections.
Hydraulic Systems:
Hydraulic equipment often operates at high pressures, making it essential to have connections that can maintain a tight seal under pressure. NPT’s self-sealing design is well-suited for hydraulic systems, where leaks can lead to pressure loss, equipment malfunction, or system failure. In hydraulic systems, NPT taper threads are used for fittings that carry hydraulic fluids through high-pressure lines, ensuring leak-proof connections that are critical for system efficiency and safety.
Advantages of NPT
Self-Sealing in High-Pressure Environments:
One of the biggest advantages of NPT threads is their ability to self-seal in high-pressure systems. As the male and female components of an NPT connection are tightened, the taper creates thread interference that forms a strong, metal-to-metal seal. This self-sealing property eliminates the need for additional sealing components in many cases, making NPT ideal for high-pressure applications such as hydraulics, gas pipelines, and industrial piping.
Commonly Available in North America:
Another key advantage of NPT threads is their widespread availability in North America. Since NPT is the standard taper thread in this region, it is easier to source compatible components, fittings, and replacement parts. This makes NPT fittings a convenient and cost-effective choice for many industries in North America, as there is no need to import specialized fittings or worry about compatibility with other systems.
Challenges of NPT
Not Compatible with BSPT Systems or Fittings:
A significant limitation of NPT is its incompatibility with BSPT threads, which are more commonly used in Europe, Asia, and other international markets. The different thread angles and pitches between NPT and BSPT make it impossible to create a reliable seal if the two thread types are mixed. This can be a challenge for systems that need to be connected across regions or when working with equipment that uses different thread standards. In such cases, adapters may be required, but it’s essential to avoid directly combining NPT and BSPT fittings, as this can lead to leaks and poor performance.
Prone to Galling with Certain Materials:
Galling is a common issue with NPT threads, particularly when working with stainless steel or other softer metals. Galling occurs when the metal threads become damaged due to friction during the tightening process, causing them to seize or weld together. This can make fittings difficult to tighten or loosen, and may even damage the threads to the point where they can no longer form a proper seal. To prevent galling, it is important to use anti-seize lubricants when working with materials prone to this issue or to choose different materials or coatings that reduce friction.
When to Use BSPT Taper Threads
Ideal Applications for BSPT Threads
Plumbing Systems:
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) is widely used in global plumbing systems, particularly in Europe and Asia, where British Standard Pipe (BSP) standards dominate. BSPT threads are the go-to choice for plumbing applications due to their reliability in forming tight, leak-proof connections. In plumbing systems, BSPT’s taper thread design helps create strong seals without the need for excessive sealants or gaskets. This makes BSPT fittings popular for use in water distribution systems, sewage pipelines, and residential plumbing in regions that follow BSP standards. Their reliable sealing properties are ideal for carrying water, gases, and other fluids through domestic and industrial pipelines.
Oil and Gas Industry:
BSPT threads are extensively used in the oil and gas industry, particularly in pipelines and offshore drilling operations. In this industry, equipment is subjected to high pressures and harsh environmental conditions, requiring fittings that can withstand stress while maintaining a secure seal. BSPT’s taper thread design ensures that connections in oil rigs, refineries, and gas transport systems remain leak-proof, even under fluctuating pressures. Whether transporting crude oil, natural gas, or refined petroleum products, BSPT threads are trusted for their ability to form tight connections in hazardous environments.
Compressed Air Systems:
BSPT is frequently used in compressed air systems, where maintaining a secure, leak-free connection is critical for efficient system performance. In air compressors and pneumatic systems, the high-pressure air needs to be transported reliably between components without pressure loss. The tapered threads of BSPT fittings allow for effective sealing under pressure, ensuring that air systems operate at full capacity without the risk of leaks or inefficiency. BSPT’s durability and reliability in pressurized environments make it a popular choice for industries that rely on air compression, such as manufacturing, automotive, and construction.
Advantages of BSPT
Common Standard in Many Parts of the World:
One of the major advantages of BSPT is its status as a common standard in many parts of the world, particularly in Europe, Asia, and other regions that follow British or ISO standards. This global acceptance ensures that BSPT components are widely available in international markets, making them easy to source and replace in regions where BSP standards dominate. For industries with international operations or those exporting equipment to multiple countries, BSPT provides global compatibility, ensuring that fittings can be sourced and used across different regions without compatibility issues.
Suitable for High-Pressure Systems:
BSPT threads are particularly well-suited for high-pressure systems, including those in the oil, gas, and compressed air industries. The tapering of BSPT threads allows them to form a strong, leak-proof seal under pressure, making them reliable for transporting fluids and gases at high pressures. Whether in a compressed air system or a gas pipeline, BSPT’s sealing properties help maintain system integrity and prevent dangerous leaks, making them ideal for demanding environments where safety and efficiency are critical.
Challenges of BSPT
Limited Availability in North America:
While BSPT is a common standard in many parts of the world, its availability in North America is relatively limited compared to NPT fittings. In regions where NPT is the standard, it may be more difficult to find BSPT fittings or components, and they may need to be imported. This can increase costs and lead to delays when replacements or new parts are needed. For companies operating in North America, relying on BSPT fittings may present sourcing challenges, especially when local suppliers primarily stock NPT components.
Not Compatible with NPT Fittings:
Like NPT, BSPT is not compatible with its counterpart due to differences in thread angle, pitch, and profile. As mentioned earlier, BSPT has a 55-degree thread angle, while NPT has a 60-degree angle, making it impossible to mix the two without risking leaks or poor performance. This incompatibility means that systems using BSPT fittings cannot be connected to NPT systems without the use of specialized adapters, which can introduce points of weakness or increase the complexity of installation. For systems that operate internationally or across regions with different standards, care must be taken to ensure the correct thread type is used consistently.
How to Choose Between NPT and BSPT
Assess Your Location
One of the first factors to consider when choosing between NPT and BSPT is geographical location. Each thread type is tied to specific regional standards.
If you are in North America, NPT is the dominant standard and is widely available for applications across industries such as plumbing, hydraulics, and gas systems.
In contrast, if you are working in Europe, Asia, or other parts of the world, BSPT is more commonly used due to its alignment with British and ISO standards. Choosing the correct thread type for your location ensures ease of sourcing components, finding replacement parts, and avoiding potential compatibility issues.
Consider System Pressure
Both NPT and BSPT threads perform well in high-pressure environments, such as hydraulic systems, gas pipelines, or industrial piping. However, it is important to use fittings that are specifically designed for your system’s pressure levels.
NPT threads excel in high-pressure systems common in hydraulic and industrial piping applications, where the tapered design creates a self-sealing connection capable of handling high stress.
BSPT threads are similarly effective for high-pressure applications like oil and gas pipelines, but it’s critical to ensure that BSPT components are used consistently to maintain pressure integrity.
Availability of Components
The availability of fittings and replacement parts is a key consideration when selecting a thread type for your system.
In North America, NPT fittings are easier to source and readily available from a wide range of suppliers. The convenience of finding replacement parts locally can reduce downtime and lower overall costs.
In international markets, particularly in Europe and Asia, BSPT fittings are more commonly available. If you operate in these regions or have systems installed in multiple countries, it may be easier to find BSPT components.
Compatibility with Existing Systems
When retrofitting, repairing, or expanding an existing system, it’s essential to match the thread type already in use.
Using the same thread type ensures compatibility and proper sealing. Mixing NPT and BSPT threads can lead to leaks due to differences in thread angle and pitch, which make them incompatible.
If you need to connect an NPT system to a BSPT system (or vice versa), specialized adapters are available, but these should be used with caution to avoid introducing weak points in the system.
Applications in Industry
Consider the industry standards applicable to your specific application.
For hydraulic systems, gas transport, and industrial piping, NPT is often the preferred choice in North America due to its widespread use and compatibility with local equipment.
For oil and gas applications, plumbing systems, or compressed air systems in Europe or Asia, BSPT is the better option due to its adherence to British and ISO standards. Industry standards ensure the safety and efficiency of your system, and using the right thread type is critical for maintaining compliance with these standards.
Conclusion
When choosing between NPT and BSPT threads, it is essential to carefully consider your system’s requirements, the location where the system will be installed, and the existing infrastructure in use. Selecting the correct thread type based on these factors ensures that your system operates efficiently, with leak-free connections that can handle the pressure and demands of the application. Whether working with high-pressure hydraulic systems or compressed air pipelines, choosing the right thread standard will lead to optimal performance and long-term reliability.
FAQ
What is the difference between NPT and BSPT threads?
NPT threads have a 60-degree thread angle, while BSPT threads have a 55-degree angle, making them incompatible with each other.
Can NPT and BSPT threads be used together?
No, NPT and BSPT threads are not compatible due to differences in thread angles and pitch, which can result in poor sealing and leaks.
Where are NPT threads commonly used?
NPT threads are primarily used in North America for high-pressure systems like hydraulic equipment, gas pipelines, and industrial piping.
Where are BSPT threads commonly used?
BSPT threads are commonly used in Europe, Asia, and international markets for plumbing systems, oil and gas pipelines, and compressed air systems.
What industries use NPT and BSPT threads?
NPT threads are widely used in industries such as hydraulics and industrial piping in North America, while BSPT threads are favored in oil, gas, and plumbing applications internationally.
How do I choose between NPT and BSPT threads?
Choose NPT if you’re in North America or need local availability, and choose BSPT for international markets or where BSP standards are prevalent. Consider the system’s pressure and compatibility with existing components.






















































































































