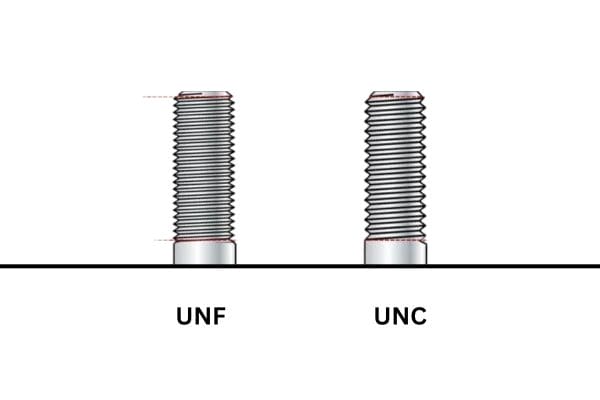
The choice between UNF and UNJF threads can significantly impact the performance and reliability of a mechanical assembly. Incorrect thread selection can lead to issues like loosening, wear, and ultimately, failure of the components involved. Therefore, engineers and designers must grasp the nuances of each thread type, including their dimensions, tolerances, and applications. This knowledge ensures optimal performance, safety, and longevity of products, especially in critical applications where failure is not an option.
What is UNF Thread?
A. Definition and Characteristics
Introduction to UNF Threads
Unified National Fine (UNF) threads are a specific type of screw thread defined by the Unified Thread Standard (UTS). These threads are designed with a finer pitch compared to their coarse counterparts, offering enhanced grip and tensile strength. This design is particularly advantageous in applications where precision and durability are paramount.
Thread Pitch and Diameter
Thread pitch refers to the distance between adjacent threads. In UNF threads, the finer pitch allows for a greater number of threads within a given length, which translates to a tighter fit and better load distribution. For instance, while a coarse thread might have a pitch of 1.0 mm, a UNF thread might have a pitch of 0.5 mm, offering enhanced mechanical performance. The diameter of the thread is equally critical; it must be selected based on the specific application requirements. A larger diameter generally provides more strength, but the pitch must also be considered to maintain the desired engagement and resistance to stripping.
Flank Angle
UNF threads are characterized by a 60-degree flank angle, which is the angle between the two sides of the thread. This angle is crucial as it affects the thread’s strength and its ability to engage with corresponding threaded components. A 60-degree angle allows for optimal stress distribution, reducing the risk of failure under load. This design feature is particularly beneficial in high-stress applications, ensuring that the threads remain intact and functional even under significant pressure.
Standardized Sizes
UNF threads are available in a range of standardized sizes, from 0-80 (with a diameter of 0.0600 inches) to 2-56 (2 inches in diameter). This standardization ensures compatibility across various applications, allowing manufacturers to interchange fasteners without concern for fit. The consistency in sizing promotes ease of use and reliability, as engineers and designers can confidently select components that will work together seamlessly.
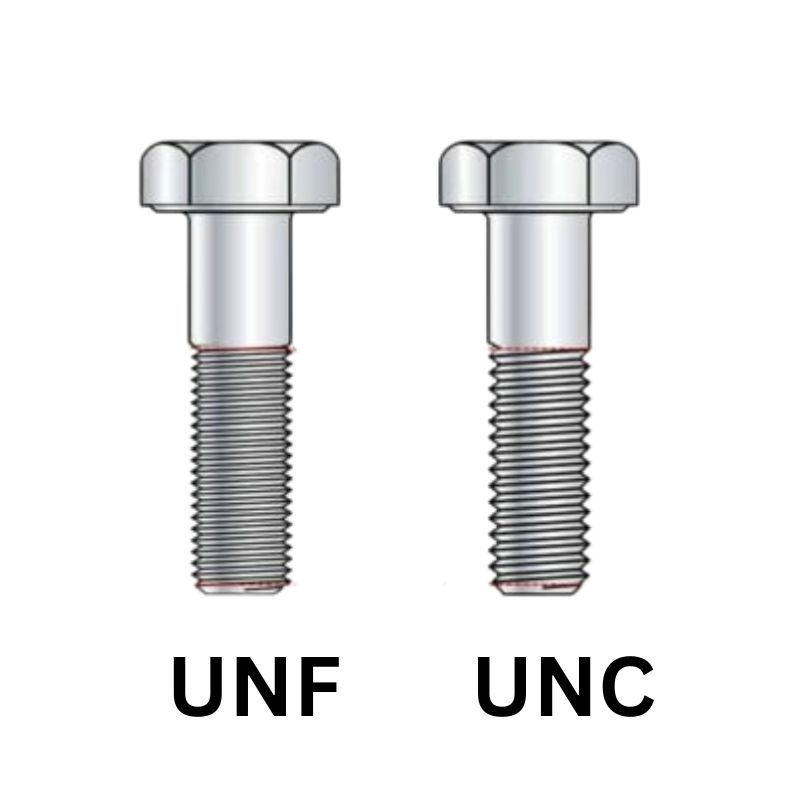

B. Applications of UNF Threads
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, UNF threads are extensively used in engine components, such as cylinder heads and valve covers. Their fine pitch allows for a strong, vibration-resistant connection that is essential for high-performance engines. Additionally, UNF threads play a crucial role in suspension systems and transmission assemblies, where precise alignment and durability are vital for safety and performance.
Aerospace Applications
Aerospace engineering often demands high-strength, lightweight materials, making UNF threads a preferred choice for structural components. They are used in critical fasteners where weight savings are essential without compromising strength. The reliability of UNF threads in these applications is crucial, as any failure could have catastrophic consequences.
Manufacturing Equipment
In manufacturing environments, UNF threads are used in machinery requiring robust and reliable connections. These threads are essential for securing components that undergo constant movement and stress, ensuring operational efficiency and safety in industrial settings.
Hydraulic Systems
UNF threads are particularly important in hydraulic fittings and connections, where pressure and fluid dynamics play significant roles. The precision of UNF threads helps maintain seals under high pressure, preventing leaks and ensuring the safe operation of hydraulic systems.
C. Common Specifications and Standards
ANSI/ASME B1.1 Standard
UNF threads conform to the ANSI/ASME B1.1 standard, which outlines the specifications for unified threads. This standard is crucial as it defines the dimensions, tolerances, and thread forms that ensure consistent quality across manufacturing processes. Adhering to this standard helps maintain interoperability among components from different manufacturers.
Thread Dimensions
Standardized thread dimensions are critical for ensuring compatibility and performance. The ANSI/ASME B1.1 standard provides detailed specifications for both major and minor diameters, as well as pitch diameter, allowing for precise fit and function in mechanical assemblies.
Tolerances
Tolerances are essential in the manufacturing of UNF threads, ensuring that major and minor diameters fall within specified limits. This precision is vital for assembly and overall performance; improper tolerances can lead to difficulties in fitting components together, increasing the risk of failure.
Industry Compliance
Compliance with industry standards is imperative for manufacturers. It not only ensures the reliability and safety of the products but also fosters trust among consumers and businesses. Adhering to these specifications helps prevent costly errors and enhances the overall quality of threaded components.
D. Benefits of Using UNF Threads
Enhanced Strength and Engagement
The finer pitch of UNF threads allows for greater engagement with the material being fastened. This characteristic reduces the likelihood of loosening, particularly in applications subject to vibration or dynamic loads, ensuring long-lasting connections that perform reliably over time.
Resistance to Vibration
UNF threads are particularly effective in dynamic applications where vibrations can lead to fastener loosening. The design of these threads provides a secure grip, maintaining the integrity of the assembly even in high-vibration environments, such as automotive engines or machinery.
Interchangeability
The standardized nature of UNF threads promotes interchangeability among different manufacturers, facilitating the sourcing of compatible fasteners. This ease of interchangeability is essential in industries where rapid assembly and maintenance are crucial, saving time and reducing costs.
Durability and Longevity
UNF threads help minimize stripping, extending the lifespan of both the fasteners and the components they connect. This durability is particularly important in applications where maintenance access is challenging, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Precision and Reliability
The precision associated with UNF threads contributes significantly to the overall integrity of mechanical assemblies. This precision not only enhances performance but also plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and reliability of products across various industries.
What is the UNJF Thread?
A. Definition and Characteristics
Introduction to UNJF Threads
Unified National Joint Fine (UNJF) threads are a specialized type of screw thread defined by the Unified Thread Standard (UTS), designed specifically for applications requiring enhanced fatigue resistance and strength. Unlike the standard UNF threads, UNJF threads feature a unique design that incorporates a larger root radius and modified thread geometry, which helps distribute stress more evenly along the thread.
Thread Pitch and Diameter
Similar to UNF threads, UNJF threads also have a finer pitch, which means there are more threads per unit length compared to coarse threads. This fine pitch increases the contact area, improving load-bearing capabilities. The diameter of UNJF threads, ranging from 0-80 to 2-56, is critical for ensuring compatibility and performance in various applications, particularly in environments subjected to high stress.
Flank Angle and Root Radius
UNJF threads maintain a 60-degree flank angle, like UNF threads, but they also feature a larger root radius. This design modification is vital for enhancing the thread’s resistance to wear and fatigue, particularly in dynamic applications where cyclic loading occurs. The larger root radius minimizes stress concentrations, reducing the likelihood of thread failure over time.
Standardized Sizes
UNJF threads are standardized in sizes that align with industry needs, promoting compatibility across different components and applications. This standardization ensures that manufacturers can easily source compatible fasteners, facilitating efficient assembly and maintenance processes.
B. Applications of UNJF Threads
Aerospace Industry
UNJF threads are predominantly used in the aerospace sector, where high performance and reliability are critical. These threads are found in structural components, such as fuselage and wing assemblies, where strength and weight considerations are paramount. The enhanced fatigue resistance of UNJF threads makes them ideal for applications subjected to repeated loading cycles, such as in aircraft takeoffs and landings.
Military Applications
In military engineering, UNJF threads are utilized in various defense systems, including weapons and vehicles. The need for high-strength, durable fasteners that can withstand extreme conditions makes UNJF threads a preferred choice. Their ability to maintain integrity under severe stress contributes to the reliability of military equipment.
Automotive Engineering
UNJF threads are also used in the automotive industry, particularly in components requiring high strength and resistance to wear. They can be found in critical fasteners for high-performance vehicles and engines, where reliability and safety are essential.
Manufacturing Equipment
In heavy machinery and manufacturing equipment, UNJF threads provide secure connections that are vital for operational efficiency. Their fatigue resistance helps ensure that machinery components remain securely fastened under continuous stress, reducing maintenance needs and downtime.
C. Common Specifications and Standards
ANSI/ASME B1.1 Standard
UNJF threads comply with the ANSI/ASME B1.1 standard, which governs the specifications for unified threads. This standard is crucial for ensuring that UNJF threads meet the necessary dimensions and tolerances, promoting quality and compatibility across various applications.
Thread Dimensions
The thread dimensions of UNJF threads are standardized, allowing for precise engineering and manufacturing processes. This includes specifications for major and minor diameters, as well as pitch diameter, which must be adhered to for optimal performance in threaded connections.
Tolerances
Tolerances for UNJF threads are critical in maintaining the integrity of assemblies. These specifications dictate allowable variations in the dimensions of the threads, ensuring a proper fit and function. Adhering to these tolerances is essential for preventing issues related to misalignment or stripping during assembly.
Industry Compliance
Compliance with established industry standards is vital for manufacturers producing UNJF threaded components. This compliance not only ensures product reliability but also builds trust with customers who rely on these fasteners in critical applications.
D. Benefits of Using UNJF Threads
Enhanced Fatigue Resistance
One of the primary benefits of UNJF threads is their enhanced fatigue resistance, making them suitable for applications involving cyclic loading. The design modifications, such as the larger root radius, help distribute stress more evenly, reducing the risk of failure under repeated use.
Improved Load Distribution
The finer pitch of UNJF threads allows for better load distribution across the threaded joint. This characteristic helps minimize stress concentrations that can lead to premature failure, ensuring a longer lifespan for both the fastener and the connected components.
Interchangeability
UNJF threads adhere to standardized specifications, which promotes interchangeability among manufacturers. This feature simplifies sourcing and reduces the complexity involved in assembly processes, allowing engineers and manufacturers to select compatible fasteners easily.
Durability in Harsh Environments
UNJF threads are designed to withstand extreme conditions, making them ideal for applications in aerospace, military, and heavy machinery. Their durability contributes to the reliability of critical systems, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacements.
Key Differences Between UNF and UNJF Threads
A. Design Specifications
1. Thread Geometry
UNF (Unified National Fine) threads feature a standard 60-degree flank angle with a consistent pitch, providing a reliable connection across various applications. In contrast, UNJF (Unified National Joint Fine) threads also maintain a 60-degree flank angle but incorporate a larger root radius. This design modification in UNJF threads helps distribute stress more evenly and reduces the risk of fatigue failure.
2. Pitch and Diameter
Both UNF and UNJF threads offer fine pitches, but UNJF threads typically have a finer pitch and larger diameter specifications for certain applications. The enhanced pitch and diameter variations in UNJF threads are intended for applications requiring superior load-bearing capabilities, particularly in high-stress environments.
3. Standardization
While both thread types are standardized under the ANSI/ASME B1.1 specification, the specific dimensions, tolerances, and design features differ. UNF threads are available in a wide range of sizes, while UNJF threads are tailored for specific applications in aerospace and heavy machinery, promoting better fit and performance in those environments.
B. Load Distribution and Strength
1. Load-Bearing Capacity
The design differences between UNF and UNJF threads directly impact their load-bearing capacities. UNF threads excel in general applications where precision and strength are important but may not perform as well under cyclic loading conditions compared to UNJF threads. The larger root radius and modified geometry of UNJF threads improve their resistance to fatigue, making them ideal for high-stress applications.
2. Stress Distribution
UNJF threads provide enhanced stress distribution due to their design features. The larger root radius reduces stress concentrations, which are critical in preventing failure in dynamic applications, such as those found in aerospace and military settings. UNF threads, while strong, may not offer the same level of stress distribution, making them less suitable for environments where cyclic loads are prevalent.
3. Overall Strength
In terms of overall strength, UNJF threads have the edge in applications requiring durability and reliability under repeated stress. They are specifically designed to maintain integrity even under extreme conditions, such as those encountered in aircraft or military equipment. UNF threads, while robust, may not withstand the same level of repeated stress without a higher risk of failure.
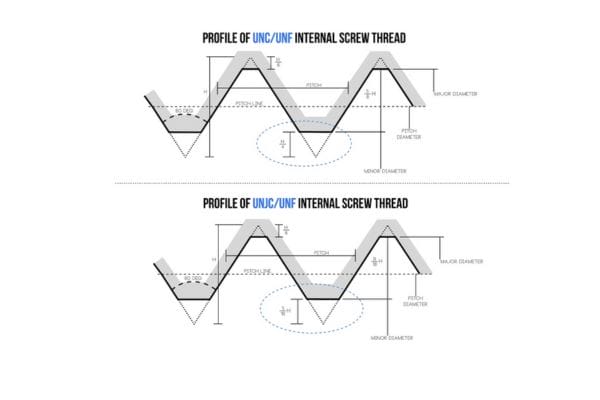
C. Tolerance and Fit
1. Tolerance Specifications
Both UNF and UNJF threads adhere to strict tolerance specifications, but the tolerances for UNJF threads are often more stringent. The precision required for UNJF threads is critical in high-performance applications, where even minor deviations can lead to significant issues. The tighter tolerances in UNJF threads ensure a more precise fit, enhancing the reliability of assemblies subjected to high loads.
2. Fit Characteristics
The fit characteristics of UNF and UNJF threads differ primarily due to their design and tolerance specifications. UNF threads are generally easier to work with in a wider range of applications, as they are designed for general use. However, the precise fit offered by UNJF threads is essential in critical applications, where a secure connection is necessary for safety and performance.
3. Assembly Considerations
When assembling components with UNF threads, manufacturers may have more flexibility regarding fit due to the wider range of tolerances. In contrast, assemblies involving UNJF threads require meticulous attention to detail to ensure that all components meet the specified tolerances. This attention to fit is particularly important in applications where safety is a concern.
Choosing Between UNF and UNJF Threads
A. Factors to Consider
When deciding between UNF and UNJF threads, several critical factors must be evaluated to ensure optimal performance and reliability for the intended application.
Mechanical Demands: Start by assessing the mechanical demands of the environment. Consider the types of loads the application will experience—whether they are static, dynamic, or a combination of both. Dynamic loads, which fluctuate over time, can significantly impact thread performance, making it essential to select a thread type capable of handling such stress.
Vibration Levels: Evaluate the vibration levels the threaded connections will be subjected to. High vibration can lead to the loosening of fasteners, and UNJF threads, with their superior fatigue resistance, may be more appropriate for these situations compared to UNF threads.
Material Compatibility: The materials being fastened are also vital. Softer materials may benefit from the finer pitch and tighter fit of UNF threads, while harder materials or applications requiring a stronger connection might necessitate the use of UNJF threads.
Standardization and Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the threads with existing components. Using standardized sizes can ease sourcing and assembly, reducing lead times and costs. Ensuring that the thread type chosen aligns with industry standards can also simplify the procurement process.
Regulatory Standards: Finally, think about any regulatory or industry standards that may dictate the type of thread required for specific applications. Industries such as aerospace and the military often have strict guidelines that must be adhered to, making thread selection critical for compliance.
B. Performance Requirements
Performance requirements are crucial in thread selection and should be meticulously evaluated.
High-Stress Applications: If the application involves high-stress or cyclic loading, UNJF threads are generally the superior choice. Their design enhances fatigue resistance and stress distribution, allowing them to endure rigorous conditions without compromising integrity. This makes them ideal for sectors such as aerospace, military, and heavy machinery, where the reliability of fasteners is paramount.
Static Loads: Conversely, if the application is less demanding and primarily involves static loads—such as connections in non-vibrating machinery—UNF threads may be sufficient. They provide a reliable connection while also being more cost-effective, allowing for efficient assembly in environments where extreme performance is not critical.
C. Cost Implications
Cost considerations play a significant role in the decision-making process for selecting between UNF and UNJF threads.
Economic Factors: Generally, UNF threads are more economical due to their wider availability and simpler manufacturing processes. Their versatility makes them suitable for a variety of applications, allowing for reduced overall production costs.
Investment in Performance: However, investing in UNJF threads may be justified for applications that demand enhanced performance and reliability, particularly where safety is a concern. Although UNJF threads often come with a higher upfront cost, their durability can lead to lower maintenance requirements and longer lifespans. This can result in significant long-term savings, particularly in critical applications where downtime can be costly.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the choice between UNF and UNJF threads should be guided by the specific performance requirements, cost considerations, and the unique demands of the application. For tailored solutions and expert advice, consulting professionals in the field is recommended. This ensures that the selected fasteners will meet safety and operational standards, contributing to the overall success of your projects.
FAQ
What are UNF and UNJF threads?
UNF (Unified National Fine) and UNJF (Unified National Fine Thread) are types of screw threads defined by the Unified Thread Standard. UNF threads have a finer pitch, while UNJF threads have enhanced fatigue resistance due to their design features.
What are the main applications for UNF threads?
UNF threads are commonly used in automotive, manufacturing, and general machinery applications, where a reliable connection is needed without extreme performance demands.
When should I use UNJF threads instead of UNF?
Use UNJF threads in applications involving high-stress or cyclic loading, such as aerospace and military applications, where enhanced strength and fatigue resistance are critical.
What are the cost differences between UNF vs UNJF threads?
UNF threads are generally more economical due to their wider availability and simpler manufacturing processes. UNJF threads may have a higher upfront cost but offer long-term savings through increased durability.
How do I choose between UNF and UNJF threads?
Consider factors such as mechanical demands, vibration levels, material compatibility, and industry standards. Evaluate performance requirements and cost implications to make an informed decision.
Are there any regulatory standards for these threads?
Yes, certain industries, particularly aerospace and military, have strict regulatory standards that may dictate the use of UNF or UNJF threads for specific applications to ensure safety and reliability.