Struggling with fittings that leak, corrode, or fail unexpectedly? Choosing the wrong supplier can lead to costly downtime, dangerous working conditions, and a constant headache of sourcing replacement parts.
Choosing reliable reusable fittings means looking beyond the price. You must assess the material quality, precision of the machining, supplier reputation, thread compatibility, and the level of quality control they can prove. These factors determine a fitting’s long-term performance and safety.
Why is Material and Plating the First Sign of Quality?
Concerned that a new fitting is already showing signs of rust? This is often the first symptom of a low-quality product, compromising its strength and contaminating your hydraulic system.
The material and plating are your first clues to a fitting’s reliability. Quality fittings use specified grades of carbon steel for strength, plated with a thick, even layer of zinc-chromate or zinc-nickel to resist corrosion. Inferior fittings use cheap steel and thin, inconsistent plating.
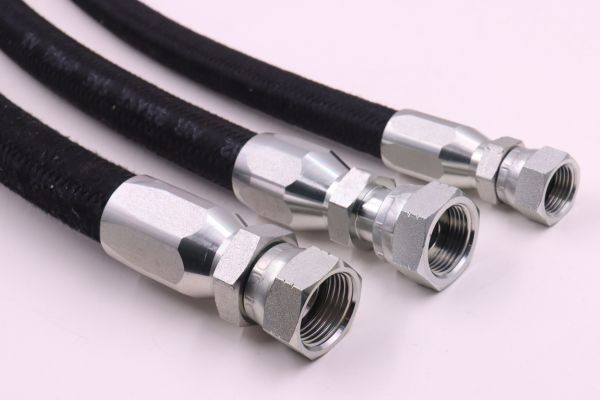

How to Judge the Base Material
While you can’t test the steel grade yourself, there are questions you can ask. Inquire about their material sourcing and ask if they can provide material certifications for their raw stock. A reputable supplier, like us at Topa, maintains these records as part of our quality control process. The weight and feel of a fitting can also be an indicator. A part made from inferior, porous steel can sometimes feel lighter or less dense than a solid, well-made equivalent. Look for a supplier who talks about using high-strength carbon steel (like 1045 steel) for their components.
Evaluating the Plating
This is something you can often judge visually.
- Uniformity: Is the color and finish even across the entire fitting? Low-quality plating often has streaks, dark spots, or areas where the coating is visibly thinner.
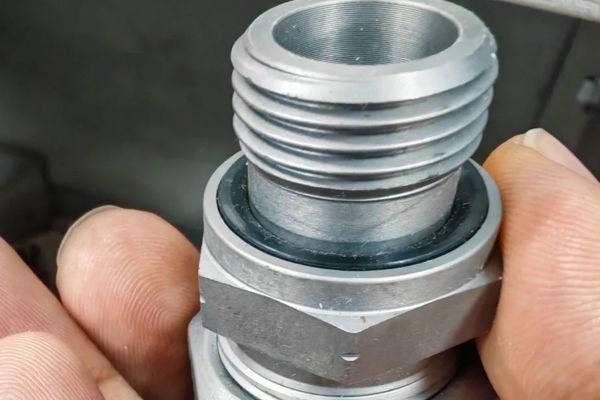
- Color: Standard commercial trivalent zinc plating is often clear (silver) or yellow. Zinc-nickel, a much higher-performance option, often has a slightly iridescent or darker silver finish. Be wary of plating that chips or flakes easily when handled.
- Corrosion Resistance: Ask the supplier for their salt spray test results. This is a standardized test (ASTM B117) that measures how many hours a part can withstand a corrosive fog before showing signs of rust.
A supplier proud of their quality will have this data readily available. For example, standard plating might offer 72-96 hours of resistance, while high-quality zinc-nickel plating can exceed 700 hours.
| Plating Type | Typical Appearance | Corrosion Resistance | Common Use Case |
| Standard Zinc (Trivalent) | Silver / Clear or Yellow | Low to Medium | General purpose, dry environments |
| High-Quality Zinc-Nickel | Iridescent Silver | Very High | Marine, chemical, or harsh environments |
| No/Poor Plating | Dull Gray, signs of rust | Very Low | Unreliable, not recommended |
How Can You Judge the Quality of the Machining?
Are you frustrated by hydraulic fittings with leaky threads or inconsistent sizes? These problems are a direct result of poor machining and a lack of precision during manufacturing.
You can judge machining quality by closely inspecting the threads, sealing surfaces, and overall finish. Reliable fittings have sharp, clean threads, smooth sealing surfaces free of burrs, and consistent dimensions. Poor quality is revealed by rough finishes, nicks, and metal shavings.

The precision of the machining directly impacts how a fitting assembles, seals, and performs under pressure. Every surface has a purpose, and any imperfection can become a failure point. A reliable supplier uses modern CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and has strict quality checks at every step of the process.
The Three-Point Inspection
When a sample arrives, perform this simple inspection:
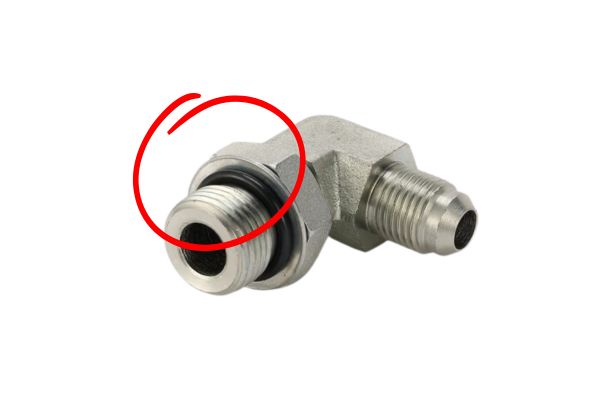
- Examine the Threads: The threads should be crisp, well-defined, and uniform. Run your nail over them (carefully). They should feel sharp but smooth, without any ragged edges or burrs. Look for any signs of cross-threading or damage from handling. A poorly cut thread will not engage smoothly and is a primary cause of leaks.
- Check Sealing Surfaces: This is the most critical area. For a JIC fitting, inspect the 37-degree flare. For an ORFS fitting, check the groove for the o-ring. These surfaces must be perfectly smooth, with no radial scratches, nicks, or dents. Any imperfection on a sealing surface is a guaranteed leak path.
- Look at the Details: Check the hex nuts. Are the corners sharp and well-defined, or are they slightly rounded and sloppy? Look inside the fitting for any leftover metal shavings or debris from the machining process. A quality-focused manufacturer has rigorous deburring and cleaning processes.
I always tell my team that one bad fitting can ruin a customer’s trust. That’s why we have multiple inspection points in our partner factories—after machining, before plating, and a final check before packaging.
Does the Supplier’s Reputation and Transparency Really Matter?
Been burned by a supplier who disappeared after a problem occurred? A low price from an unknown source is a huge gamble when your business relies on functioning equipment.
Yes, reputation and transparency are paramount. A reliable supplier has a proven track record, positive testimonials, and is open about their processes. They stand behind their product with warranties and responsive after-sales support, proving they are a partner, not just a vendor.
Anyone can set up a website and claim to be a manufacturer. The real test is how they operate. Are they transparent about their identity? Are they a trading company or a factory? At Topa, we are upfront: we are a specialized trading company with a highly-skilled team and deep, long-term partnerships with our factories. We encourage factory visits because we are confident in our partners’ capabilities and our own quality control processes on-site.
How to Vet a Supplier’s Reputation
- Check Their History: How long have they been in business? A company with a decade or more of export experience, like us, has likely navigated and solved a wide range of production and logistics challenges.
- Look forAuthenticity: Scrutinize their website and marketing materials. Does it look professional? Do they show actual photos of their team, facility, and products, or just generic stock photos? Look for “About Us” sections that are specific and credible.
- Test Their Knowledge: Engage their sales or technical team with specific questions about materials, pressure ratings, or application advice. Their answers will quickly reveal their level of expertise. A simple “I don’t know, but I will find out” is a much better answer than a wrong one.
A supplier who is open, honest, and professional in communication is far more likely to provide a product that is made with the same level of care.
What Do Thread Standards and Compatibility Tell You About a Fitting?
Ever ordered fittings that didn’t match your hoses or ports? This frustrating mistake costs time and money, bringing your project to a halt while you reorder the correct parts.
Adherence to international thread standards (like JIC, BSPP, NPT) is a hallmark of a reliable supplier. It guarantees compatibility and interchangeability. A supplier who offers a wide range of standard fittings demonstrates technical expertise and a commitment to global quality benchmarks.

This might seem technical, but it’s fundamentally about precision and professionalism. The hydraulic world runs on standards. These standards ensure that a -08 JIC fitting you buy from one reputable manufacturer will work with a -08 JIC hose end from another.
Key Standards to Know
A knowledgeable supplier should be fluent in these common standards:
- JIC (Joint Industry Council): Has a 37-degree flare sealing surface. Very common in North America.
- NPT (National Pipe Taper): A tapered thread that seals by metal-on-metal wedging. Also common in North America.
- BSPP (British StandardPipe Parallel): Parallel threads that require a bonded seal or O-ring to seal. Common everywhere else.
- BSPT (British StandardPipe Taper): The British equivalent of NPT.
- ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal): A flat face with an O-ring groove, offering excellent leak resistance.
Why This Matters for Reliability
A supplier’s ability to produce and correctly label fittings according to these diverse standards tells you several things:
- Technical Competence: They have the engineering knowledge and machinery to produce these precise geometries.
- Global Experience: They have likely worked with customers in different markets and understand their specific needs.
- Quality Control: They must have tools like thread gauges and profile projectors to verify that their parts meet the required dimensional tolerances.
When you ask a supplier for a “G1/4 BSPP” fitting and they ask what that is, you know you’re talking to the wrong company. A reliable partner will not only understand your request but might also ask clarifying questions to ensure you get the exact part you need for your application.
How Does Packaging and Handling Indicate a Supplier’s Professionalism?
Have you ever received an order of fittings that were loose, dirty, or damaged in transit? This shows a lack of care and can mean your brand-new parts are unusable.
Professional packaging is a clear indicator of a reliable supplier. Quality fittings should be clean, properly protected with thread caps, bagged in logical quantities, and shipped in sturdy, well-labeled cartons. This shows respect for the product and the customer.

What to Look For in Good Packaging
- Individual Protection: At a minimum, critical sealing surfaces and threads should be protected by plastic caps or netting. This prevents them from getting damaged by banging against other fittings during shipping.
- Cleanliness: The parts should be free of oil, grease, and metal debris. They should be ready to install right out of the bag.
- Logical Grouping: Fittings should be bagged in sensible quantities (e.g., 10, 25, 50 per bag) with a clear label identifying the part number and quantity. This makes receiving and inventory management much easier.
- Durable Outer Packaging: The inner bags should be placed in strong, double-walled cardboard boxes that can withstand the rigors of international shipping. The box should be clearly labeled with your order information.
A supplier who invests in good packaging is signaling that they are proud of their product and want it to arrive in your hands in perfect condition. It’s a final, tangible piece of evidence of their commitment to quality.
Why is Supplier Responsiveness as Important as Product Quality?
Waiting days for a quote or an answer to a simple technical question? This poor communication wastes your time and signals that you will likely face the same delays with your order.
A reliable supplier pairs a quality product with responsive service. Fast replies to inquiries, quick quotations, and proactive communication about order status are signs of a professional team that respects your time and values your business. This service is part of the total product.
The Hallmarks of a Responsive Supplier
- Fast Inquiry Response: You should receive an acknowledgment of your inquiry within a few hours and a detailed reply within one business day. Time zone differences are a reality, but a 24-hour turnaround is a professional standard.
- Quick and Clear Quotations: Quotes should be easy to understand, with clear pricing, part numbers, minimum order quantities, and estimated lead times. Our goal is to provide quotations rapidly so you can make your decisions quickly.
- Proactive Order Updates: A good supplier doesn’t wait for you to ask. They provide updates when your order enters production, when it’s ready, and when it has shipped, including tracking information.
- Accessible Support: When a problem arises—a shipping delay, a question about installation—how easy is it to get someone on the phone or in a chat who can help solve it? A reliable partner doesn’t hide behind emails.
Excellent after-sales support is just as important. A reliable supplier stands behind their product. If there is an issue, they work with you to resolve it quickly. This peace of mind is often worth more than a few cents saved on the unit price.
Conclusion
Choosing reliable reusable fittings means assessing the whole picture: materials, machining, supplier reputation, standards, packaging, and service. This diligence protects you from the high cost of failure.
At Topa, we are dedicated to being the reliable partner you need. We deliver competitively priced, high-quality fittings backed by a team committed to fast communication and excellent service. We understand your challenges and are built to solve them.
If you are looking for a supplier you can trust for both standard and custom hydraulic fittings, contact the Topa team today for a quote, and let us show you what reliability really means.