As temperatures drop, the physical properties of the materials used in these hoses can change significantly. This can lead to challenges such as reduced flexibility, increased brittleness, and a higher risk of failure. Therefore, it is essential to comprehend how these factors influence the performance of metal hoses under cold conditions to ensure reliability and safety in applications.
Basics of Metal Hoses
A. Definition and Construction of Metal Hoses
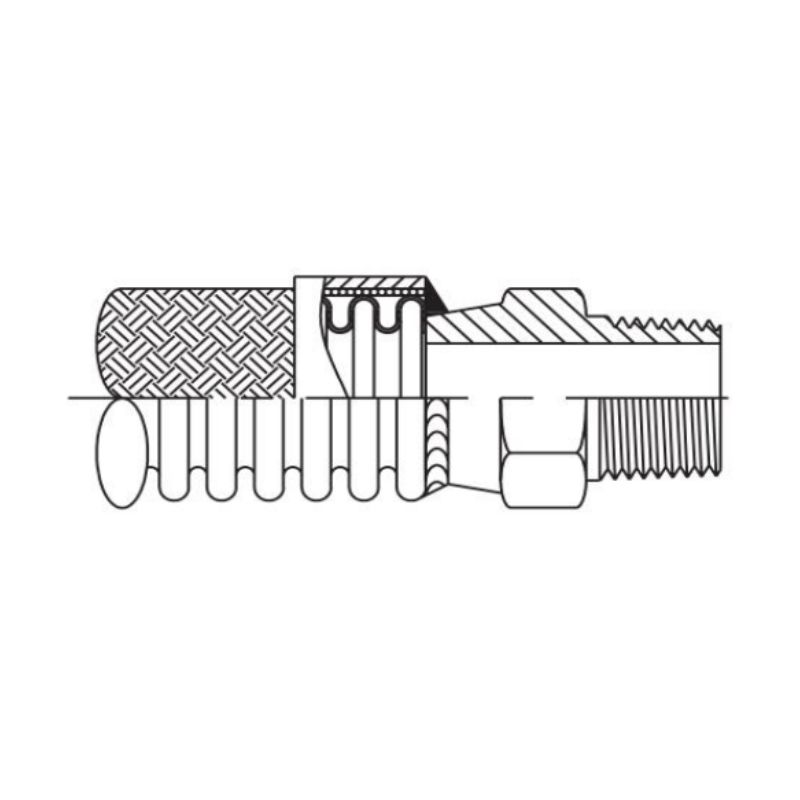
Metal hoses are flexible piping systems designed to convey fluids and gases in various industrial applications. Unlike rubber or plastic hoses, metal hoses are constructed from metal, providing superior durability, strength, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures. They consist of a corrugated inner tube, which allows for flexibility and movement, surrounded by a braid or external jacket that provides added strength and protection against external pressures.
The construction of a metal hose typically includes the following components:
Inner Tube: The core of the hose, often corrugated, which allows for bending and flexing without kinking.
Braid or Jacket: An outer layer made from woven metal wire, usually stainless steel, which enhances pressure ratings and provides structural integrity.
End Fittings: These are connectors attached to each end of the hose, which can be welded, threaded, or flanged, facilitating easy integration into piping systems.
This combination of features makes metal hoses ideal for applications that require flexibility while maintaining a strong resistance to physical damage, high temperatures, and corrosive environments.
B. Common Materials Used in Metal Hoses
Metal hoses can be constructed from various materials, each selected for its specific properties. The most common materials include:
Stainless Steel: The most widely used material due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and durability. Stainless steel hoses can withstand a broad range of chemicals, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Alloy Steel: Used in applications requiring high strength and durability, especially at elevated temperatures. Alloy steels can provide better performance in specific environmental conditions compared to standard stainless steel.
Monel and Inconel: Nickel-based alloys that offer exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. These materials are often employed in aerospace and chemical processing applications.
The choice of material greatly affects the performance characteristics of the hose, including flexibility, pressure rating, and resistance to environmental factors.
C. Typical Applications and Environments for Metal Hoses
Metal hoses are utilized across numerous industries due to their versatility and reliability. Some typical applications include:
Chemical Processing: Metal hoses are used to transport aggressive chemicals and fluids at varying temperatures and pressures, ensuring safe handling and minimizing the risk of leaks.
Aerospace: In the aerospace sector, metal hoses are critical for fuel and hydraulic fluid transport, especially in environments exposed to extreme temperatures and pressures during flight.
Automotive: Metal hoses are often used in exhaust systems, fuel lines, and other high-temperature applications within vehicles, providing the necessary durability and flexibility.
Food and Beverage Industry: Certain metal hoses, specifically those made from sanitary-grade materials, are employed in the transport of food products and beverages, where hygiene and safety are paramount.
Cryogenics: In applications involving cryogenic fluids, metal hoses are designed to withstand extremely low temperatures without losing structural integrity or performance.
Low-Temperature Effects on Metal Hoses
A. How Low Temperatures Affect Material Properties
Understanding the effects of low temperatures on metal hoses is critical for ensuring their reliability in cold environments. The materials used in metal hoses exhibit specific changes in properties when exposed to low temperatures.
Impact on Flexibility and Ductility
At lower temperatures, the flexibility of metal hoses can decrease significantly. This is primarily due to the reduced ductility of metals, which can become stiffer and less pliable. For instance, stainless steel, commonly used in metal hoses, may lose some of its ability to bend without kinking or cracking. As the temperature drops, the metal’s microstructure may change, leading to increased rigidity. This reduced flexibility can pose challenges in applications where the hoses must navigate tight bends or are subjected to dynamic movements.
Risk of Brittle Failure
Another critical concern at low temperatures is the increased risk of brittle failure. Metals generally become more brittle as temperatures decrease, particularly those that are not specifically formulated to withstand such conditions. Brittle failure occurs when a material breaks suddenly without significant plastic deformation. In metal hoses, this can lead to catastrophic failures, resulting in leaks or ruptures that can compromise system integrity. It is crucial to select materials with good low-temperature impact toughness to mitigate this risk, particularly in applications that experience frequent thermal cycling.

B. Effects of Thermal Contraction on Metal Hoses
Thermal contraction is another significant factor when dealing with low-temperature applications. As temperatures drop, the materials in metal hoses contract. This contraction can lead to several issues:
Dimensional Changes: Metal hoses can shrink in length and diameter, which may affect their fit and seal within a piping system. If not accounted for, this contraction can result in gaps that may lead to leaks, especially at connection points where fittings are used.
Stress Concentration: The contraction can create stress concentrations in the metal hose, particularly at bends and connections. This stress can further exacerbate the risk of fatigue and failure over time, especially if the hose experiences repeated thermal cycling.
Impact on Performance: Properly accounting for thermal contraction during installation and operation is essential. Engineers must consider the specific coefficients of thermal expansion for the materials used in the metal hoses and their fittings to ensure a reliable and leak-free system.
C. Influence of Environmental Factors
Various environmental factors can also influence the performance of metal hoses in low-temperature applications:
Pressure: The operating pressure can significantly affect how a metal hose behaves in low temperatures. High pressures combined with low temperatures can amplify the risks associated with brittleness and reduced ductility. Engineers must ensure that the hose’s pressure rating is sufficient for the intended application, considering potential pressure spikes that can occur due to thermal changes.
Fluid Type: The type of fluid being conveyed through the metal hose also plays a vital role in performance. Certain fluids may have lower freezing points or can become more viscous at low temperatures, affecting the flow characteristics. For example, oil may thicken in cold conditions, which can create additional pressure within the hose and increase the likelihood of rupture if the hose is not rated for such conditions.
External Environmental Conditions: Factors such as humidity, wind chill, and exposure to elements can also impact the performance of metal hoses. For instance, if a hose is exposed to cold, wet conditions, the risk of ice formation or condensation can affect its performance and longevity. Protective measures, such as insulation or heating, may be necessary to mitigate these risks.
Performance Standards for Low-Temperature Applications
A. Relevant Industry Standards and Certifications
When working with metal hoses in low-temperature applications, adhering to industry standards and certifications is essential for ensuring safety, performance, and reliability. Several key organizations set forth guidelines that manufacturers and users must follow:
ASTM Standards: The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides numerous standards relevant to metal hoses. Notable among them is ASTM A240, which specifies the requirements for stainless steel sheets and strips for pressure vessels and general applications, ensuring the materials used can withstand low-temperature conditions. ASTM F1476 also focuses on the performance of flexible metal hoses, addressing aspects critical to their operation in various environments.
ISO Standards: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established standards such as ISO 10380, which pertains to metallic flexible hoses. This standard outlines the requirements for the construction, testing, and marking of metal hoses, ensuring they can withstand the stresses encountered in low-temperature applications.
Other Applicable Standards: Additional standards from organizations like the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) may also apply. These standards cover various aspects of performance and safety in industries that commonly use metal hoses, ensuring that products meet specific operational criteria.
Adherence to these standards is crucial for manufacturers to ensure their products are fit for low-temperature environments, helping to mitigate risks associated with material failure and operational inefficiencies.
B. Testing Methods for Low-Temperature Performance
To ensure that metal hoses perform adequately under low-temperature conditions, several testing methods are utilized:
Cryogenic Testing: This testing involves subjecting metal hoses to extremely low temperatures, often below -150°C (-238°F), to evaluate their flexibility, ductility, and risk of brittle failure. During cryogenic testing, hoses are assessed for any physical changes, leaks, or structural weaknesses.
Pressure Testing: Low-temperature applications often involve high-pressure scenarios. Therefore, pressure testing at both ambient and low temperatures is critical. This includes hydrostatic testing, where hoses are filled with water and pressurized to ensure they can withstand operational pressures without leaking or bursting.
Thermal Cycling Tests: These tests simulate the conditions that hoses will experience during actual use, subjecting them to repeated cycles of heating and cooling. This method helps evaluate the hose’s ability to withstand the stresses associated with thermal expansion and contraction, which can lead to fatigue over time.
Bend Radius Testing: Since metal hoses are often required to navigate tight spaces, testing the minimum bend radius at low temperatures is essential. This test evaluates how well the hose maintains integrity and flexibility when subjected to bends, ensuring it does not kink or fail.
These testing methods are crucial for verifying that metal hoses can perform reliably in low-temperature applications, ensuring safety and operational effectiveness.
Selecting the Right Metal Hose for Low Temperatures
A. Key Factors to Consider
When selecting metal hoses for low-temperature applications, several critical factors must be evaluated to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Material Selection (e.g., Stainless Steel, Alloys)
The choice of material is paramount in determining how a metal hose will perform in low-temperature environments. Stainless steel is the most commonly used material due to its excellent corrosion resistance and overall durability. However, not all stainless steels are created equal. Certain grades, such as 316 and 321, are specifically designed to maintain flexibility and ductility at low temperatures.
For applications requiring even greater performance, high-performance alloys like Monel and Inconel may be appropriate. These materials provide superior strength and resistance to both corrosion and thermal stress, making them suitable for extreme conditions. When selecting a material, it is crucial to consider the specific temperature range, as well as the environmental factors such as chemical exposure.
Hose Design and Configuration
The design and configuration of the hose can significantly affect its performance in low-temperature applications. Key design aspects include the hose’s diameter, length, and bend radius. A hose that is too long or has an inappropriate bend radius may be prone to kinking or stress concentrations, which can lead to premature failure.
Additionally, the construction type—whether it features a corrugated inner tube and a braided outer layer—can influence flexibility and pressure ratings. Choosing a hose with the right balance of flexibility and rigidity is essential to accommodate the specific operational requirements of the application. Consulting with manufacturers can help identify optimal designs for particular environments.

B. Recommendations for Specific Low-Temperature Environments
Different low-temperature environments require tailored solutions for metal hose selection. Here are some recommendations:
Cryogenic Applications:
For applications involving cryogenic liquids, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) or liquid nitrogen, it is critical to select hoses made from specialized low-temperature alloys. These hoses should be designed to minimize thermal loss and maintain structural integrity at extreme temperatures. Look for hoses that have been cryogenically tested and certified.
Aerospace Applications:
In aerospace applications, metal hoses must endure not only low temperatures but also high pressures and rapid thermal cycling. Hoses made from high-quality stainless steel, such as 321, are recommended, as they offer the necessary strength and flexibility. Ensure that the hoses meet specific aerospace standards, including those from ASTM and SAE.
Industrial Refrigeration:
For refrigeration applications, selecting hoses that can handle the specific refrigerants being used is vital. Hoses should be compatible with low-temperature refrigerants and designed to minimize the risk of leakage. Stainless steel hoses with reinforced braiding are often ideal for these applications due to their resistance to pressure and flexibility.
C. Importance of Consulting Manufacturer Specifications
Consulting manufacturer specifications is crucial when selecting the right metal hose for low-temperature applications. Manufacturers provide detailed information about the materials used, construction methods, and performance ratings, including temperature limits and pressure capabilities.
Performance Data: This data helps engineers determine if the hose can withstand the specific environmental conditions expected in their application. Specifications often include test results that demonstrate the hose’s performance at low temperatures, which is essential for risk assessment.
Material Certifications: Manufacturers typically offer certifications for the materials used, ensuring compliance with industry standards. This information is vital for regulatory compliance, especially in industries such as aerospace and food processing, where safety is paramount.
Installation Guidelines: Manufacturers also provide guidance on proper installation techniques to avoid common pitfalls, such as improper bending or incorrect fitting types, which can lead to premature failure in low-temperature applications.
Conclusion
Regular inspections and adherence to industry standards are essential to avoid premature failure and ensure longevity. Moreover, understanding the relevant performance standards, testing methods, and case studies can help inform decisions and instill confidence in the chosen solutions.
FAQ
What materials are best for low-temperature metal hoses?
Stainless steel grades like 316 and 321 are commonly used, along with high-performance alloys such as Monel and Inconel, which provide superior strength and resistance.
How do low temperatures affect metal hoses?
Low temperatures can reduce flexibility, increase brittleness, and cause thermal contraction, leading to potential leaks or failures if not properly managed.
What should I consider when selecting a metal hose for low temperatures?
Key factors include the hose material, design, application requirements, and adherence to industry standards and manufacturer specifications.
How can I ensure the longevity of metal hoses in low-temperature applications?
Regular inspections, proper installation, and following maintenance guidelines are essential to ensure durability and performance.
Are there standards for metal hoses used in low-temperature environments?
Yes, various industry standards, including those from ASTM and ISO, outline the requirements for metal hoses, ensuring safety and reliability in low-temperature applications.
Can metal hoses be used in cryogenic applications?
Yes, specialized metal hoses made from low-temperature alloys are designed to handle cryogenic applications, maintaining flexibility and integrity at extreme temperatures.





