Introduction
Hydraulic cylinders operate in extreme environments and face severe challenges far beyond normal working conditions. Conventional sealing solutions are often inadequate in these environments, resulting in reduced equipment performance, increased failure rates, and even affecting the operational safety of the entire system. From polar cold to high desert temperatures, from salt spray corrosion at sea to high-intensity wear in mines, these harsh conditions place unprecedented demands on hydraulic sealing systems. In this paper, we will take a closer look at the latest technological innovations in hydraulic cylinder sealing systems designed for extreme environments.
Understanding Extreme Environmental Challenges
Temperature Extremes
Temperature variations represent one of the most significant challenges for hydraulic cylinder seals:
Cold Environment Challenges (-40°C to 0°C)
- Material Embrittlement: Standard elastomers lose flexibility and become brittle
- Increased Fluid Viscosity: Causes sluggish operation and higher starting pressures
- Thermal Contraction: Creates potential leak paths as materials contract differently
- Ice Formation: Moisture can freeze around rod seals, causing damage during operation
Hot Environment Challenges (80°C to 200°C+)
- Accelerated Aging: Heat speeds chemical degradation of seal materials
- Reduced Material Strength: Elastomers soften and extrude under pressure
- Fluid Breakdown: Hydraulic fluids lose viscosity and lubricity
- Thermal Expansion: Creates interference issues and increased friction
Chemical Exposure
Many industrial environments expose hydraulic cylinders to aggressive chemicals:
- Acid/Alkaline Environments: Mining, chemical processing, and waste management
- Hydrocarbon Exposure: Oil and gas, petrochemical, and fuel handling applications
- Solvent Contact: Cleaning operations, paint applications, and manufacturing processes
- Oxidizing Agents: Water treatment, bleaching operations, and oxidative environments
Particulate Contamination
Abrasive particles represent a major threat to seal integrity:
- Mining Dust: Contains hard silica particles that abrade seal surfaces
- Metal Particles: From manufacturing processes can embed in softer seal materials
- Airborne Contaminants: Desert sand, volcanic ash, and industrial particulates
- Process Materials: Cement, coal, grain, and other process materials can infiltrate seal areas
Pressure and Cycling Demands
Extreme applications often involve challenging mechanical conditions:
- High-Pressure Operation: Offshore and high-performance applications exceeding 350 bar
- Pressure Spikes: Shock loading causing momentary pressure exceeding normal limits
- Rapid Cycling: High-frequency operation generating heat and accelerating wear
- Long Dwell Periods: Extended static positioning causing seal adhesion and set
Advanced Sealing Material Innovations
Next-Generation Elastomers
Recent elastomer developments specifically address extreme environment limitations:
Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR)
Temperature Range: -40°C to +150°C
Key Advantages:
- Excellent resistance to petroleum-based fluids
- Superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to standard NBR
- Good abrasion resistance for particulate environments
- Maintains flexibility at lower temperatures than standard nitrile
Optimal Applications: Oil and gas, mining equipment, outdoor construction equipment
Fluoroelastomers (FKM/Viton®)
Temperature Range: -20°C to +200°C
Key Advantages:
- Exceptional chemical resistance to most hydrocarbons
- Outstanding high-temperature performance
- Excellent resistance to compression set
- Good resistance to steam and hot water
Optimal Applications: High-temperature processing, chemical exposure, steam environments
Perfluoroelastomers (FFKM)
Temperature Range: -15°C to +325°C
Key Advantages:
- Near-universal chemical resistance
- Highest temperature capability of any elastomer
- Excellent compression set resistance
- Long-term reliability in aggressive environments
Optimal Applications: Chemical processing, semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace
Advanced Polymer Composites
Non-elastomeric materials offer unique advantages in extreme applications:
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) Compounds
Temperature Range: -200°C to +260°C
Key Advantages:
- Near-universal chemical resistance
- Extremely low friction coefficient
- Zero stick-slip behavior
- Excellent high and low-temperature performance
Limitations:
- Poor elasticity requires special profile designs
- Higher leakage rates than elastomers
- Limited abrasion resistance unless modified
Innovations:
- Filled PTFE with carbon, glass, bronze, or MoS₂ for improved wear resistance
- Spring-energized designs to maintain contact pressure
- Layered composite structures combining PTFE with elastomer backings
UHMWPE (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene)
Temperature Range: -200°C to +80°C
Key Advantages:
- Exceptional abrasion resistance
- Very low friction coefficient
- Excellent impact resistance
- Good chemical resistance to many substances
Optimal Applications: Abrasive environments, food processing, cryogenic applications
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
Temperature Range: -60°C to +250°C
Key Advantages:
- High mechanical strength and rigidity
- Excellent wear resistance
- Good chemical resistance
- Radiation resistance
Optimal Applications: High-pressure applications, radiation environments, high-temperature mechanical systems
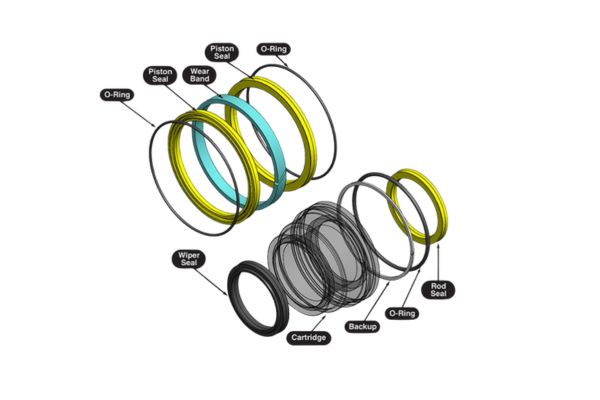
Innovative Composite Sealing Systems
Modern extreme environment seals often combine multiple materials:
Dual-Material Sealing Systems
Configuration: PTFE primary seal with elastomer energizer
Advantages:
- Combines chemical resistance of PTFE with elasticity of rubber
- Compensates for wear through continuous energization
- Provides redundant sealing capability
- Adaptable to temperature fluctuations
Applications: Chemical processing, temperature cycling environments
Layered Composite Seals
Configuration: Multiple layers of different materials bonded together
Advantages:
- Each layer provides specific performance characteristics
- Can include reinforcement materials for stability
- Optimized for specific environmental challenges
- Provides gradual property transitions
Applications: Offshore equipment, extreme pressure applications
Innovative Seal Designs for Extreme Environments
Advanced Profile Engineering
Seal profile geometry significantly impacts performance in extreme conditions:
Step-Cut Profiles
Design Features: Stepped cutting edge with precise contact area
Advantages:
- Reduced friction while maintaining sealing effectiveness
- Better resistance to spiral failure
- Improved fluid film maintenance
- Less heat generation during operation
Best Applications: High-speed applications, temperature-sensitive environments
Bidirectional Pressure-Activated Designs
Design Features: Symmetrical profile that energizes under pressure from either direction
Advantages:
- Eliminates need for separate seals for different directions
- Improves sealing as system pressure increases
- Reduces inventory requirements
- Prevents installation errors
Best Applications: Double-acting cylinders, systems with pressure reversals
Anti-Extrusion Profiles
Design Features: Integrated anti-extrusion rings or reinforced edges
Advantages:
- Prevents seal material from extruding into clearance gaps
- Allows operation at higher pressures
- Extends seal life in high-pressure applications
- Maintains sealing effectiveness as parts wear
Best Applications: High-pressure systems, applications with larger clearances
Multi-Stage Sealing Systems
Complex environments often require multiple sealing elements:
Tandem Sealing Arrangements
Configuration: Multiple seals arranged in series
Advantages:
- Provides redundancy if primary seal fails
- Can handle pressure spikes more effectively
- Distributes wear across multiple components
- Allows for specialized function of each seal
Applications: Safety-critical systems, high-reliability requirements
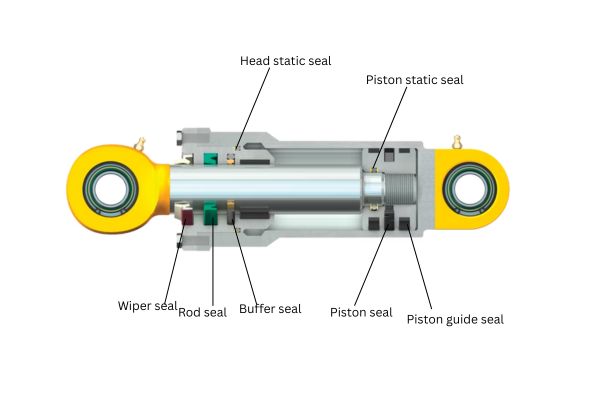
Buffer Sealing Systems
Configuration: Primary seal with secondary buffer seal and controlled fluid chamber
Advantages:
- Prevents direct environmental contamination of primary seal
- Can include monitoring of buffer chamber condition
- Extends primary seal life significantly
- Allows for specialized buffer fluids
Applications: Highly contaminated environments, applications requiring extended service intervals
Environmental Exclusion Systems
Configuration: Multiple wiper and excluder elements before main sealing system
Advantages:
- Prevents contaminants from reaching primary seals
- Staged removal of different contaminant types
- Protects expensive primary sealing elements
- Often field-replaceable without major disassembly
Applications: Mining, construction, agricultural equipment
Surface Engineering and Coating Technologies
Advanced Rod Surface Treatments
The hydraulic cylinder rod surface directly impacts seal performance and longevity:
Hard Chrome Alternatives
Technologies:
- High Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) chromium carbide coatings
- Nickel-chromium composite platings
- Plasma-applied ceramic coatings
Advantages:
- Superior hardness (up to 1200 HV versus 700 HV for chrome)
- Better corrosion resistance, especially in salt environments
- Improved wear resistance against abrasive particles
- More environmentally friendly than hexavalent chrome processes
Applications: Marine environments, mining equipment, chemical processing
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coatings
Properties:
- Extremely low friction coefficient (0.1 or lower)
- Very high hardness (2000-3000 HV)
- Chemical inertness
- Thin coating (1-5 μm) maintains dimensional precision
Advantages:
- Dramatically reduces break-away friction
- Improves efficiency and reduces heat generation
- Excellent compatibility with most seal materials
- Enhances corrosion resistance
Applications: High-efficiency systems, food processing, medical equipment

Engineered Surface Texturing
Technologies:
- Laser micro-texturing creating controlled patterns
- Micro-dimpling for fluid retention
- Controlled roughness profiles
Advantages:
- Improves lubrication film maintenance
- Reduces seal friction and wear
- Enhances sealing effectiveness
- Can trap contaminant particles away from sealing interface
Applications: High-precision equipment, long-life applications
Barrel Surface Innovations
Internal cylinder surfaces also benefit from advanced treatments:
Plateau Honing Techniques
Process: Multi-stage honing creating plateaued surface with controlled valley depth
Advantages:
- Provides fluid retention while maintaining smooth bearing surface
- Reduces break-in period
- Improves seal life by reducing abrasion
- Maintains consistent performance throughout service life
Applications: Premium hydraulic cylinders, precision applications
Nikasil® and Composite Nickel-Silicon Carbide Coatings
Properties: Electrodeposited nickel matrix with embedded silicon carbide particles
Advantages:
- Exceptional hardness and wear resistance
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Can be applied to aluminum and other lightweight materials
- Allows for tighter tolerances and improved efficiency
Applications: Lightweight cylinder designs, corrosive environments
Implementation Strategies for Extreme Environments
Environment-Specific Selection Guidelines
Arctic/Cold Environment Solutions
Recommended Materials:
- Low-temperature HNBR or specialized fluorosilicone elastomers
- PTFE composites for extremely low temperatures
- Special low-temperature polyurethanes
Design Considerations:
- Increased clearances to accommodate thermal contraction
- Specialized low-temperature hydraulic fluids
- Pre-heating systems for critical applications
- Multiple wiper seals to prevent ice and snow ingress
High-Temperature Environment Solutions
Recommended Materials:
- FKM or FFKM elastomers
- PEEK-based composites
- High-temperature PTFE compounds
Design Considerations:
- Enhanced cooling systems
- Heat shields and insulation
- Specialized high-temperature hydraulic fluids
- Increased clearances for thermal expansion
Chemically Aggressive Environment Solutions
Recommended Materials:
- FFKM for universal chemical resistance
- PTFE for acid/base environments
- Specialized compound FKM for specific chemical exposures
Design Considerations:
- Sacrificial anodes for galvanic protection
- Chemical-resistant external coatings
- Buffer fluid systems to isolate primary seals
- Monitoring systems for seal condition
Abrasive/Particulate Environmental Solutions
Recommended Materials:
- Polyurethane for excellent abrasion resistance
- UHMWPE for extreme abrasion applications
- Filled PTFE with wear-resistant additives
Design Considerations:
- Multiple wiper and scraper stages
- Advanced filtration systems
- Rod boots and protective covers
- Positive pressure systems to prevent ingress
Maintenance and Monitoring Strategies
Predictive Maintenance Approaches
Condition Monitoring Technologies:
- Integrated pressure sensors detecting seal bypass
- Temperature monitoring identifying friction increases
- Fluid analysis protocols for wear particle detection
- Automated stroke counting and duty cycle recording
Implementation Benefits:
- Prevents catastrophic failures
- Optimizes maintenance intervals based on actual conditions
- Reduces unplanned downtime
- Extends overall system life
Specialized Maintenance Protocols
Cold Environment Maintenance:
- Proper warm-up procedures before operation
- Special low-temperature greases for exposed components
- Moisture removal protocols to prevent freezing
- Insulation covers during extended shutdowns
Hot Environment Maintenance:
- Regular cooling system inspection and maintenance
- Heat shield integrity verification
- More frequent fluid analysis and replacement
- Thermal imaging to identify potential issues
Corrosive Environment Maintenance:
- Regular washing and neutralization procedures
- Sacrificial anode replacement schedules
- Protective coating inspection and repair
- Seal condition verification through leakage testing
Abrasive Environment Maintenance:
- Regular wiper seal replacement
- Compressed air cleaning of exposed rod surfaces
- Rod boot inspection and replacement
- More frequent filter element replacement
Case-Specific Selection Guide
Application-Based Recommendations
| Environment Type | Primary Challenge | Recommended Seal System | Surface Treatment | Maintenance Focus |
| Arctic Mining | Cold temperatures, abrasive particles | Low-temp polyurethane wipers, PTFE/HNBR primary seals | HVOF coating with enhanced surface finish | Warm-up procedures, wiper maintenance |
| Desert Oil & Gas | Heat, sand, hydrocarbon exposure | FKM wipers, PTFE/FKM primary seals | DLC coating with micro-texturing | Cooling system maintenance, regular cleaning |
| Offshore Marine | Salt corrosion, temperature cycling | Multiple wipers, PTFE/HNBR composite seals | Nickel-chromium composite plating | Corrosion protection, water exclusion |
| Chemical Processing | Aggressive chemicals, thermal cycling | FFKM or specialized FKM systems | Ceramic coating or specialized stainless | Chemical compatibility verification, buffer monitoring |
| Steel Mill | Extreme heat, scale, rapid cycling | High-temp FKM, reinforced PTFE composites | HVOF with enhanced hardness | Cooling system maintenance, wiper replacement |
| Food Processing | Washdown chemicals, temperature variation | FDA-compliant HNBR or PTFE | Electropolished stainless or FDA coatings | Sanitation procedures, chemical compatibility |
| Forestry/Logging | Organic debris, impact loading, outdoor exposure | Heavy-duty polyurethane, dual-wiper systems | Hard chrome or HVOF with textured surface | Debris removal, impact damage inspection |
Conclusion
The development of sealing technology for hydraulic cylinders in extreme environments has greatly expanded the operating range of hydraulic systems. By understanding the specific challenges posed by different extreme environments and selecting the appropriate sealing technology, you can significantly improve reliability, extend service intervals and reduce total cost of ownership.
If you have any hydraulic cylinder requirements, please feel free to contact us and Topa can customize the most suitable hydraulic cylinder for your requirements!





