A mismatched thread or seal can bring your entire operation to a standstill. These small errors lead to persistent leaks, create serious safety hazards, and result in costly downtime while you hunt for the correct component.
This definitive N-Z glossary decodes the language of hydraulic connections. It explains terms from NPT threads and O-Ring seals to torque specifications, empowering you to build reliable, leak-free systems every time.
NPT to O-Ring Boss?
A pipe thread connection keeps leaking, despite being tightened repeatedly. Overtightening has now cracked the valve body, turning a small leak into a major repair job and extended downtime for the machinery.
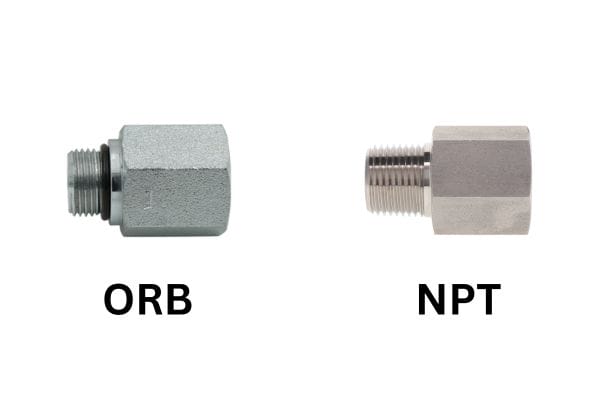
NPT is a tapered pipe thread that requires sealant. An O-Ring Boss (ORB) fitting uses a straight thread and a high-durability O-ring, providing a far more reliable seal for modern hydraulic systems.
American Threads and Sealing Methods
In the Americas, tapered pipe threads are a legacy standard that we still supply frequently, but we always advise customers on their limitations compared to modern O-ring seals.
- NPT (National Pipe Taper): This is the most common tapered pipe thread in the United States. The male and female threads are both tapered, and the seal is theoretically made on the flanks of the threads. In practice, a sealant like pipe dope or liquid thread sealant is always required to fill the helical leak path that exists. We strongly advise against using PTFE tape, as slivers can break off and contaminate the hydraulic system.
- NPTF (National Pipe Taper Fuel): Also known as a “Dryseal” thread, NPTF is an improvement on NPT. The threads are designed to crush and deform at the root and crest during assembly, creating a metal-to-metal seal without sealant. While this is the theory, we find that in high-pressure or high-vibration applications, using a liquid sealant is still the best practice to guarantee a leak-free joint.
- O-Ring: An elastomeric loop with a round cross-section, used as a seal. In hydraulic fittings, they are typically made from 90 durometer NBR (Nitrile) or Viton for high-temperature applications. They are the core technology behind the most reliable hydraulic sealing methods.
- O-Ring Boss (ORB): Also called SAE Straight Thread, this fitting (governed by SAE J1926-1) uses a straight, parallel thread. The seal is not made by the threads but by an O-ring that sits in a groove on the male fitting and compresses into a chamfered “boss” on the female port. We consider this the standard for reliable port connections on valves, pumps, and cylinders. It is vastly superior to NPT for high-pressure hydraulics.
ORFS to PSI?
A fitting on a hydraulic excavator persistently leaks under high pressure spikes. The metal-to-metal flare connection can’t handle the system’s intense impulse cycles, causing constant maintenance issues and safety concerns.
O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings offer superior leak prevention in demanding applications. PSI is the unit of measure for pressure, defining the force a fitting must withstand.

Advanced Sealing and Pressure Metrics
When a customer needs absolute, zero-leak reliability, we almost always guide them to ORFS. The design principle is simple and extremely effective.
- ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal): This fitting (SAE J1453) is our top recommendation for high-vibration and high-pressure applications. As the name suggests, it seals with an O-ring in the face of the male fitting, which is compressed onto a flat face on the female fitting. The threads solely provide clamping force and are not involved in sealing. This soft seal design isolates the connection from vibration and is extremely resistant to leaks caused by pressure impulses.
- Parallel Thread: Any thread form where the male and female threads are parallel to each other (not tapered). These threads cannot create a seal by themselves and always require a separate sealing mechanism, such as a bonded seal (BSPP) or an O-ring (ORB).
- Port: A generic term for the connection point on a hydraulic component where fluid enters or exits. Ports can be found on pumps, motors, cylinders, and valves, and they are machined to accept a specific fitting type, such as NPT, ORB, BSPP, or a four-bolt flange.
- PSI (Pounds per Square Inch): The primary unit of pressure measurement in the United States and some other regions. All fittings have a maximum pressure rating in PSI, which must not be exceeded.
| Fitting Type | Sealing Method | Vibration Resistance | Pressure Rating |
| NPT/NPTF | Metal-to-Metal (Taper) | Poor | Medium |
| JIC | Metal-to-Metal (Flare) | Fair | High |
| ORB | O-Ring (in Port) | Good | High |
| ORFS | O-Ring (in Face) | Excellent | Very High |
Quick Disconnect to Reusable Fitting?
Connecting and disconnecting hydraulic lines on a tractor implement is slow and messy. Using standard fittings leads to significant fluid spillage and allows contaminants to enter the open lines.
A quick disconnect coupling allows for fast, tool-free connections with minimal spillage. Reusable fittings are an older technology allowing for field assembly with hand tools, now largely replaced by crimp fittings.

Functionality and Assembly Methods
Speed of service and ease of use are critical in many applications, especially agriculture and construction. This is where quick disconnects excel.
- Quick Disconnect (or Quick Coupling): This is a two-part fitting (male and female half) that allows for rapid connection and disconnection of a hydraulic line without tools. Internal valves in both halves automatically close when disconnected, preventing fluid loss and minimizing contamination. We supply several types:
- Poppet Style (ISO 7241-A): The classic, general-purpose “AG” style coupling.
- Flat Face (ISO 16028): A superior no-drip design that is easy to clean and prevents contamination. It’s the standard for skid steers and other construction equipment.
- Race: This refers to the machined track in a fitting or bearing that contains ball bearings. In a female swivel fitting (like a JIC), the race allows the nut to spin freely for easy assembly.
- Reusable Fitting: A type of fitting that can be attached to a hose using only wrenches. It typically consists of a socket that threads over the hose and a nipple that threads into the socket, compressing the hose to create a seal. We stock these for certain low-pressure or legacy applications, but for any modern, high-pressure system, a crimped fitting is a far safer and more reliable choice. They are useful for emergency field repairs where a crimper is not available.
SAE to Seat Angle?
A customer orders a “3/4 inch SAE fitting” and receives the wrong part. The term “SAE” is too general, as the organization defines many different fitting types, including flare, O-ring, and flange fittings.
SAE is the standards body that defines most hydraulic fittings used in North America. The seat angle is the specific angle of the conical surface where a fitting makes its seal.
Defining Standards and Geometry
“SAE” is not a type of fitting; it’s the organization that writes the standards. Being specific is crucial for ordering parts. When a customer asks for an SAE fitting, we have to ask clarifying questions to determine exactly which standard they need.
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers): This professional organization sets the technical standards for countless components in the US, including the most common hydraulic fittings. Important SAE standards include:
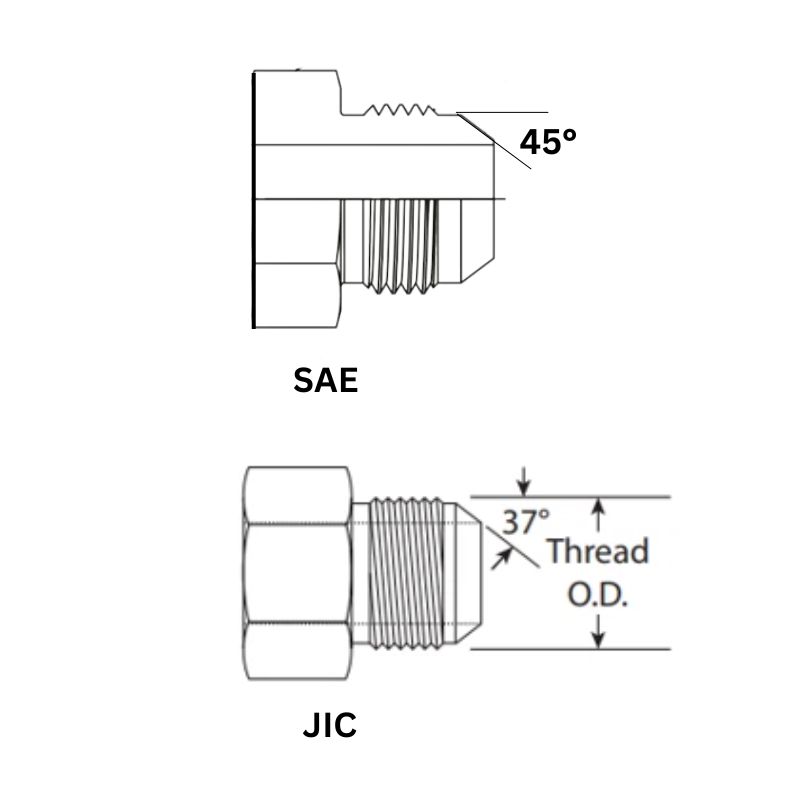
- SAE J514: Covers JIC 37° flare fittings and SAE 45° flare fittings.
- SAE J1453: Covers O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings.
- SAE J1926-1: Covers O-Ring Boss (ORB) fittings.
- SAE J518: Covers four-bolt flange fittings.
- SAE 45° Flare: This fitting looks similar to JIC but has a 45° seat angle. It is commonly used in lower-pressure applications like automotive brake lines, fuel lines, and refrigeration, but is not suitable for modern high-pressure hydraulic systems. JIC 37° and SAE 45° are not interchangeable.
- Seal: A general term for any device used to prevent the leakage of fluid. In hydraulic fittings, this can be a metal-to-metal seal (like on a JIC fitting) or an elastomeric seal (like an O-ring or bonded seal).
- Seat Angle: The angle of the sealing surface on a cone-style fitting. This is a critical identifying feature. JIC uses a 37° angle, while SAE flare fittings use a 45° angle. Mismatched seat angles will not seal and will damage both fittings.
Skive to Swivel?
A new hose assembly fails because the swivel nut was overtightened during installation. The hose was twisted, putting constant stress on the reinforcement wires and causing a premature rupture near the fitting.
Skiving is the (now mostly obsolete) practice of removing the hose cover before crimping. A swivel allows a fitting’s nut to rotate independently, preventing hose twist during installation.

Assembly Practices and Fitting Features
Proper assembly technique is just as important as selecting the right parts. Understanding features like “no-skive” and “swivel” is key to a fast, reliable, and long-lasting installation.
- Skive: The act of removing the outer rubber cover of a hydraulic hose before crimping a fitting on. This was required for older fitting types to allow the ferrule to grip the wire reinforcement directly. We primarily sell “no-skive” fittings, a modern design with a more aggressive ferrule that can bite through the cover to grip the reinforcement. No-skive is faster, easier, and protects the reinforcement from corrosion.
- Staple-Lok: Also known as a “Steck-O” fitting, this is a unique connection style used heavily in underground mining. It uses a smooth male probe that inserts into a female half, and the two are held together by a large U-shaped staple. It is a robust, compact, and easy-to-assemble connection for tight spaces.
- Stem: The component of a hose fitting that is inserted into the inner tube of the hose. It is also sometimes called the nipple or insert.
- Swivel: A feature of a fitting (usually the female half) that allows the nut to rotate independently of the fitting body. This “live swivel” is crucial because it allows the connection to be tightened without imparting any twist to the hose. A hose installed with even a slight twist will have a dramatically reduced service life.
Thread Pitch to Zinc Plating?
A metric fitting won’t thread into a port, even though the diameter seems correct. The thread pitch is wrong, a subtle but critical detail that prevents the connection from being made.
Thread pitch is the distance between threads and is a critical dimension for identifying fittings. Zinc plating is the most common protective coating used to prevent corrosion on steel hydraulic fittings.

Identification Details and Material Protection
The final details of identification and material science are what separate a professional from an amateur. Using tools like calipers and pitch gauges is a daily activity in our business.
- Thread Pitch: A critical measurement for identifying a thread. For metric threads, it’s the distance in millimeters between two adjacent thread crests (e.g., 1.5mm). For imperial threads (like UNF), it’s measured in Threads Per Inch, or TPI (e.g., 12 TPI). A fitting with the correct diameter but the wrong pitch will not engage properly.
- Torque: The rotational force applied to a fitting when tightening it. Every fitting type has a recommended assembly torque.
- Under-torquing: The fitting will leak or blow off.
- Over-torquing: The fitting can be damaged, flares can crack, O-rings can be extruded, and threads can be stripped. Following the manufacturer’s torque specifications is essential for a reliable seal.
- Viton® (FKM): A brand name for a Fluoroelastomer. We supply O-rings and seals made from Viton for applications involving high temperatures or aggressive chemicals that would destroy standard NBR (Nitrile).
- Working Pressure: The maximum pressure a fitting is rated to handle continuously in service. This should never be exceeded. The working pressure of a full hose assembly is always limited by its lowest-rated component (either the hose or one of the fittings).
- Zinc Plating: Most steel hydraulic fittings are electroplated with a layer of zinc to protect them from rust. Standard plating offers moderate corrosion resistance. We also supply fittings with higher-performance plating (often called Zinc-Nickel or similar) that can withstand over 720 hours of salt spray testing, making them ideal for marine or other highly corrosive environments.
Conclusion
This N-Z glossary completes our ultimate guide. Mastering these terms is vital for anyone who specifies, builds, or maintains hydraulic systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety.





