Proper sizing of hydraulic fittings directly influences a system’s efficiency and performance. When fittings are correctly sized, they optimize fluid flow, minimize pressure drops, and reduce the risk of leaks and failures. Conversely, incorrectly sized fittings can lead to significant issues, including reduced operational efficiency, increased wear and tear on components, and costly downtime.
Understanding Hydraulic Fittings
A. Definition and Function of Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic fittings are mechanical components that serve as junction points within hydraulic systems, allowing the connection of hoses, pipes, and tubes. Their primary function is to facilitate the flow of hydraulic fluid between various parts of the system, such as pumps, actuators, and valves. Hydraulic fittings play a critical role in maintaining system pressure and fluid integrity by ensuring secure and leak-free connections. They are designed to withstand high pressure and extreme conditions, making them essential for the safe and efficient operation of hydraulic machinery.
The function of hydraulic fittings extends beyond mere connection. They are integral to regulating flow rates and maintaining the system’s overall efficiency. Properly selected and installed fittings can minimize turbulence and pressure drops, thereby enhancing the performance of the hydraulic system. Conversely, poor-quality or incorrectly sized fittings can lead to leaks, inefficiencies, and even catastrophic system failures.
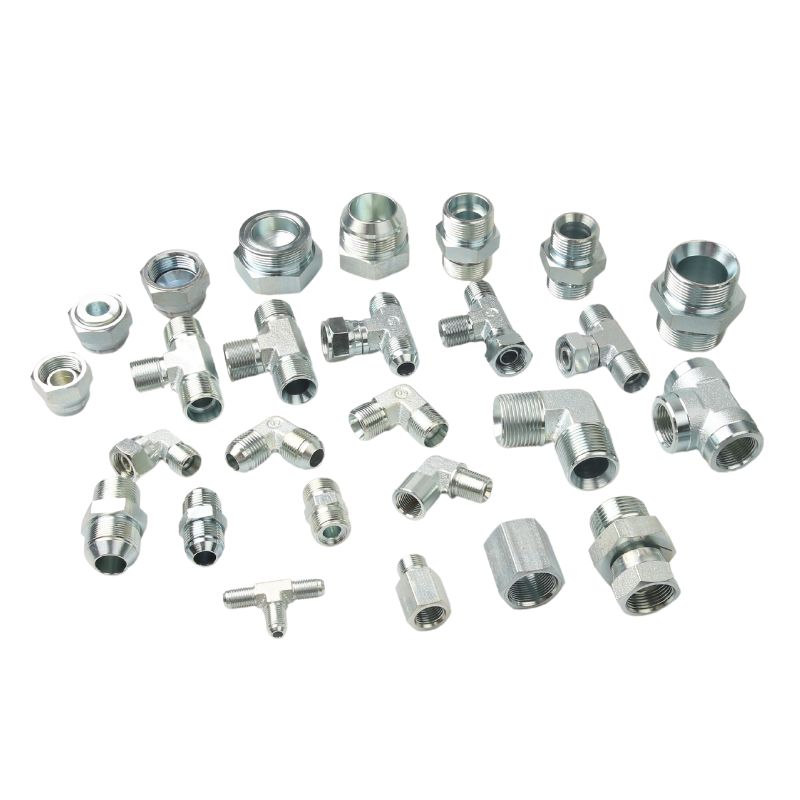
B. Types of Hydraulic Fittings
There are various types of hydraulic fittings, each designed for specific applications and requirements. Some of the most common types include:
Connectors: These fittings are used to connect hoses or pipes. They come in different configurations, such as male and female threads, and are available in various sizes to match the corresponding hoses.
Adapters: Adapters enable connections between different types of fittings or components. They are crucial in systems that utilize a mix of metric and imperial components, allowing for compatibility across varying standards.
Elbows: These fittings allow for directional changes in fluid flow, typically at 90 or 45 degrees. Elbows are essential for routing hoses and pipes in confined spaces.
Tees: T-shaped fittings facilitate the branching of fluid lines, allowing fluid to be diverted to multiple paths from a single source.
Caps and Plugs: These fittings are used to close the end of a hose or pipe, preventing fluid leakage when a line is not in use.
Flanges: Flanged fittings create a stable connection by bolting two components together. They are commonly used in high-pressure applications where a robust connection is essential.
Quick Couplers: These fittings allow for rapid connection and disconnection of hoses and equipment without the need for tools, enhancing operational efficiency.
Each type of fitting has its specific applications and advantages, making it important to choose the right type based on the system’s requirements.

C. Common Applications in Various Industries
Hydraulic fittings find applications across a wide range of industries due to their versatility and reliability. Some notable sectors include:
Construction: Hydraulic systems power heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. Fittings in these applications must withstand high pressures and extreme conditions, ensuring that equipment operates smoothly and efficiently.
Agriculture: Tractors and other agricultural equipment utilize hydraulic systems for functions like steering and lifting. Durable hydraulic fittings are essential for maintaining the integrity of these systems under harsh farming conditions.
Manufacturing: In manufacturing, hydraulic systems are used for automation, material handling, and metal forming. Accurate sizing and selection of fittings are critical for ensuring the efficiency and safety of production processes.
Aerospace: Hydraulic systems in aircraft rely on precise fittings to manage flight controls and landing gear operations. The stringent standards in the aerospace industry require high-quality, reliable fittings that can perform under extreme conditions.
Marine: In marine applications, hydraulic systems are employed for steering and other operational functions. Fittings must be resistant to corrosion and saltwater exposure to ensure longevity and reliability.
Automotive: Hydraulic fittings are crucial in vehicles for braking and steering systems. Their reliability directly impacts vehicle safety and performance.
The Significance of Proper Sizing
A. Effects of Incorrect Sizing on System Performance
Proper sizing of hydraulic fittings is crucial for the optimal performance of hydraulic systems. Incorrect sizing can significantly hinder the efficiency of fluid flow, leading to various operational challenges. When fittings are either too large or too small, the system struggles to maintain the required pressure and flow rates, which are essential for proper function.
For instance, oversized fittings may cause turbulence in the hydraulic fluid, resulting in a drop in pressure and a decrease in the system’s overall efficiency. Conversely, undersized fittings can restrict flow, causing increased resistance and leading to overheating of the hydraulic fluid. This inefficiency can translate to higher operational costs, increased energy consumption, and reduced overall productivity.
Moreover, incorrect sizing can lead to imbalances within the hydraulic system, affecting the performance of connected components. For example, if the fittings do not allow for adequate fluid delivery to actuators, it may result in sluggish operation or failure to perform required tasks, thereby compromising the entire hydraulic system’s functionality.
B. Common Issues Caused by Improper Fitting Sizes
Improperly sized hydraulic fittings can lead to several common issues that can adversely affect the hydraulic system:
Leaks: One of the most immediate problems with incorrect sizing is leakage. If fittings are too loose, they can allow hydraulic fluid to escape, leading to significant fluid loss. Leaks not only reduce system efficiency but can also create hazardous working conditions.
Pressure Loss: Incorrectly sized fittings can cause fluctuations in system pressure. This instability can hinder the operation of critical components, resulting in inconsistent performance and potential system failures.
Increased Wear and Tear: When fittings do not match the required specifications, additional strain is placed on the hydraulic system. This strain can lead to premature wear of hoses, pumps, and other components, necessitating frequent repairs or replacements.
Overheating: Restricted flow caused by undersized fittings can lead to overheating of the hydraulic fluid. Elevated temperatures can degrade the fluid’s properties, reduce lubrication effectiveness, and ultimately compromise the integrity of the entire system.
System Failures: In severe cases, improper sizing can lead to catastrophic failures, where critical components may fail altogether, causing costly downtime and potential safety hazards.

C. Benefits of Accurate Sizing
Accurate sizing of hydraulic fittings brings numerous benefits that enhance both system efficiency and safety:
Enhanced Efficiency: Properly sized fittings ensure optimal fluid flow, which minimizes resistance and turbulence. This efficiency translates to lower energy consumption and improved performance of the hydraulic system, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Improved Safety: Accurate sizing reduces the risk of leaks and system failures, contributing to a safer working environment. Ensuring that hydraulic systems operate within their intended parameters helps to protect personnel and equipment.
Longevity of Components: Correctly sized fittings help to maintain the health of the hydraulic system by reducing strain on hoses, pumps, and other components. This results in longer service life for these parts and fewer maintenance requirements.
Consistent Performance: Accurate sizing helps maintain stable pressure and flow rates, leading to predictable and reliable operation of hydraulic machinery. Consistent performance is crucial in industries where precision is essential, such as aerospace and manufacturing.
Reduced Downtime: By preventing issues related to improper sizing, organizations can minimize unscheduled maintenance and repair work, ensuring that systems remain operational and productive.
Key Factors in Sizing Hydraulic Fittings
A. Fluid Type and Properties
The characteristics of the hydraulic fluid used in a system play a crucial role in determining the appropriate fitting size.
Viscosity Considerations: Viscosity, or the thickness of the fluid, affects how easily it flows through the system. Higher-viscosity fluids, such as certain oils, require larger fittings to ensure adequate flow rates, as they move more slowly than low-viscosity fluids. Conversely, if the fittings are too large for the viscosity, it can lead to turbulence and inefficiencies. Understanding the viscosity at the operating temperature is essential for selecting fittings that allow for smooth and efficient fluid movement.
Temperature Range: The operating temperature of the hydraulic fluid is another critical factor. Different fluids have varying properties at different temperatures, affecting their viscosity and overall behavior. High temperatures can cause certain materials to degrade, which can affect fitting performance. Thus, selecting fittings that can withstand the temperature extremes of the operating environment is vital for maintaining system integrity and efficiency.
B. System Pressure Requirements
Pressure is a fundamental aspect of hydraulic systems, and understanding it is essential for proper fitting sizing.
Understanding Pressure Ratings: Every fitting has a pressure rating that indicates the maximum pressure it can handle without failing. It is essential to consult manufacturer specifications to ensure that the fittings selected can withstand the pressures they will encounter in operation.
Matching Fittings to System Pressure: Once the system pressure requirements are established, fittings must be matched accordingly. If fittings are rated lower than the system pressure, there is a risk of failure, which can lead to leaks or catastrophic failures. Conversely, using overly robust fittings may increase costs unnecessarily. Properly matching fittings to system pressure is key to optimizing performance and safety.
C. Pipe and Hose Specifications
The specifications of the pipes and hoses used in a hydraulic system are vital in determining fitting sizes.
Diameter Considerations: The diameter of the pipes and hoses dictates the size of the fittings required. Proper sizing ensures that fluid flows efficiently without unnecessary restrictions. When selecting fittings, it is essential to measure the inner diameter of the hoses or pipes accurately to find compatible fittings that allow for optimal flow rates.
Wall Thickness and Material Type: The wall thickness of hoses and pipes also influences fitting selection. Thicker walls can withstand higher pressures, which is critical in high-stress applications. Additionally, the material type affects the fitting choice, as different materials have varying tolerances to pressure, temperature, and corrosion. For example, metal fittings may be required for high-pressure applications, while plastic fittings may suffice for lower-pressure systems.

D. Compatibility with Existing Components
Ensuring that hydraulic fittings are compatible with existing system components is crucial for seamless operation.
Thread Types and Standards: Different hydraulic systems may utilize various thread types and standards, such as NPT, BSP, or JIC. Properly matching these thread types is essential for ensuring a secure connection that prevents leaks. Mismatched threads can lead to improper fittings that may loosen over time, increasing the risk of failure.
Material Compatibility (e.g., Metal vs. Plastic): Compatibility of materials between fittings and connected components is critical. Certain fluids can degrade specific materials, leading to failures. For instance, using plastic fittings in a system with highly corrosive fluids may not be suitable. It is vital to consider the chemical compatibility of fittings with the hydraulic fluid and other system materials to ensure long-term reliability.
E. Flow Rate Requirements
Flow rate is a significant factor that directly influences fitting sizing and overall system performance.
Calculating Necessary Flow Rates: Understanding the flow rate required for the hydraulic system is essential for selecting the right fittings. This calculation typically considers the demand of actuators, cylinders, and other components in the system. Accurate flow rate calculations help in selecting fittings that can handle the desired fluid volume without restrictions.
Impact on Fitting Size Selection: Flow rate requirements dictate the diameter and size of the fittings. Larger flow rates necessitate larger fittings to minimize pressure drops and turbulence. If the fittings are too small for the required flow, it can lead to increased wear on the system and inefficient operation. Therefore, proper alignment of flow rate requirements with fitting sizes is crucial for achieving optimal performance.
F. Environmental Conditions
The operating environment significantly affects the selection and sizing of hydraulic fittings.
Factors Like Temperature and Exposure: Environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can impact the performance and longevity of hydraulic fittings. Fittings used in extreme temperatures must be rated accordingly, while those exposed to corrosive elements may require specific materials to ensure durability.
Choosing Durable Fittings for Harsh Environments: In harsh environments, such as those found in marine or industrial applications, selecting durable fittings that can withstand these conditions is essential. Fittings made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials are often preferable in these scenarios. Ensuring that fittings are rated for the specific environmental challenges they will face can prevent failures and enhance the reliability of the hydraulic system.
Best Practices for Sizing Hydraulic Fittings
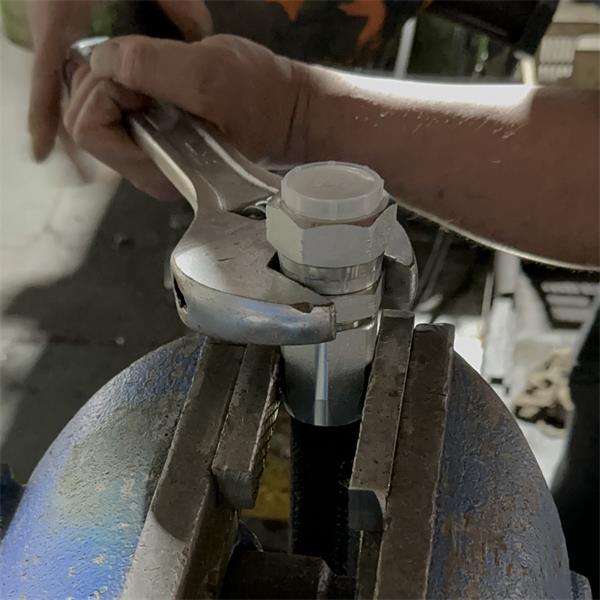
A. Measurement Techniques
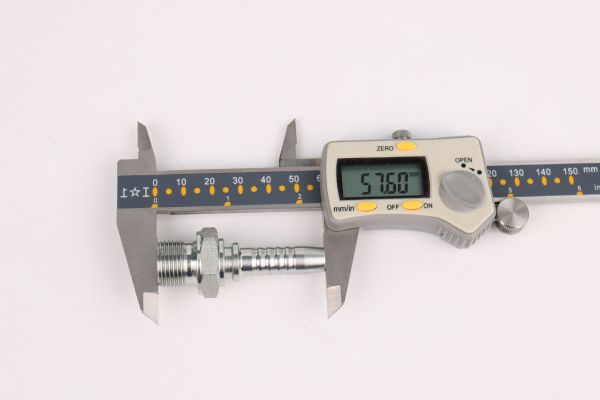
Accurate measurement is the foundation of effective hydraulic fitting sizing. Employing the right tools and methods is essential to ensure precision.
Tools and Methods for Accurate Measurement: Common tools for measuring include calipers, tape measures, and micrometers. Calipers are particularly useful for measuring the inner and outer diameters of hoses and pipes, as they can provide precise readings. When measuring threaded fittings, it’s crucial to account for the thread type and pitch to ensure compatibility. Additionally, digital measuring tools can offer enhanced accuracy and ease of use, especially in complex systems.
Importance of Taking Multiple Measurements: To minimize errors, it’s advisable to take multiple measurements at various points along the pipe or hose. This practice helps account for any irregularities or deformities that may exist, ensuring a more reliable measurement. Variations in diameter can occur due to wear, manufacturing tolerances, or damage, making it essential to verify measurements before selecting fittings.
B. Consulting Manufacturer Specifications
Understanding and adhering to manufacturer specifications is vital for achieving optimal performance and safety in hydraulic systems.
Utilizing Datasheets and Manuals: Manufacturer datasheets provide essential information regarding pressure ratings, material compatibility, and sizing recommendations for fittings. These documents often include detailed charts and tables that outline fitting dimensions and application guidelines. By consulting these resources, professionals can ensure that they select fittings that meet or exceed the requirements of their specific hydraulic systems.
Importance of Adhering to Manufacturer Guidelines: Following manufacturer guidelines not only aids in selecting the correct fittings but also helps maintain warranty coverage and ensures compliance with industry standards. Using fittings outside their specified ratings or without following recommended practices can lead to failures and safety hazards. Thus, it is crucial to thoroughly review manufacturer documentation before making any fitting selections.
C. Regular Maintenance and Reassessment
Ongoing maintenance and periodic reassessment of hydraulic fittings are critical for long-term system performance and reliability.
Routine Checks for Wear and Tear: Regular inspection of hydraulic fittings can help identify signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Fittings should be checked for leaks, signs of fatigue, or deterioration, especially in high-stress environments. Early detection of issues can prevent more significant failures and costly repairs down the line. Creating a maintenance schedule that includes visual inspections and functional tests can enhance the longevity of hydraulic components.
When to Resize Fittings: As hydraulic systems age or undergo modifications, it may become necessary to resize or replace fittings. Factors that may trigger a reassessment include changes in system pressure, fluid type, or operational requirements. Additionally, if leaks or performance issues are identified, it is essential to evaluate whether the current fittings are suitable for the application. When resizing, professionals should follow the same meticulous measurement and compatibility checks as during the initial installation to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
As hydraulic systems continue to evolve, so too must our approach to maintaining and optimizing them. The call to action for readers is clear: implement these best practices to ensure that your hydraulic fittings are correctly sized and maintained. Whether you are involved in system design, installation, or maintenance, your attention to detail in fitting selection and sizing will pay dividends in terms of efficiency and safety.
FAQ
What are hydraulic fittings?
Hydraulic fittings are components that connect hoses, pipes, and tubes in hydraulic systems, allowing the flow of hydraulic fluid while ensuring secure and leak-free connections.
How do I measure for hydraulic fittings?
Use tools like calipers or tape measures to accurately measure the inner and outer diameters of hoses and pipes. Taking multiple measurements is recommended to account for any irregularities.
What materials are commonly used for hydraulic fittings?
Hydraulic fittings can be made from various materials, including metal (like stainless steel or brass) for high-pressure applications and plastic for lower-pressure systems. Material selection should consider compatibility with the hydraulic fluid and environmental conditions.
What should I consider when selecting hydraulic fittings?
Consider factors such as fluid type, system pressure requirements, pipe specifications, compatibility with existing components, flow rate needs, and environmental conditions.
How often should I inspect hydraulic fittings?
Routine checks should be conducted regularly to identify wear and tear, leaks, or other issues. It’s advisable to assess fittings whenever the hydraulic system undergoes changes or shows signs of malfunction.
Why is proper sizing of hydraulic fittings important?
Proper sizing ensures optimal fluid flow, prevents leaks, reduces pressure loss, and enhances the overall efficiency and safety of hydraulic systems.