As a procurement manager, you face a constant dilemma. Using standard fittings that don’t quite fit leads to messy workarounds, creating extra leak points and assembly headaches that ultimately cost you money.
Custom hydraulic fittings are the ideal solution when standard parts force you to use multiple adapters, create leak points, or fail to meet requirements for space or performance. They simplify designs, increase reliability, and can even reduce the total cost of ownership for your product.
What Are the Benefits of Standard Fittings?
Your project timelines are tight and budgets are even tighter. The thought of sourcing a unique, custom-made part can seem like a recipe for delays and high costs.
Standard fittings are the backbone of the hydraulics industry for a reason. They offer immediate availability, a low per-unit cost from mass production, and guaranteed interchangeability. For most conventional equipment designs, they are the fastest and most cost-effective choice by far.

The Power of Mass Production and Low Cost
Standard fittings like a -8 JIC male are produced in runs of tens of thousands. This economy of scale is powerful. The tooling and machine programming have been perfected over years, leading to incredibly fast and efficient production. This massive volume means the per-unit cost is very low. For procurement managers in price-sensitive markets, the low quote price of a standard fitting is a significant advantage. It allows you to build your equipment cost-effectively and remain competitive.
Immediate Availability and Simplified Logistics
One of the biggest advantages of standard fittings is that they are “off-the-shelf” items. Suppliers like us maintain large inventories of the most common sizes and types. This means that when you place an order, the lead time is often just a matter of picking and packing. This speed is critical for meeting tight production schedules and for urgent repair needs. It also simplifies your inventory management, as you are dealing with common SKUs that have stable supply chains.
Guaranteed Interchangeability
Standardization is a promise of reliability. When you buy a fitting specified to a certain standard (e.g., SAE J514 for JIC fittings), you are buying a guarantee of interchangeability.
- The 37° flare angle will be correct.
- The thread form (UN/UNF) will be precise.
- The overall dimensions will meet the defined tolerances.
This means you can design your equipment with confidence, knowing that a -6 BSPP fitting will always mate correctly with a -6 BSPP port, regardless of the supplier. This drastically reduces your risk and simplifies maintenance for your end customer.
| Standard | Sealing Method | Common Regions / Applications |
| JIC 37° Flare | Metal-to-metal cone | North America, Global / General Purpose |
| DIN 24° Cone | Metal-to-metal + O-ring | Europe / Mobile, Industrial |
| BSPP 60° Cone | Metal-to-metal cone | UK, Commonwealth / General Purpose |
| ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) | O-ring compression | Global / High Vibration, High Pressure |
When Do Standard Fittings Fall Short?
Your engineers have designed a compact new machine, but there is one port buried in a tight corner. You find yourself trying to connect four different standard adapters just to make a 90-degree turn.
Standard fittings begin to fail when your design pushes the boundaries of conventional assembly. They fall short in tight spaces, create an unacceptable number of potential leak points, or cannot provide the specific material or performance characteristics your unique application demands. This is where a custom solution becomes a necessity, not a luxury.

A standard fitting forces you to compromise your design to fit the part. A custom fitting allows you to design the perfect part to fit your design. Every time you add an adapter, you add two more threaded connections, two more seals, more assembly time, and another SKU to your inventory.
Overcoming Space Constraints
Modern equipment design is all about power density—getting more performance out of a smaller package. In mobile hydraulics, agricultural machinery, and compact industrial power units, space is at a premium. A standard off-the-shelf elbow might be too long, or its swing radius might interfere with another component. A custom fitting can be designed with a specific, non-standard angle (e.g., 67 degrees), a shorter drop length, or a reduced hex size to fit into a space where no standard part could.
Meeting Special Performance Requirements
Sometimes, your application has needs that no standard part can meet.
- Special Materials: Your equipment might operate in a highly corrosive marine environment, requiring fittings made from SS316L or even Monel, which are not standard stock.
- Higher Pressure: Your design may call for pressures exceeding the rating of a standard fitting, requiring a custom part with heavier walls and improved thread engagement.
- Unique Flow Paths: You might need to merge two fluid lines into a single port using a special Y-shaped fitting to improve flow characteristics and reduce turbulence.
How Do You Start the Customization Process?
You have identified the need for a custom part, but the next step seems daunting. How do you communicate a complex technical requirement to a manufacturer, especially one overseas?
The process begins with providing a clear design. The best way is to supply a technical drawing or a 3D CAD model. However, even a clear, dimensioned hand sketch or an existing physical sample is enough for us to begin the process of quoting and creating a prototype for your approval.
Step 1: Providing the Design
Your input is the starting point. The quality of your input determines the speed and accuracy of our quote.
- The Gold Standard (CAD Files): A 3D model in a universal format like .STEP or .IGS is ideal. This allows us to instantly measure the part, calculate material weight, and feed the design directly into our CAM software to program the CNC machines. This is the fastest path to a quote.
- The Silver Standard (Technical Drawings): A 2D PDF drawing with all dimensions, angles, thread types (e.g., 1/2″ NPT), tolerances, material (e.g., Carbon Steel 45#), and plating requirements (e.g., Trivalent Zinc, 96hr salt spray) is excellent.
- The Starting Point (Sketches or Samples): We can work from a clear hand sketch. Be sure to label all critical lengths, hex sizes, and thread types. Alternatively, you can send us a physical sample of a part you need replicated or modified, and we can reverse-engineer it for you.
Step 2: Define Application Requirements
The first step is to understand where and how the fitting will be used. This information is essential for engineers and suppliers.
Key parameters include:
- Pressure rating: Define both working pressure and surge pressure. A wrong assumption can cause leaks or burst failures.
- Temperature range: Consider fluid and ambient temperatures. Extreme heat or cold may demand special seals or metals.
- Fluid type: Hydraulic oil, water-glycol, or aggressive chemicals may require unique materials.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to salt spray, abrasive dust, vibration, or UV radiation affects lifespan.
Collecting this data ensures that every later design choice is technically sound.
Step 3: Choose Connection Standards
Connection types define compatibility with hoses, ports, and equipment. Standard threads simplify sourcing and replacement.
Common options:
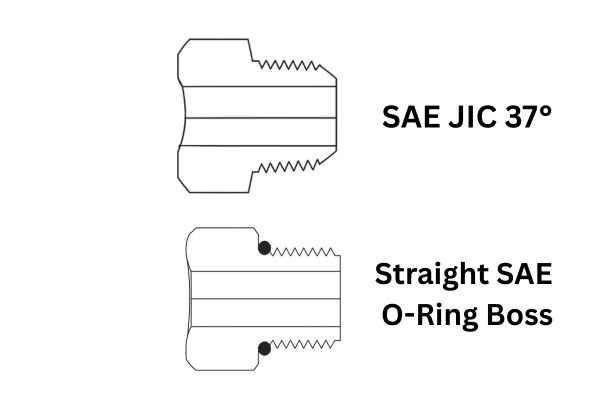
- JIC (37° flare) for widespread industrial use.
- ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) for high-pressure, leak-free performance.
- BSP and NPT for international compatibility.
- SAE straight threads for mobile equipment.
If no standard matches, engineers may recommend a proprietary thread or geometry. While more costly, it ensures precise integration in unique systems.
Step 4: Select Materials
Material choice balances cost, durability, and corrosion resistance.
- Carbon steel: Affordable, widely used in construction and agriculture.
- Stainless steel (304/316): Provides superior corrosion resistance for marine or offshore use.
- Brass: Suitable for low-pressure and chemical applications.
- Special alloys: Duplex stainless, Inconel, or titanium are used for aerospace and extreme conditions.
Tip: Material selection directly impacts price, lead time, and long-term reliability.
Step 5: Confirm Quantities and Lead Time
Production planning ensures realistic delivery and pricing.
- Small batches often cost more per unit because of setup and tooling.
- Larger runs reduce cost per piece and improve supply stability.
- Lead time usually ranges from 4 to 8 weeks. Custom alloys or coatings may extend this further.
How Is the Cost of a Custom Fitting Calculated?
You know that a custom part can solve your problem, but you’re a procurement manager. Your biggest question is: “What will it cost?” You worry that the word “custom” is just a substitute for “expensive.”
The total cost has two parts: a one-time Non-Recurring Engineering (NRE) or tooling charge, and the per-unit price. The per-unit price itself is based on material and machine time. Importantly, this per-unit cost drops significantly as your order quantity increases, making it much more affordable at volume.
Understanding these cost components demystifies the price. Unlike a standard part, the first custom part is the most expensive one to make because it carries the entire setup cost. But once that is paid, the price for subsequent parts can become very competitive.
The NRE/Tooling Cost
This is a one-time, upfront investment to prepare for production. It can include:
- Programming Time: The time it takes for our engineers to program the CNC machines.
- Custom Tooling: If the part requires a special shape, we may need to order a custom-ground cutting tool.
- Forging Dies: For very high-volume parts, creating a forging die is a significant upfront cost, but it dramatically reduces the material waste and machining time for each part later.
For simple modifications to existing standard parts, this NRE cost can be very low or even zero.
Material and Machining Costs
This is the core of the per-unit price.
- Material Cost: This is determined by the weight of raw material used to make the part. Stainless steel costs more than carbon steel. A complex part that generates a lot of waste material will have a higher material cost component.
- Machining Time: This is the cost of running the CNC machine. A more complex part with many features takes longer to machine and will have a higher price. This is where our DFM suggestions can save you money.
Can Customization Go Beyond Just the Fitting?
You’ve solved the technical problem with a custom fitting. But what about your brand identity? Your product is unique, but the components look just like everyone else’s.
Absolutely. At Topa, customization goes far beyond just the shape of the part. We regularly provide custom laser etching of logos and part numbers directly onto the hydraulic fittings. We also offer custom kitting and packaging services to streamline your assembly process and reinforce your brand identity right down to the component level.

For many of our customers, especially those who sell premium equipment or service kits, these value-added services are just as important as the fitting itself. These details communicate a higher level of quality and professionalism to the end-user.
Custom Marking and Part Numbers
A simple but powerful option is laser etching. We can engrave your company logo, a unique internal part number, or a manufacturing date code directly onto one of the hex flats of the fitting.
- Benefits for You: Reinforces your brand. Makes it easy for your purchasing and inventory teams to identify parts without having to refer to a bag or box label.
- Benefits for Your Customer: Simplifies re-ordering. Makes their maintenance technicians’ jobs easier. Projects an image of a professional, integrated system.
Custom Kitting and Packaging
This is a major efficiency driver for our customers with assembly lines. Instead of ordering five different fittings and a bag of O-rings, you can order a single kit from us.
- What it is: We pre-assemble a specific set of components into a single, sealed bag with one master part number.
- Your Advantage: Your assembly line worker grabs one bag and has everything they need. This drastically reduces “time-on-task” and eliminates errors from picking incorrect parts. We can also print your logo and part number on the bag.
Special Materials and Plating
This is another form of customization that we handle frequently. While standard zinc plating is common, your application may have special requirements. We can provide documentation and certification for many custom options:
- High-Corrosion Resistance: Plating certified to withstand over 240, 480, or even 720 hours in a salt spray test.
- RoHS Compliance: Ensuring all materials and plating meet the European “Restriction of Hazardous Substances” directive.
- Specific Material Grades: Sourcing and certifying specific grades of stainless steel or other alloys for demanding chemical or temperature environments.
Conclusion
Standard fittings offer speed and low cost, while custom fittings provide precision solutions that increase reliability and can lower your total cost. The key is to analyze your need and find a trustworthy manufacturing partner who can deliver a complete, value-added solution.
FAQ
When should I choose custom hydraulic fittings instead of standard ones?
Choose custom fittings when standard parts require multiple adapters, cause space issues, or fail to meet your system’s performance or pressure needs.
Are custom hydraulic fittings always more expensive?
Not necessarily. While there’s an initial setup cost, the per-unit price drops significantly with higher quantities—often becoming competitive with standard parts.
What information do I need to provide for a custom fitting quote?
Provide a CAD model or technical drawing showing dimensions, thread type, material, and plating. If unavailable, a labeled hand sketch or physical sample also works.
How long does it take to produce custom hydraulic fittings?
Typical lead time is 4–8 weeks, depending on material availability, complexity, and surface treatment requirements.
Can I add my company logo or part number to the fittings?
Yes. We offer laser etching for logos, serial numbers, and date codes, helping reinforce your brand and simplify inventory management.
What materials can be used for custom hydraulic fittings?
Options include carbon steel, stainless steel (304/316), brass, and special alloys like Monel or Inconel, chosen based on corrosion resistance, pressure, and cost.





