Metric Port Fittings: Key Considerations for Hydraulic Systems
Introduction
Selecting the proper fitting for hydraulic systems is crucial to ensure efficient and leak-free operations. Incorrect fittings can lead to system failures, leaks, and costly downtime. Understanding the different types of metric ports is essential for making informed choices. The most common metric ports used in hydraulic systems are DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel), and ISO 6149. Each type has its specifications, applications, and compatibility requirements, which must be considered to maintain the integrity and performance of the hydraulic system.
Types of Metric Ports
DIN Ports
DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) ports are standardized in Germany and widely utilized across numerous industrial applications due to their robustness and versatility. These ports are specifically designed to handle high-pressure environments, making them an ideal choice for sectors where durability and reliability are paramount. Commonly found in manufacturing, automotive, and heavy machinery industries, DIN ports are engineered to meet stringent performance criteria, which is why they are often seen in hydraulic systems that demand high precision and robustness.
DIN ports feature a 24-degree cone angle, providing a secure and leak-proof connection when paired with the appropriate fittings. This design not only enhances the reliability of the hydraulic system but also ensures that the connections remain stable even under extreme pressures. Their widespread use in critical applications underscores their importance in maintaining the efficiency and safety of hydraulic systems.
Compatibility with Specific Fittings
The success of DIN ports in hydraulic systems largely depends on their compatibility with specific fittings that adhere to the same DIN standards. Fittings designed for DIN ports are characterized by their 24-degree cone angle, which matches the port design to create a secure and leak-proof connection. This compatibility is crucial for ensuring the integrity of the hydraulic system, as mismatched fittings can lead to leaks, pressure drops, and potential system failures.
When selecting fittings for DIN ports, it is essential to verify that they conform to the same DIN standards. This ensures not only a proper fit but also optimal performance under the specified operating conditions. The use of standardized fittings simplifies maintenance and replacement processes, as components from different manufacturers that meet the DIN standards can be interchangeably used without compromising the system’s performance.

ISO 6149 Ports
ISO 6149 ports are internationally standardized and widely recognized for their high performance and reliability in hydraulic systems. These ports are designed to meet stringent international standards, making them suitable for a variety of demanding applications, including mining, oil and gas, and industrial machinery. The ISO 6149 standard ensures that the ports and fittings are compatible and can withstand high pressures and harsh operating conditions.
The robust design of ISO 6149 ports makes them an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications where reliability and performance are paramount. These ports are engineered to provide a secure and leak-proof connection, even under extreme pressures, making them ideal for use in critical hydraulic systems that operate in challenging environments.
Compatible Fittings and Benefits
Fittings compatible with ISO 6149 ports are designed to provide superior leak resistance and durability. These fittings typically feature an O-ring seal, which forms a tight and reliable seal with the port, preventing fluid leakage and ensuring the integrity of the hydraulic system. The use of O-rings also simplifies the installation process, as the fittings can be easily screwed into place without requiring excessive torque.
The benefits of using ISO 6149 fittings include their ability to withstand high pressures and harsh operating conditions. This makes them suitable for demanding applications where performance and reliability are critical. The standardized design of ISO 6149 ports and fittings ensures compatibility across different manufacturers, allowing for easy replacement and maintenance without compromising the system’s performance.
Identifying the Correct Fitting
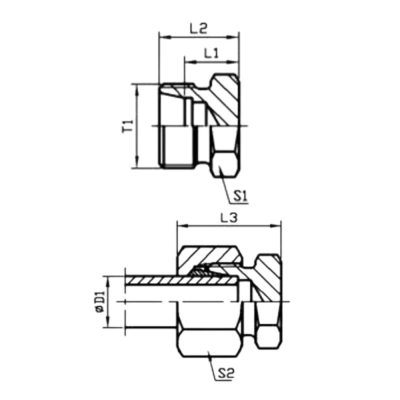
Thread Identification
Techniques for Identifying Thread Types
Identifying the correct thread type is crucial for ensuring a proper fit in hydraulic systems. Proper thread identification techniques include:
Measuring the Thread Pitch:
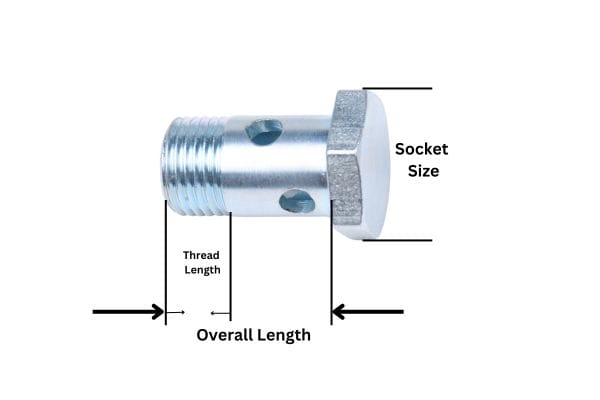
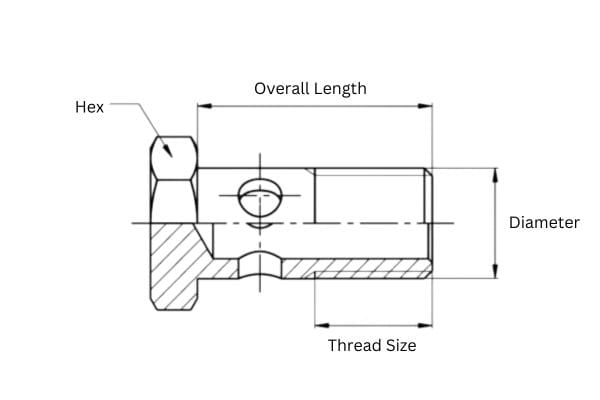
Thread pitch refers to the distance between adjacent threads. It is typically measured in millimeters for metric threads. Using a thread pitch gauge, which has multiple blades of different pitches, can help identify the correct pitch by matching the blade that fits the threads without gaps.
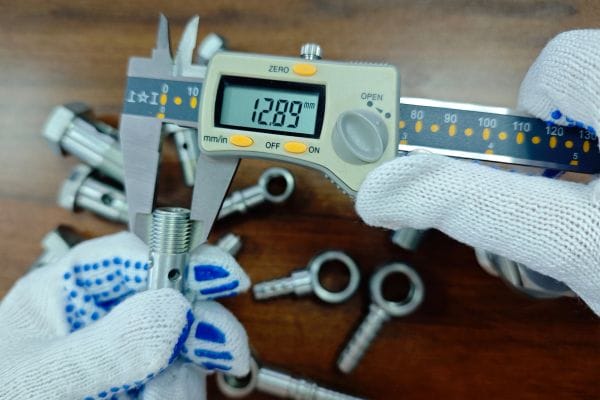
Measuring the Thread Diameter:
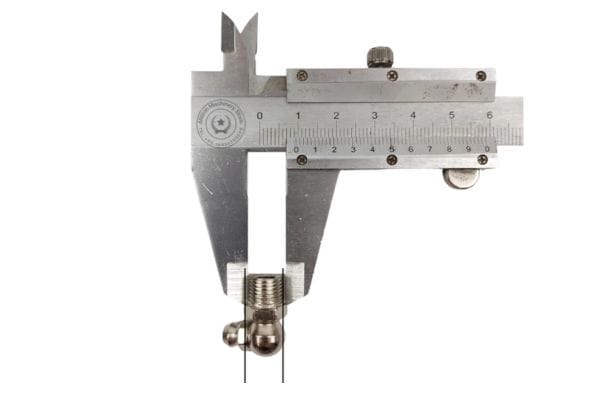
The thread diameter is the outer diameter of the thread, also known as the major diameter. This can be measured using a caliper. Ensuring accurate measurement is vital, as slight variations can lead to mismatched fittings.
Using Thread Gauges:
Thread gauges come in various sizes and are used to match the internal and external threads of the fittings and ports. These gauges help verify the size and type of the threads, ensuring compatibility.
Comparing to Standards:
Cross-referencing the measurements with standard charts (like ISO, DIN, or BSPP standards) helps in identifying the correct thread type. These charts provide detailed specifications for different thread types, aiding in accurate identification.
Importance of Accurate Measurement
Accurate measurement of threads is fundamental to the correct selection of fittings, preventing issues such as cross-threading, leaks, and system failures. Here’s why precision is essential:
Preventing Leaks:
Incorrect thread identification can lead to poor fitting connections, resulting in leaks. Leaks not only reduce system efficiency but can also lead to contamination and potential environmental hazards.
Avoiding Cross-Threading:
Cross-threading occurs when threads do not match correctly, causing damage to both the fitting and the port. This can lead to costly repairs and system downtime.
Ensuring System Integrity:
Properly identified and matched threads maintain the integrity of the hydraulic system, ensuring consistent pressure and performance. Accurate measurements guarantee that the fittings will handle the system’s operational requirements without failure.
Sealing Methods
Different Sealing Techniques
Sealing methods are essential for maintaining the integrity of hydraulic systems and preventing fluid leaks. The two most common sealing techniques are:
O-ring Seals:
O-rings are circular elastomer seals that fit into a groove and compress between the fitting and port, creating a seal. They are widely used due to their reliability and ease of installation.
Bonded Seals (Dowty Seals):
Bonded seals consist of a metal washer with a vulcanized rubber sealing ring bonded to the inside. They provide a high-pressure seal by compressing the rubber element when the fitting is tightened.

Pros and Cons of Each Method
O-ring Seals:
Pros:
Reusable: O-rings can be reused multiple times if they are not damaged, making them cost-effective.
Easy to Replace: O-rings are simple to replace, which is advantageous during maintenance.
Versatile: Available in various materials (e.g., nitrile, Viton), O-rings can be selected based on the system’s operating conditions.
Cons:
Degradation Over Time: O-rings can degrade due to environmental factors such as temperature, chemical exposure, and aging.
Requires Proper Groove Design: The groove must be correctly designed to ensure effective sealing and avoid extrusion under pressure.
Bonded Seals:
Pros:
High-Pressure Resistance: Bonded seals are excellent for high-pressure applications due to the robust sealing provided by the metal-to-rubber bond.
Durable: The metal washer provides structural integrity, protecting the rubber seal from damage.
Cons:
Single-Use: Bonded seals are typically single-use, as the rubber element can be compressed permanently after the initial installation.
Harder to Replace: Replacing bonded seals can be more challenging compared to O-rings, requiring more effort and potentially higher costs.
Selection Guidelines
Compatibility Considerations
Ensuring Fitting and Port Match
Ensuring that the fitting matches the port type is crucial for preventing leaks and maintaining system efficiency. A mismatch between the fitting and port can lead to several issues, including inadequate sealing, cross-threading, and compromised system integrity. To avoid these problems, follow these steps:
Cross-Referencing Standards:
Utilize industry standards such as ISO, DIN, and BSPP to verify the compatibility of fittings and ports. These standards provide detailed specifications that can help ensure a proper match.
Manufacturers often provide compatibility charts or technical documents that specify which fittings are suitable for their ports.
Using Compatible Components:
Always use components from reputable manufacturers that adhere to industry standards. This practice reduces the risk of incompatibility and ensures high-quality connections.
If components from different manufacturers are being used, ensure they are cross-referenced for compatibility.
Avoiding Cross-Threading and Leaks
Proper alignment and careful installation are key to avoiding cross-threading, which can damage both the port and the fitting, leading to leaks. To achieve a leak-free and secure connection:
Correct Alignment:
Ensure that the threads of the fitting and port are aligned correctly before tightening. Misalignment can cause cross-threading, which damages the threads and creates potential leak points.
Hand-tighten the fitting initially to confirm proper alignment. Once aligned, use the appropriate tool to achieve the final torque.
Material and Coating Selection
Material Choices
The choice of material impacts the durability and performance of fittings. Common materials include:
Steel:
High strength, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Cost-effective compared to other materials.
Often used in general industrial and hydraulic applications where high pressure is a factor.
Stainless Steel:
Offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments, including marine and chemical applications.
Higher cost but provides superior durability and longevity.
Suitable for sanitary and high-purity applications due to its resistance to contamination and easy cleaning.
Brass:
Good corrosion resistance, suitable for medium-pressure applications.
Easier to machine, making it a preferred material for complex fittings.
Commonly used in plumbing, gas applications, and systems requiring moderate pressure and corrosion resistance.
Importance of Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Corrosion resistance is vital for extending the lifespan of fittings, especially in harsh environments where exposure to chemicals, moisture, or saltwater is prevalent. The right material and coating can significantly enhance the longevity and reliability of the system:
Material Selection:
Choose materials that inherently resist corrosion, such as stainless steel, for applications exposed to harsh environments.
For cost-sensitive projects, coated steel can provide a balance between durability and affordability.
Coating Options:
Zinc plating or galvanization can enhance the corrosion resistance of steel fittings, making them suitable for less severe environments.
Nickel or chrome plating offers superior corrosion protection and is often used in more demanding applications.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Matching Fittings to System Specifications
Ensuring that fittings can withstand the system’s pressure and temperature requirements is essential for safety and performance. Properly matched fittings prevent failures and ensure reliable operation:
Consulting Manufacturer Specifications:
Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for pressure and temperature ratings of the fittings. These ratings are typically provided in technical datasheets or catalogs.
Ensure that the selected fittings can handle the maximum pressure and temperature conditions of the hydraulic system.
Understanding System Requirements:
Assess the operational conditions of the system, including normal and peak pressures and temperatures. Select fittings that can consistently perform under these conditions.
Safety Margins and Performance Requirements
Incorporating safety margins in the selection process ensures that fittings operate reliably under varying conditions, reducing the risk of failure. Consider these factors:
Safety Margins:
Choose fittings with pressure and temperature ratings higher than the maximum operating conditions of the system. This margin provides a buffer against unexpected spikes and ensures long-term reliability.
Common practice is to select fittings rated for at least 1.5 times the system’s maximum pressure.
Performance Requirements:
Evaluate the dynamic and static conditions of the hydraulic system. Dynamic conditions involve varying pressures and temperatures, while static conditions involve constant pressures and temperatures.
Ensure fittings can handle both types of conditions without compromising performance or safety.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Leak Prevention
Common Causes of Leaks
Leaks in hydraulic systems can arise from several factors, each of which needs to be carefully managed to maintain system integrity. The most common causes of leaks include:
Improper Fitting Selection:
Using the wrong type of fitting for the specific port can result in poor sealing and leaks. This often happens when fittings are not cross-referenced with the appropriate standards, leading to mismatches.
Incorrect Installation:
Incorrectly installed fittings, such as those that are over-tightened or under-tightened, can lead to leaks. Over-tightening can damage threads and seals, while under-tightening can leave connections too loose to maintain a proper seal.
Wear and Tear:
Over time, seals and fittings can degrade due to wear and tear, leading to leaks. This is particularly common in systems that operate under high pressure or in harsh environments.
Poor Quality Components:
Using low-quality fittings and seals can compromise the integrity of the hydraulic system. These components may not meet the necessary standards for pressure and temperature, leading to premature failure.

Troubleshooting and Rectification Techniques
Effective troubleshooting and rectification techniques are essential for maintaining system performance and preventing leaks from escalating into more significant issues:
Inspecting Connections:
Regularly inspect all connections in the hydraulic system to identify any signs of leaks. Look for drips, wet spots, or discoloration around fittings and seals.
Use a UV dye and black light to detect leaks that might not be visible to the naked eye.
Replacing Worn Seals:
Replace seals that show signs of wear, such as cracks, hardening, or deformation. O-rings and bonded seals should be checked regularly and replaced as part of a preventive maintenance schedule.
Ensuring Proper Torque Application:
Follow manufacturer recommendations for the correct torque values during installation. Use a calibrated torque wrench to ensure that fittings are neither over-tightened nor under-tightened.
Avoid using pipe wrenches or other non-calibrated tools that can easily apply excessive force.
Using Thread Sealants and Lubricants:
Apply appropriate thread sealants or lubricants to ensure a better seal and facilitate easier installation. Ensure that the sealant is compatible with the hydraulic fluid and the materials of the fittings and ports.
Compatibility Issues
Addressing Mismatched Fittings and Ports
Mismatched fittings and ports are a common source of leaks and inefficiencies in hydraulic systems. Ensuring compatibility through proper selection and cross-referencing standards can prevent these issues:
Cross-Referencing Standards:
Verify that the fittings and ports conform to the same standards (e.g., DIN, ISO, BSPP). Cross-reference the specifications provided by manufacturers to ensure compatibility.
Utilize standardized charts and tools to match threads accurately.
Ensuring Proper Fit:
Double-check measurements such as thread pitch, diameter, and angle to ensure that fittings will match the ports correctly.
Conduct a dry fit before the final installation to ensure that components align correctly without forcing.
Solutions for Hybrid Systems with Mixed Fittings
Hybrid systems with mixed fittings require careful management to ensure compatibility and prevent leaks. Using adapters and ensuring proper sealing can help in managing these systems effectively:
Using Adapters:
Employ adapters that are designed to bridge different fitting types and standards. Ensure that the adapters are of high quality and compatible with the system’s pressure and temperature requirements.
Verify that adapters provide a secure and leak-proof connection between different types of fittings.
Ensuring Proper Sealing:
Use appropriate sealing methods, such as O-rings or bonded seals, to ensure that connections remain leak-proof even when different fitting types are used.
Check for compatibility of sealing materials with the hydraulic fluid and the environmental conditions of the system.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
Implement a regular maintenance schedule to inspect and replace worn or incompatible components in hybrid systems. This proactive approach can prevent leaks and system failures.
Train personnel to recognize and address compatibility issues promptly, ensuring that they understand the importance of maintaining a secure and efficient hydraulic system.
Conclusion
Selecting the right metric port fittings is crucial for the performance, safety, and longevity of hydraulic systems. Understanding the different types of metric ports, identifying the correct fittings, and following best practices for installation and maintenance are essential for achieving optimal results. The correct fitting selection ensures a secure, leak-free connection, maintaining system pressure and performance. Proper selection also helps in preventing system failures and reducing maintenance costs.
FAQ
Metric fittings are used to connect various components within hydraulic systems, ensuring secure, leak-proof connections that maintain system pressure and efficiency.
To identify the correct thread type, measure the thread pitch and diameter using a thread gauge or caliper, and compare these measurements with standard charts (e.g., ISO, DIN, BSPP).
The main types of metric ports include DIN ports, BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) ports, and ISO 6149 ports, each designed for specific applications and standards.
Accurate measurement ensures the correct selection of fittings, preventing issues such as leaks and cross-threading, which can damage components and compromise system integrity.
O-ring seals provide a reliable and reusable seal, are easy to replace, and are available in various materials to suit different operating conditions.
To prevent leaks, ensure proper fitting and port compatibility, follow correct installation procedures (including proper torque application), regularly inspect connections, and replace worn seals promptly.