You need to connect hydraulic lines, but making the wrong choice leads to leaks, inefficiency, and costly downtime. It’s a decision that can impact your entire operation’s productivity.
Use threaded fittings for permanent, high-strength connections. Choose quick couplings for applications requiring frequent, fast connection and disconnection, like on attachments. This simple rule guides you to the right choice every time.
What is the Core Difference in How They Work?
You see two different fittings. They both connect hoses, but choosing the wrong one can cost you valuable time and money.
Threaded fittings, like JIC or ORFS, use wrenches to create a high-strength, permanent seal. Quick couplings use a sleeve and locking-ball mechanism for instant, tool-free connection, with internal valves to prevent fluid loss.
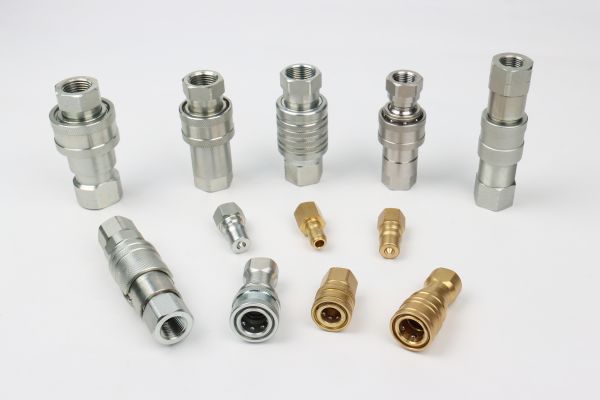

The Mechanics of a Threaded Fitting
Threaded fittings achieve their seal through immense clamping force.
- The Seal: The seal is created either by a metal-to-metal flare (like on a 37° JIC) or by compressing a soft seal like an O-ring (like on an O-Ring Face Seal fitting).
- The Threads: The threads themselves do not seal. Their only job is to provide the mechanical strength to pull the two halves together and maintain that force against high pressure and vibration.
- Installation: This process requires tools, typically two wrenches, to achieve the proper torque. It’s a deliberate and permanent method.
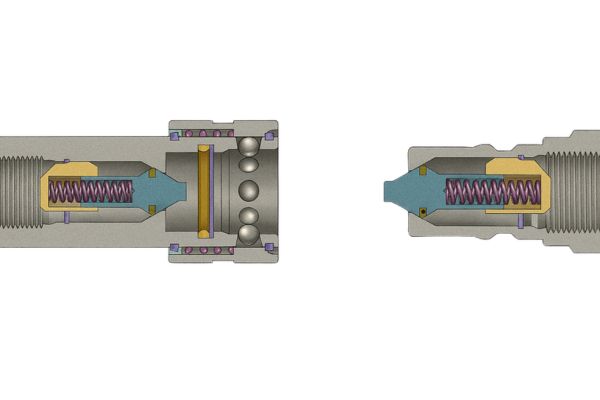
The Anatomy of a Quick Coupling
Quick couplings are engineered for speed and convenience. Their design is more complex, with multiple moving parts working together.
- Male & Female Halves
- The system consists of a male plug and a female coupler.
- Both must match the same profile standard (e.g., ISO A, ISO B, Flat Face).
- Locking Mechanism
- The female coupler contains a retractable sleeve.
- This sleeve controls a set of locking balls that fall into a groove on the male plug.
- Once locked, the two halves are secured without tools.
- Internal Valves
- Both halves contain spring-loaded poppet valves.
- When disconnected, the springs hold the valves closed, preventing fluid leaks.
- When connected, the valves push against each other and open, allowing flow.
| Feature | Threaded Fittings | Quick Couplings |
| Seal Method | Metal-to-metal flare (e.g., 37° JIC) or soft seal like O-ring (ORFS) | Internal spring-loaded valves (poppets) align and open for flow |
| Threads Role | Provide clamping force, not sealing | Not used for sealing; locking is via balls and sleeve |
| Connection Parts | Two threaded halves joined permanently | Male plug + female coupler with locking balls |
| Locking Mechanism | Achieved by tightening with wrenches | Sleeve + locking balls secure the male plug |
| Installation | Requires tools (usually 2 wrenches) and torque | Tool-free, connect/disconnect by hand |
| Use Case | Permanent, high-strength connections | Fast, temporary, or frequently connected systems |
When Are Quick Couplings the Obvious Choice?
You’re constantly swapping hydraulic attachments. Wasting time with wrenches and cleaning up oil spills is killing your productivity.
Quick couplings are essential for any application requiring frequent connection and disconnection. They are perfect for agricultural implements, construction attachments, and mobile diagnostic equipment. Speed and convenience are their primary benefits.
Agricultural and Forestry Attachments
Think of a tractor. It needs to connect to a plow, a seeder, a baler, and a mower. Or a forestry machine swapping between a harvester head and a grapple. Using threaded fittings here would be a nightmare. Quick couplings allow for these changes to happen in seconds, without tools and with minimal fluid loss.
Construction Equipment Versatility
Excavators and skid steers are tool carriers. The value of the machine is its ability to use different attachments.
- Hydraulic breakers for concrete
- Augers for drilling holes
- Grapples for handling debris
- Compaction wheels for soil stabilization
Quick couplings, especially spill-free flat-face models, are the only practical way to manage this rapid swapping of tools on a job site.
Diagnostic and Testing Points
Quick couplings aren’t just for heavy attachments. They also play a key role in system monitoring. By placing them at critical test points, maintenance crews can:
- Snap on a pressure gauge
- Take a reading instantly
- Diagnose issues without halting production
This avoids opening permanent lines, reducing downtime and the risk of contamination. A small investment in couplings translates into faster troubleshooting and safer maintenance.
| Application Area | Why Quick Couplings Are Used | Example Uses |
| Agriculture & Forestry | Fast attachment changes without tools, minimal fluid loss | Tractors with plows, seeders, balers, mowers; forestry harvesters & grapples |
| Construction Equipment | Enable rapid swapping of work tools on carriers | Excavators with breakers, augers, grapples, compaction wheels |
| Diagnostics & Testing | Allow quick, safe connection of gauges for system monitoring | Pressure checks and troubleshooting in industrial systems |
When Should You Always Use Threaded Fittings?
Quick couplings are great for speed, but they’re not the answer to every problem. In many cases, threaded fittings are the safer, stronger, and more reliable choice. They’re designed for permanence and can withstand the harshest pressures, vibrations, and environments.
Permanent, High-Pressure Connections
Threaded fittings shine where a connection isn’t meant to come apart. Examples include:
- Hydraulic pumps to valves
- Cylinders to rigid lines
- Manifold block assemblies
In these cases, the system operates under constant high pressure. A threaded connection, tightened to the correct torque, provides the clamping force needed to maintain a leak-free seal day after day.

Environments with Extreme Vibration
Machines like crushers, drilling rigs, or heavy mining equipment generate strong shock loads. Quick couplings could loosen or wear out here. Threaded fittings are better because:
- Their metal-to-metal design resists loosening
- Proper torque and thread engagement provide stability
- They can handle repeated vibration without fatigue failures
Critical Safety Applications
When a leak could endanger workers or damage expensive equipment, threaded fittings are the obvious choice. For example:
- Brake systems on heavy vehicles
- Aircraft hydraulic systems
- High-pressure lifting equipment
These applications demand maximum security. Threaded fittings with either a flare or O-ring seal eliminate unnecessary risk.
Compact or Confined Installations
Quick couplings are bulky and add length to a line. Threaded fittings, on the other hand, fit neatly into tight assemblies. They are often the only practical option in:
- Hydraulic control blocks
- Instrumentation panels
- Systems where space is at a premium
| Situation / Environment | Why Threaded Fittings Are Better | Typical Examples |
| Permanent, High-Pressure | Provide strong, leak-free seal under constant load | Pumps to valves, cylinders to lines, manifolds |
| Extreme Vibration | Metal-to-metal design resists loosening, stable with torque | Crushers, drilling rigs, mining equipment |
| Critical Safety Systems | Maximum security, no tolerance for leaks | Aircraft hydraulics, heavy-vehicle brakes, lifting gear |
| Compact Installations | Smaller size, no added bulk | Control blocks, instrumentation panels, tight spaces |
How Do They Compare on Pressure Rating and Flow?
You chose a fitting, but now your hydraulic attachment feels sluggish. The wrong connection type is choking your system’s performance and wasting power.
Threaded fittings typically offer higher pressure ratings and less flow restriction. Quick couplings, because of their complex internal valves, introduce a pressure drop and often have a lower maximum working pressure than a similarly sized threaded fitting.

Pressure Rating
Threaded Fittings
- Designed for permanent, high-strength connections.
- Can routinely handle pressures above 6,000 psi (420 bar), depending on size and material.
- With proper torque, they resist vibration and shock loads better than couplings.
- Common choice in high-pressure pumps, cylinders, and manifolds.
Quick Couplings
- Pressure rating is generally lower due to internal complexity (valves, springs, and seals).
- Standard models: 3,000–4,000 psi (200–275 bar).
- Heavy-duty or flat-face types can reach 5,000–6,000 psi (350–420 bar), but still less robust than a threaded joint under extreme conditions.
- Used in mobile equipment and diagnostic ports rather than permanent high-pressure lines.
Flow Characteristics
Threaded Fittings
- Provide a straight-through bore with minimal restrictions.
- Larger internal diameter compared to couplings of the same hose size.
- Best for high-flow systems where efficiency and low pressure drop are critical.
Quick Couplings
- Internal valves (poppet or flat-face) create flow restrictions.
- This causes higher pressure drop compared to threaded fittings.
- Acceptable for attachments, tools, or testing points where convenience outweighs flow efficiency.
| Feature | Threaded Fittings | Quick Couplings |
| Pressure Rating | Up to 6,000+ psi (420+ bar) | Typically 3,000–4,000 psi; heavy-duty up to 5,000–6,000 psi |
| Flow Path | Straight, unrestricted | Restricted by internal valves |
| Pressure Drop | Minimal | Higher, due to valve design |
| Best Use Case | Permanent, high-pressure, high-flow lines | Frequent connection/disconnection, mobile tools, diagnostics |
The Impact of Pressure Drop
Every component in a hydraulic system creates some restriction to flow, which results in a loss of pressure. The complex path fluid takes through a quick coupling’s valves creates a much higher pressure drop than the smooth, open path of a threaded fitting. This robs your attachment of power and generates waste heat. Sizing the quick coupling correctly for your system’s flow rate is critical to minimize this effect.
What Are the Interchangeability Standards?
You bought a new quick coupler, but it won’t connect to your existing equipment. Now your job is on hold, and your brand-new part is useless.
Threaded fittings use well-defined global standards (JIC, BSPP) that are usually interchangeable. Quick couplings have many different profiles (ISO A, ISO B, Flat Face) that are physically incompatible with each other. Verifying the profile is essential.
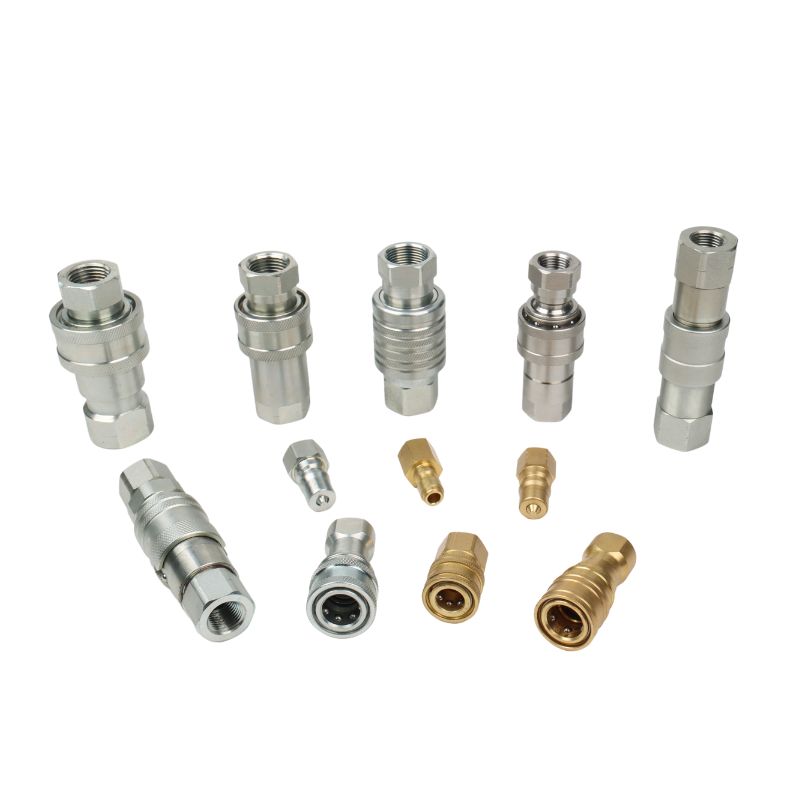

Common Quick Coupler Profiles
- Agricultural Interchange (ISO 5675): The classic, rounded “poppet” style found on many older tractors.
- ISO A (ISO 7241-1 A): A general-purpose industrial poppet interchange. Very common.
- ISO B (ISO 7241-1 B): A different industrial poppet interchange, not compatible with ISO A.
- Flat Face (ISO 16028): The modern standard. The flat faces are easy to clean, minimize spillage, and prevent dirt from entering the system. This is what we recommend for most new applications.
The Simplicity of Threaded Standards
Threaded fittings are much easier to manage. Global standards ensure near-universal interchangeability, meaning parts from different manufacturers will fit if they follow the same specification.
- JIC (SAE J514): Any JIC fitting from any brand will mate correctly with another JIC. The 37° flare angle and straight thread dimensions are standardized.
- ORFS (ISO 8434-3 / SAE J1453): All O-ring face seal fittings conforming to this standard will connect interchangeably, ensuring a reliable seal.
- BSPP (BS 5200 / ISO 1179): Common in Europe and other markets, BSPP threads also follow strict definitions, making them interchangeable across suppliers.
What is the Difference in Cost and Longevity?
Cost
Threaded Fittings
- Simple design, mass-produced, and widely standardized.
- Lower upfront cost compared to couplers.
- Best choice when you need many permanent connections without frequent disassembly.
Quick Couplings
- More complex internal parts: springs, valves, locking balls, and seals.
- Higher manufacturing cost.
- Flat-face spill-free couplers are the most expensive, but they save money by reducing fluid loss and cleanup costs.
- Worth the price if fast tool changes or diagnostic access improve productivity.
Longevity
Threaded Fittings
- Extremely durable when installed once and left in place.
- Withstands years of vibration, pressure, and environmental stress if tightened correctly.
- Failure usually comes from overtightening, thread damage, or corrosion, not from wear.
Quick Couplings
- Moving parts (sleeves, springs, seals) wear over time.
- Frequent connect/disconnect cycles shorten lifespan, especially in dirty environments.
- Flat-face designs last longer than old-style poppets because they resist contamination and reduce seal wear.
- Require periodic inspection and seal replacement to maintain performance.
| Feature | Threaded Fittings | Quick Couplings |
| Upfront Cost | Low | Higher (especially flat-face models) |
| Service Life | Long if left undisturbed | Shorter due to moving parts and seals |
| Maintenance | Minimal once installed | Needs periodic cleaning and seal changes |
| Best Value | Permanent, low-cost connections | High-productivity applications with frequent changes |
Conclusion
Choose correctly to maximize reliability and efficiency. Use permanent threaded fittings for the machine’s core system and select quick couplings for attachments and points that require frequent access.
At Topa, we know every minute of downtime means lost opportunities. That’s why we offer a complete range of hydraulic fittings, hoses, and quick couplings designed for reliability and fast delivery. All products are inspected 100% before shipment to guarantee performance in your toughest applications.
Now is the perfect time to place your order. By confirming your purchase early, you secure competitive pricing, shorter lead times, and priority in our production schedule. Whether you need standard parts or customized solutions with logo and packaging, our team is ready to support you.
FAQ
What materials are quick couplers and threaded fittings made from?
Most are made from carbon steel with zinc plating. For corrosive or marine environments, stainless steel or brass options are also available.
Do quick couplers and threaded fittings come in different sizes?
Yes. Standard sizes range from 1/8” to 2” depending on the series. Always match the fitting size to your hose and system flow requirements.
Are replacement seals available for quick couplers?
Yes. O-rings and valve seals can be replaced to extend service life. Using the correct material (NBR, Viton, EPDM) ensures compatibility with your hydraulic fluid.
Can threaded fittings and quick couplers handle different fluids?
Both can be used with hydraulic oil, water-glycol, and some synthetic fluids. Always check material compatibility before use.
Do these products meet international standards?
Yes. Threaded fittings are produced to SAE, ISO, DIN, or BSP standards. Quick couplers follow ISO 5675, ISO 7241-1 A/B, or ISO 16028 profiles for interchangeability.
What is the temperature range for quick couplers and threaded fittings?
Typically –20°C to +120°C with standard seals. For higher or lower temperatures, special seal materials like Viton or PTFE can be used.





