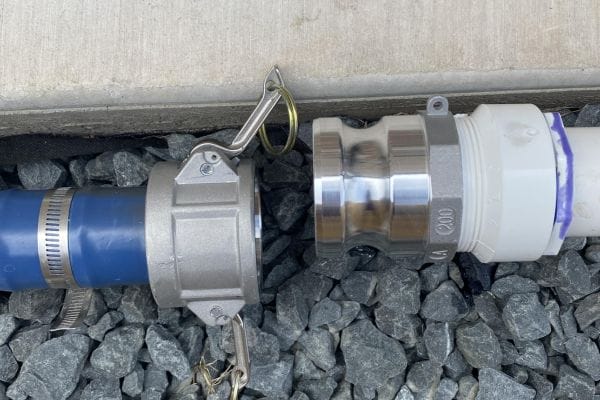
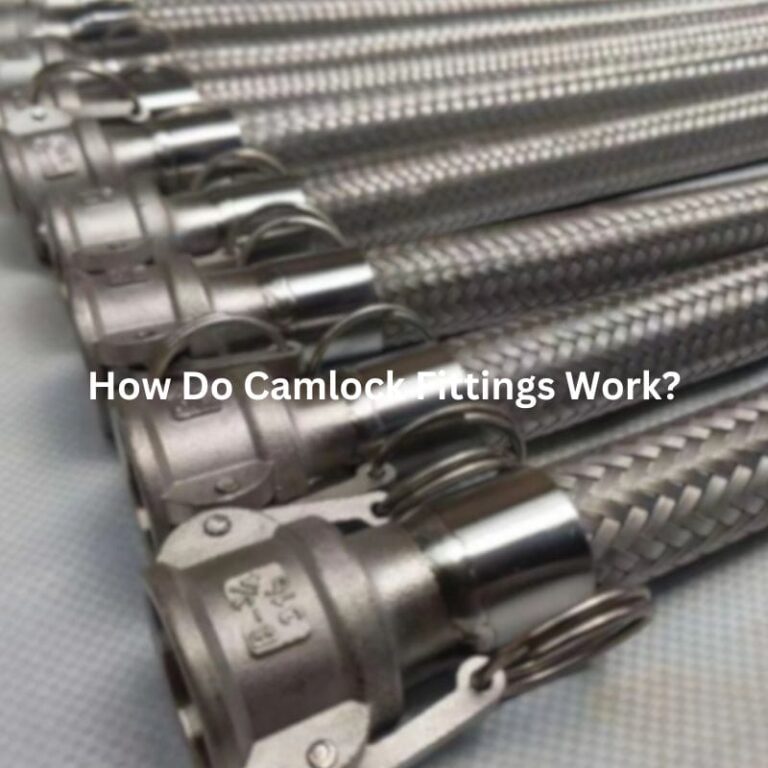
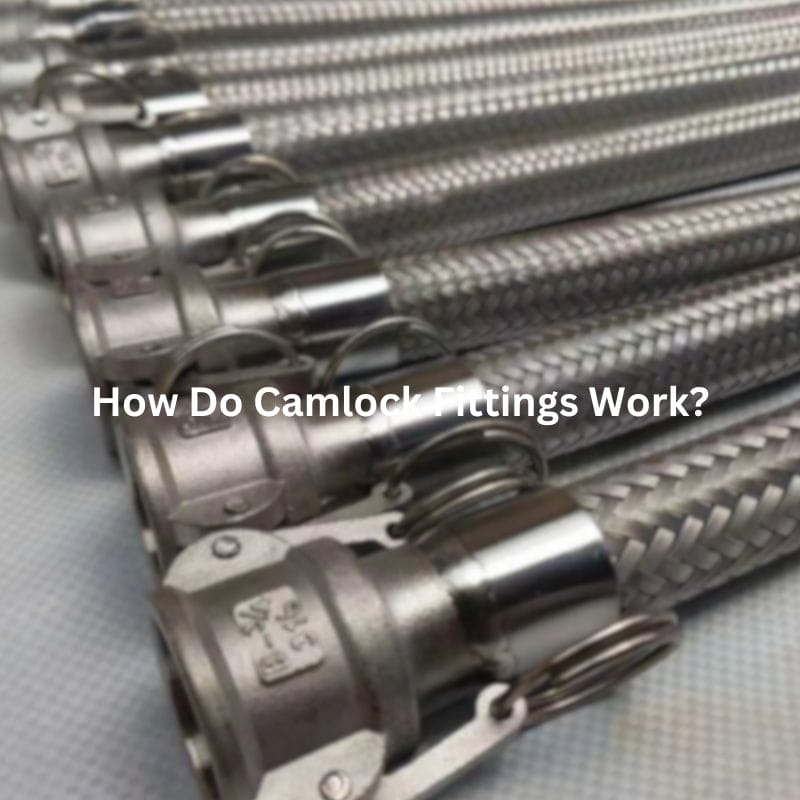
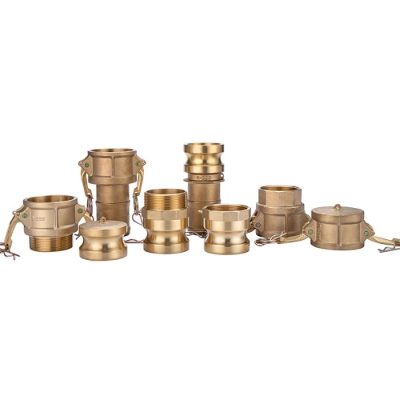
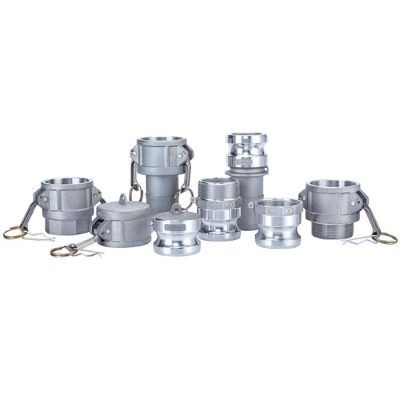
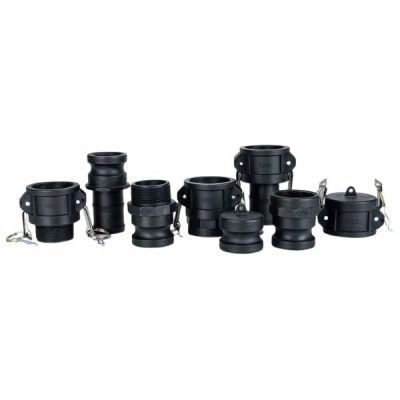
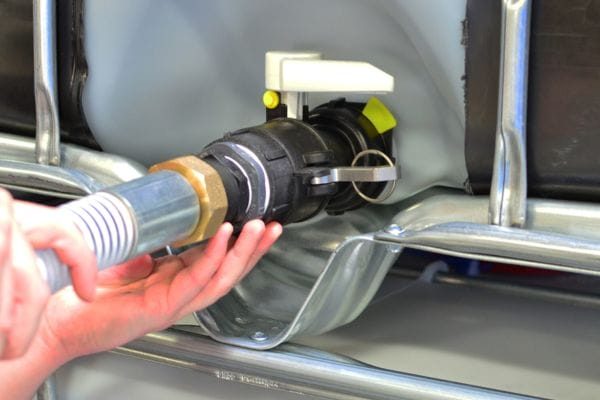
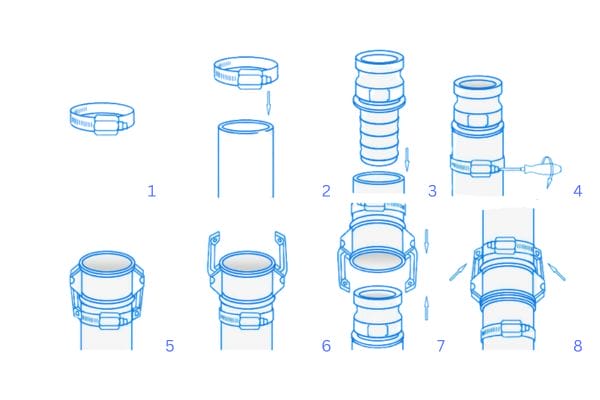
Camlock fittings, also known as cam and groove couplings, are a type of quick-connect coupling widely used to join hoses, pipes, and other fluid transfer equipment. They consist of two parts: a male coupler and a female adapter, which are connected using a locking mechanism that allows for a secure, leak-proof connection.
The Basics of Camlock Fittings
Camlock fittings are a type of quick-connect coupling that are widely used for fluid transfer. The mechanism behind how these fittings work is both simple and effective, making them an essential component in industries that require fast, secure, and reliable fluid handling.
Understanding the Camlock Coupling Mechanism
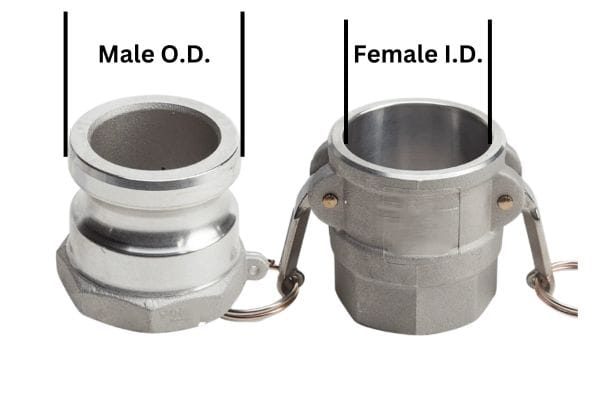
At the heart of a camlock fitting is its cam-locking mechanism. This system consists of a male coupler and a female adapter. The male coupler features a set of grooves along the outer edge, while the female adapter has cam arms or levers that engage with these grooves. To make a connection, the male and female parts are brought together, and the cam levers are pressed down over the grooves. Once the levers are engaged, they apply pressure to lock the two components firmly in place.
The design of the camlock system is incredibly efficient for quick-connect and quick-disconnect operations. The cam arms pivot over the coupler grooves and form a tight, leak-proof connection without requiring additional tools. This allows operators to secure or release the fitting with minimal effort, ensuring a smooth workflow in fluid transfer applications.

Key Components of a Camlock Fitting
Each camlock fitting consists of a few key components that work together to form a reliable and durable connection.
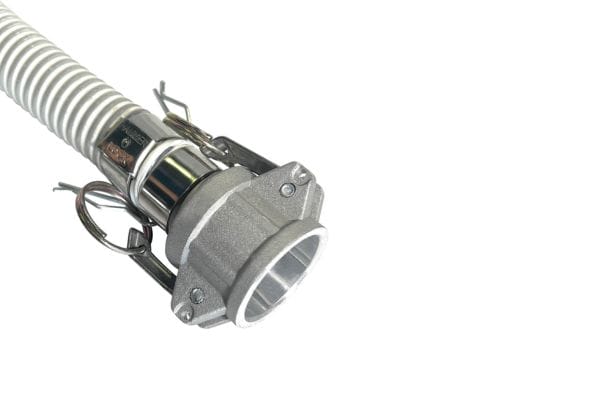
Male Coupler: This part features a grooved edge designed to fit into the female adapter. The grooves are where the cam levers engage to create a tight seal. Male couplers come in various sizes and materials, such as stainless steel, brass, and aluminum.
Female Adapter: The female part of the camlock fitting is designed to mate with the male coupler. It typically has a smooth interior that corresponds to the outside diameter of the male coupling. The female adapter houses the cam arms or levers, which are the moving parts responsible for locking the connection.
Cam Levers: The cam arms, or levers, are essential for locking the coupling into place. They are pressed down over the grooves of the male coupler, and once engaged, they provide the mechanical force needed to keep the connection secure under pressure.
Seals and Gaskets: To prevent leaks, camlock fittings often include seals or o-rings that sit between the male and female components. These seals form a barrier that prevents fluids from escaping, ensuring that the connection remains tight and secure. The material of the seals may vary, with common options being rubber, PTFE, or silicone, depending on the fluid being handled.
Locking Pins or Locks: Some camlock fittings incorporate additional locking mechanisms, such as pins or locks, to further secure the connection, especially in high-pressure or high-flow applications.
How Camlock Fittings Ensure Secure Connections
The reliability of camlock fittings lies in their robust design, which ensures that the connection is secure and leak-free. When the cam levers are pressed down over the male coupler’s grooves, the locking arms apply a strong clamping force. This clamping ensures that the connection remains tightly sealed even when exposed to high pressures, fluctuating temperatures, or rough handling.
In addition to the cam-locking mechanism, the seals or gaskets in the fitting play an important role. As the two parts of the camlock fitting come together, the seals compress, creating a strong barrier against fluid leakage. This is particularly important in applications where the safe containment of liquids or gases is essential, such as in chemical processing, fuel transfer, or food production.
Another key aspect of the secure connection is the material quality of the camlock fittings. Materials such as stainless steel and brass are corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for harsh environments where exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures could cause other materials to degrade over time. The combination of quality materials, effective sealing, and the cam-locking mechanism guarantees that camlock fittings provide a secure and long-lasting connection in a variety of industrial applications.
The ease of connection and disconnection also enhances the overall safety and security of the system. Operators can quickly disconnect camlock fittings in emergency situations or for routine maintenance, and the connection will remain secure while in use, offering peace of mind throughout the entire process.
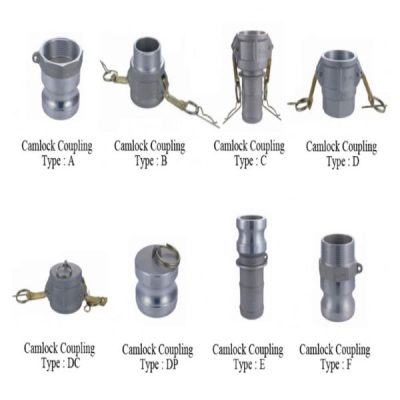
Types of Camlock Connectors
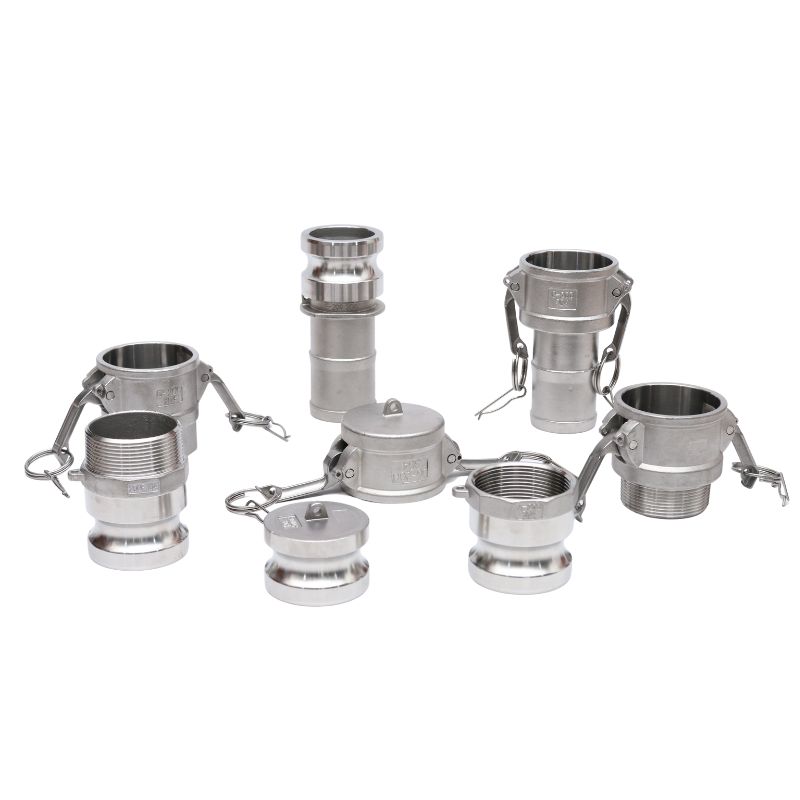
Camlock fittings are designed to provide reliable, quick connections for a wide variety of applications. The designations A through F refer to different types of camlock connectors, each offering unique combinations of male and female parts to suit specific fluid handling requirements. Let’s take a closer look at each type:
Type A: Male Adapter with Female Thread
The Type A camlock fitting features a male adapter that is fitted with a female thread on the opposite side. This configuration is commonly used in applications where a threaded connection is needed on one side of the coupling. Type A fittings are typically paired with female-threaded connections on equipment or piping systems, making them ideal for environments where a secure, threaded connection is required.
Type B: Female Coupler with a Male Thread
The Type B fitting has a female coupler that is fitted with a male thread. This makes it ideal for connecting to threaded equipment or pipes, where a male-threaded adapter is required to complete the connection. The design allows for a secure seal when connecting to male-threaded systems.
Type C: Female Coupler with a Hose Tail
Type C connectors have a female coupler and a hose tail, making them perfect for fluid transfer applications where a hose needs to be securely attached. The hose tail end allows for easy hose connection, while the female coupler provides a robust, leak-free seal.
Type D: Female Coupler with a Female Thread
Type D fittings feature a female coupler with a female thread on the opposite end. This type is typically used when you need to connect a male-threaded pipe or equipment to a female-threaded system. It’s often used when two female threaded components need to be connected securely.
Type E: Male Adapter with a Hose Tail
The Type E camlock fitting includes a male adapter on one side and a hose tail on the other, making it ideal for applications where a hose needs to be connected to a male-threaded pipe or valve. The hose tail end provides a secure fit for flexible hoses, while the male adapter ensures a tight seal with female-threaded equipment.
Type F: Male Adapter with a Male Thread
The Type F camlock fitting features a male adapter with a male thread. This configuration is used when you need to connect a female-threaded pipe or equipment to male-threaded connections, often in systems that require male-to-male connections for secure fluid handling.
Choosing the Right Camlock Connector for Your Needs
Selecting the right camlock fitting involves carefully considering several factors to ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety for your fluid handling needs. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing the best camlock connector for your application:
Material Compatibility
Stainless Steel: Best for use in corrosive or high-temperature environments. Stainless steel camlocks offer superior resistance to both corrosion and heat, making them ideal for harsh applications such as chemical processing and offshore oil rigs.
Brass: Ideal for non-corrosive applications like fuel transfer, as it provides excellent resistance to corrosion from chemicals and oils.
Aluminum: A lightweight and cost-effective option, making aluminum camlocks ideal for less aggressive environments like water transfer or low-pressure systems.
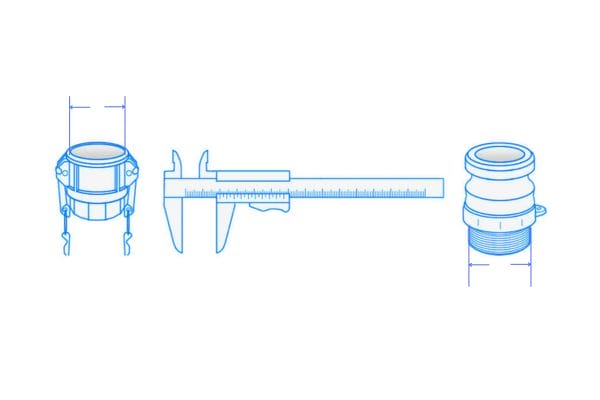
Size and Pressure Ratings
The size of the camlock fitting must match the hose diameter and flow rate required by your system. The pressure rating of the camlock fitting should be checked to ensure it can handle the operational load without failure. Larger sizes and high-pressure ratings are often required for heavy-duty applications like oil and gas or industrial manufacturing.
Seal Material
Camlock fittings use different types of seals (often O-rings) to ensure a tight, leak-proof connection. The material of the seal should be compatible with the fluids being transferred. For example:
EPDM seals are excellent for water and general-purpose use.
Viton seals are suitable for oils, chemicals, and high-temperature applications.
Application Type
Consider whether you need a quick-connect fitting for frequent disconnections, or whether a permanent or semi-permanent connection is sufficient. Camlock fittings are often the go-to choice for systems where rapid connections and disconnections are required, such as agriculture, firefighting, and water management systems.
Regulations and Standards
It’s essential to ensure that your camlock fittings meet relevant industry standards such as ISO or ANSI to guarantee safety and reliability. These standards help ensure the fittings are suitable for use in specific applications, particularly when handling hazardous or pressurized fluids.
How Do Camlock Fittings Work?
The Functionality of Camlock Connectors
Camlock connectors work on a simple yet highly efficient quick-connect system that allows users to securely connect and disconnect hoses, pipes, or other fluid transfer equipment without requiring special tools or excessive force. The connectors operate using a male coupler and a female adapter, which are joined together using the camlock coupling mechanism.
When connecting, the male coupler features a grooved end that fits into the female adapter. Once inserted, the user operates the lever cams, which are located on the female adapter. The cam levers, when pressed down, lock into the grooves on the male coupler, effectively sealing the connection. This action ensures a secure and tight bond, preventing fluid leakage or accidental disconnections during transfer.
The coupling mechanism is designed to be user-friendly and quick, making it ideal for environments where fluid transfer needs to be done rapidly and with minimal downtime.
The Role of Camlock Seals in Fluid Transfer
One of the key components that ensures leak-proof performance in camlock fittings is the use of seals. These seals, usually made from rubber or elastomeric materials, are located within the female adapter or around the male coupler. They play a crucial role in ensuring that the connection remains tight even under pressure.
When the camlock coupling is locked in place, the seals compress between the male and female parts, creating a secure barrier that prevents fluid leakage. This is especially important in applications where the transfer of chemicals, fuels, or other hazardous fluids is involved. The seals also act as a protective barrier against contaminants, ensuring that the fluids being transferred remain pure and uncontaminated.
High-quality seals made of resistant materials are essential for long-lasting and reliable performance, particularly in harsh conditions. The sealing properties also ensure the integrity of the fluid transfer system, reducing the risk of spills, environmental hazards, and costly downtime.
The Camlock Lock Mechanism Explained
The lock mechanism is what sets camlock fittings apart from many other types of industrial couplings. The camlock lock mechanism involves the use of cam levers or arms that are attached to the female adapter. These levers serve as a locking system that secures the connection between the male coupler and female adapter.
The process works as follows:
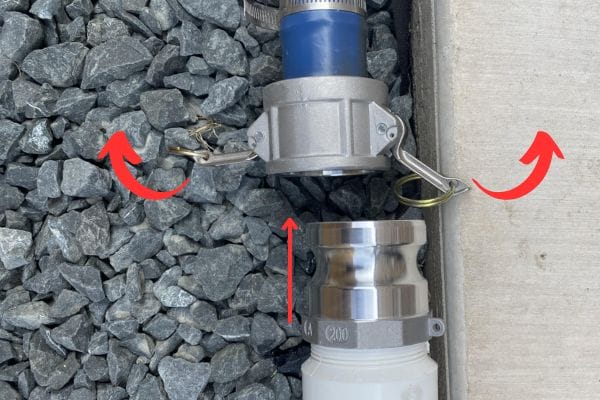
Insertion: The male coupler is inserted into the female adapter, with the groove on the male fitting aligning with the camlock levers on the female adapter.
Lever Action: The user pushes down on the cam levers, which apply pressure to the male coupler. The levers engage with the grooves on the male fitting, locking the two pieces together.
Secured Connection: Once the levers are in place, the connection is secured. The locking mechanism ensures that the coupling remains intact, even under high pressure or movement, and prevents accidental disconnections.
The locking mechanism offers several benefits:
It provides a tight seal, preventing fluid leakage.
It eliminates the need for extra tightening tools, saving time and effort.
It ensures safety by keeping the connection intact, reducing the risk of spills or accidents.
This lock mechanism makes camlock fittings ideal for heavy-duty applications and environments where a reliable connection is crucial.
How the Camlock Coupling Quickly Connects and Disconnects
One of the standout features of camlock fittings is the ability to quickly connect and disconnect hoses and pipes without the need for tools or excessive force. This fast coupling process makes camlock fittings especially valuable in industries where time is of the essence, such as firefighting, chemical transfer, or construction.
Here’s how the quick-connect feature works:
Initial Setup: The male coupler is aligned with the female adapter. Depending on the type of camlock fitting, this can involve aligning grooves and seals for proper fitment.
Engagement: The user presses the cam levers down to lock the two parts in place. As the levers engage with the grooves, they apply pressure, ensuring a secure, leak-proof connection.
Sealing: The seals inside the fitting compress, ensuring that there is no room for fluid leakage, even when the system is under pressure.
Disconnection: When it’s time to disconnect, the process is equally simple. The user lifts the cam levers, which release the locking mechanism, allowing the male coupler to be easily removed from the female adapter.
This design eliminates the need for screws, bolts, or other complex joining mechanisms, making it a preferred solution when rapid and frequent connections are required.
The ability to quickly disconnect also reduces downtime in high-demand environments and minimizes the risk of fluid backflow or accidental contamination when the fittings are being removed.
Camlock Fittings vs Other Types of Industrial Fittings
When it comes to choosing the right industrial fitting, it’s essential to compare camlock fittings with other popular types. While camlock fittings are renowned for their quick-connect functionality and versatility, there are other fitting options like threaded fittings and quick disconnect fittings that may suit specific needs depending on the application. Let’s explore how camlock connectors stack up against these alternatives.
How Camlock Connectors Compare to Threaded Fittings
Threaded fittings and camlock connectors are two of the most commonly used types of industrial fittings. They each have their advantages, but camlocks stand out in several ways:
Ease of Use: One of the most significant advantages of camlock fittings over threaded fittings is their quick-connect and quick-disconnect capabilities. With threaded fittings, the connection process requires aligning the threads, tightening them with tools, and ensuring the proper seal. In contrast, camlock fittings lock into place with a simple lever mechanism, offering faster assembly and disassembly without the need for tools. This makes camlocks a more efficient choice for applications that require frequent or rapid connection and disconnection.
Leak Resistance: Both threaded and camlock fittings can be leak-resistant, but camlocks provide a better seal in some situations, especially when coupled with high-quality seals (such as EPDM or Viton). The pressure from the cam lever ensures a tight fit, which may outperform threaded connections that are prone to loosening over time or under vibration.
Application Versatility: Threaded fittings are often used for permanent or semi-permanent connections in piping systems where a robust, long-term connection is needed. Camlock fittings, on the other hand, excel in temporary connections—ideal for industries like agriculture, firefighting, and fluid transfer systems, where quick, secure, and frequently adjusted connections are necessary.
Durability: Threaded fittings tend to be more durable for high-pressure systems or where a permanent, tight seal is required. However, camlock fittings are incredibly durable in their own right, especially in heavy-duty applications like oil and gas or chemical handling, thanks to the use of materials like stainless steel or aluminum.
In summary, threaded fittings are ideal for permanent, high-pressure applications, while camlock connectors provide speed, ease of use, and flexibility in fluid transfer systems requiring frequent connections.
Camlock vs Quick Disconnect Fittings: What’s the Difference?
Quick disconnect fittings (also known as quick-connect fittings) are similar to camlock fittings in that they both offer the convenience of fast connection and disconnection. However, the mechanisms and applications for each type differ slightly.
Mechanism
Camlock Fittings: Utilize a cam lever system that secures the connection by pressing down on the levers that engage with the grooves of the male coupler. This creates a tight, leak-proof seal that is easy to engage and disengage.
Quick Disconnect Fittings: Usually use a push-button or spring-loaded mechanism. You push the button to release the coupling, or sometimes, you simply pull the two parts apart. They are designed for quick coupling and uncoupling but generally lack the positive-locking feature of camlocks.
Security and Sealing
Camlocks: Known for stronger, more secure connections. The cam-locking mechanism provides extra pressure on the seal, reducing the chances of leakage under pressure. The quick-connect feature is highly efficient, yet the cam lever ensures the connection is tighter and more stable than most push-button quick disconnects.
Quick Disconnects: These can be less secure, as the connection might not be as tight as camlocks, depending on the specific model. Many quick-disconnect fittings rely on a simple spring or ball lock, which can sometimes result in less security compared to a camlock fitting’s positive-locking mechanism.
Applications
Camlock Fittings: Ideal for heavy-duty applications, including fluid transfer, industrial manufacturing, agriculture, and firefighting, where secure connections are paramount, and there’s a need for frequent and quick disconnects. Camlocks are typically used for more rigorous tasks involving high pressure and high flow rates.
Quick Disconnect Fittings: Often used in applications that require lower pressure and medium flow. These fittings are common in smaller-scale operations like HVAC systems, pneumatic systems, and water supply lines. They provide convenience but are not usually designed for extreme conditions.
Durability and Material
Camlock Fittings: Typically made from durable materials like stainless steel, brass, or aluminum, making them well-suited for high-pressure systems, harsh chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
Quick Disconnect Fittings: While available in similar materials, these tend to be less durable when compared to camlocks, especially under heavy-duty conditions.
Conclusion
When you choose the right camlock connector, you’re not just investing in a fitting, but ensuring the smooth operation and safety of your fluid systems
FAQ
What are camlock fittings used for?
Camlock fittings are used for quick and secure connections in fluid transfer systems. They are commonly used in industries such as agriculture, firefighting, oil and gas, and chemical processing for connecting hoses, pipes, and equipment without the need for tools.
How do camlock fittings work?
Camlock fittings work by using a male coupler and a female adapter. The male coupler fits into the female adapter, and cam levers are engaged to lock the connection, ensuring a tight, leak-proof seal.
What materials are camlock fittings made from?
Camlock fittings are typically made from stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and plastic. The material choice depends on the application, with stainless steel being best for high-temperature or corrosive environments and brass for fuel transfer.
Can camlock fittings handle high pressure?
Yes, camlock fittings are designed to handle high-pressure fluid transfer. However, the pressure rating can vary depending on the material and size of the fitting, so it’s important to choose a fitting with the appropriate pressure rating for your system.
How do I choose the right camlock fitting for my application?
To choose the right camlock fitting, consider factors like material compatibility, hose diameter, pressure ratings, and the specific application requirements.
Are camlock fittings easy to install?
Yes, camlock fittings are easy to install due to their quick-connect mechanism. You simply align the male and female parts, engage the cam levers, and the connection is secured without the need for tools.