One of the primary causes of hydraulic hose failure is improper routing. When hoses are not routed correctly, they’re more likely to experience stress, abrasion, and other issues that can significantly shorten their lifespan and compromise system safety.
Understanding Hydraulic Hose Dynamics
Basic Mechanics of Hydraulic Hoses
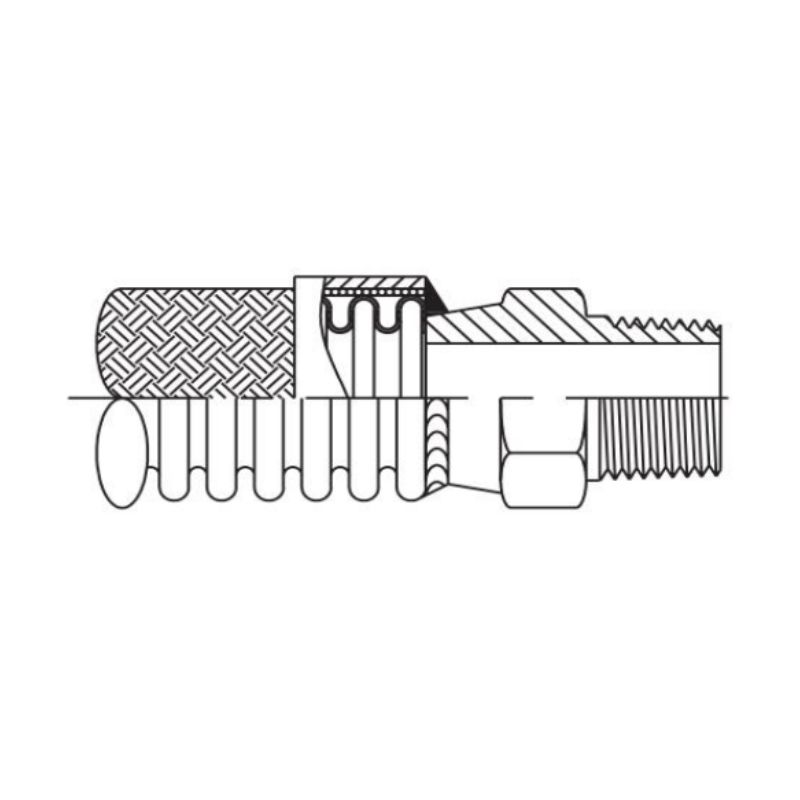
Hydraulic hoses are specially engineered to transport pressurized hydraulic fluid between different components of a hydraulic system. They are constructed from several layers, including an inner tube, reinforcement layers, and an outer cover. The inner tube carries the fluid, while the reinforcement layer—typically made of braided or spiral-wound steel or synthetic fibers—provides the strength needed to withstand high pressures. The outer cover protects the hose from environmental factors, such as abrasion and chemical exposure.
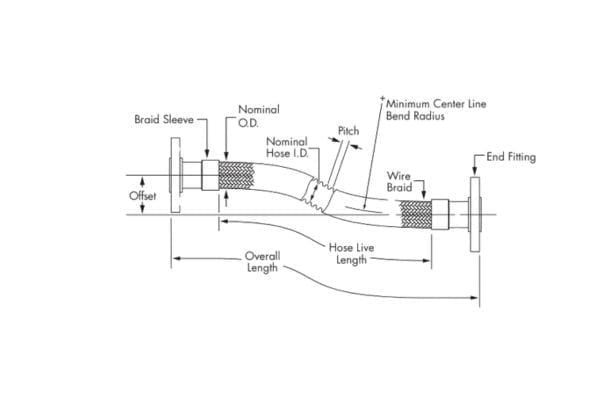
Under pressure, hydraulic hoses expand and contract, responding to the fluctuations in fluid pressure and the movement of connected components. In most cases, hoses can elongate by up to 2% or contract by 4% depending on the construction. This flexibility allows hoses to adapt to the movement of system components; however, it also makes proper routing essential to prevent overextension, which can stress hose connections or even cause the hose to pull out of fittings.
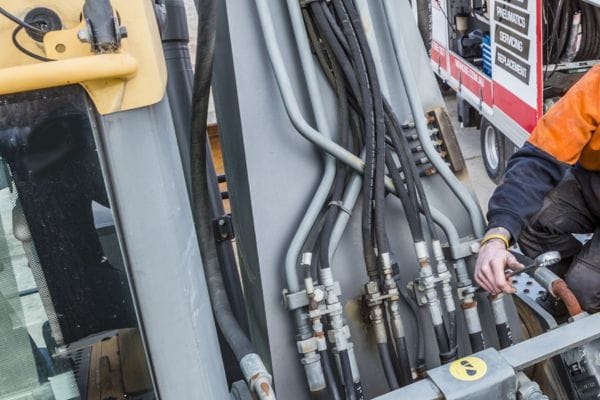

Factors Leading to Hose Failure
Hydraulic hoses face a range of stressors during operation. Some of the most common causes of hose failure include:
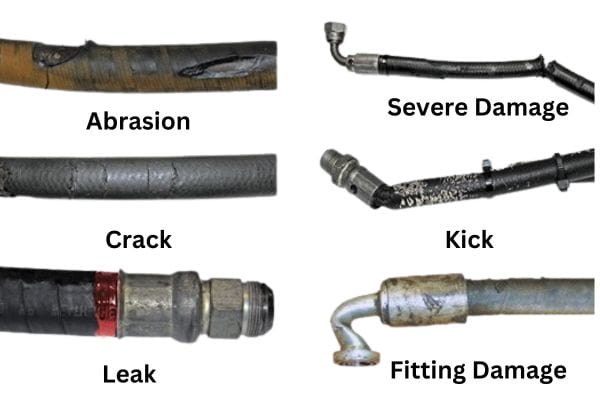
Abrasion: When hoses rub against other surfaces or each other, the outer cover can wear away, exposing reinforcement layers to potential damage.
Twisting: Twisting misaligns the reinforcement layers inside the hose, weakening its ability to handle pressure and causing premature wear.
Excessive Bending: Bending a hose beyond its minimum bend radius can lead to reinforcement damage and drastically reduce its pressure capacity.
Heat Exposure: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, either from the fluid or the environment, can degrade hose materials, leading to cracks and failures.
Improper Clamping or Support: Lack of proper support or incorrect clamping positions can cause hoses to sag, kink, or chafe, all of which contribute to accelerated wear.
Pressure Surges: High or fluctuating pressures can weaken the reinforcement over time, leading to leaks or bursts.
By understanding these factors, operators can take preventive measures, such as using protective sleeves or clamps and adhering to routing guidelines to reduce unnecessary wear on hoses.
Role of Environment in Hose Durability
The environment in which hydraulic hoses operate greatly influences their longevity and performance. Temperature, pressure, and exposure to chemicals or abrasive surfaces all impact hose durability:
Temperature: Extreme heat can cause hoses to harden and crack, while extreme cold can make them stiff and more prone to brittleness. Specialized hose covers and protective sleeves can help manage these temperature effects.
Pressure: Higher pressures put greater stress on the hose’s reinforcement layer. Ensuring that hoses operate within their specified pressure rating is essential to avoid overloading the hose, which leads to early degradation.
Surrounding Conditions: Hoses operating near machinery or sharp surfaces may experience abrasion or puncture. Additionally, hoses exposed to harsh chemicals or UV rays can experience rapid degradation of the outer cover.
Key Tips for Effective Hydraulic Hose Routing
Allow for Slack
One of the foundational principles of hydraulic hose routing is to allow for slight slack in the hose length to accommodate natural expansion and contraction. When a hydraulic system is pressurized, hoses experience minor elongation or contraction—up to 2% elongation or 4% contraction depending on the hose construction. This flexibility is essential to absorb system vibrations and allow components to move without causing tension in the hose. If a hose is too short, it can pull on the fittings, leading to leaks, connection loosening, or even complete disconnection, which can pose significant safety hazards. However, it’s equally important not to allow too much slack, as excess hose length can cause sagging, increasing the chance of snagging on equipment or rubbing against other components.
Proper slack ensures that the hose can expand and contract as needed, enhancing system reliability and reducing stress on the hose fittings, which ultimately extends the hose’s service life.
Respect Minimum Bend Radius
The bend radius is the minimum radius a hose can be bent without compromising its structural integrity or performance. Each hose has a specified minimum bend radius, typically outlined in the manufacturer’s documentation, based on its size and reinforcement type. Exceeding this minimum bend radius—by bending the hose too sharply—places excess stress on the reinforcement layers, creating small gaps between strands or even causing strands to kink. This strain reduces the hose’s ability to withstand pressure, leading to a higher likelihood of bursting, leaks, or failure in high-pressure environments.
Respecting the minimum bend radius is crucial for maintaining the hose’s pressure rating and ensuring that fluid flows smoothly without causing turbulence. A general guideline is to avoid any bend in the hose closer than twice the outside diameter of the hose to its fitting. When routing in tight spaces, using elbow fittings or adapters can help prevent the need for sharp bends, ensuring the hose’s integrity and extending its operational lifespan.
Avoid Twisting the Hose
Twisting is another common routing mistake that can severely impact the functionality and lifespan of a hydraulic hose. When a hose is twisted during installation, it misaligns the reinforcement layers, weakening the hose’s ability to handle pressure and making it vulnerable to early failure. Even a slight twist can reduce the hose’s pressure tolerance by as much as 90%, leading to potential bursts, leaks, or detachment from fittings.
To avoid twisting, always install hoses with the layline (the continuous line of information printed along the hose with the part number, pressure rating, etc.) in a straight orientation. If the layline appears twisted like a candy cane, it’s an indication that the hose was installed with a twist. Ensuring the layline remains aligned during installation helps prevent twists, allowing the hose to function as designed under pressure without compromising the reinforcement structure.
Using Fittings and Adapters for Optimal Routing
Choosing the Right Elbow Fittings
Selecting the appropriate elbow fittings, such as 45- or 90-degree elbows, can make a significant difference in hydraulic hose routing. Elbow fittings are essential for installations where a hose must bend immediately near the connection point. Rather than forcing the hose into a tight bend, which can strain the reinforcement and reduce its pressure capacity, a 45- or 90-degree elbow allows the hose to connect smoothly while maintaining the recommended bend radius. Generally, a hose should remain straight for at least twice its outside diameter before any bend. If this isn’t possible due to spatial constraints, an elbow fitting is the best solution to prevent excessive stress and ensure that high-speed fluid flow does not impact the hose core directly, which can lead to premature wear.
Using the right elbow helps avoid sharp, abrupt bends that can interfere with the smooth flow of hydraulic fluid, thereby reducing pressure loss and enhancing system efficiency.

Minimizing Connection Points
Each additional connection point in a hydraulic system introduces a potential leak path, complicates the installation, and can increase assembly time and cost. By minimizing the use of adapters and fittings, operators can improve the overall integrity of the hydraulic system. Fewer connections reduce the risk of leaks and make the installation process simpler and more efficient. For example, instead of using multiple fittings to achieve a desired hose route, choosing one strategically placed adapter or elbow fitting can serve the same purpose with fewer potential weak points.
Where possible, select fittings that allow for a direct and clean route without multiple connectors or complex assembly configurations. A streamlined setup not only reduces leak risk but also makes future maintenance easier, as there are fewer components to inspect, tighten, or replace.
Using Adapters to Ease Routing
Adapters are valuable tools in hydraulic routing, as they can adjust the hose’s orientation to follow the contours of the equipment or machinery. This flexibility allows for more straightforward, efficient routing, particularly when space is limited or when hoses must avoid interference with other components. Adapters can also be used to change the thread configuration or angle of the hose connection, making it possible to route hoses more closely along the contours of the machine, reducing overall hose length and avoiding hard bends.
Managing Abrasive Influences
Identifying Abrasion Points
Abrasion is one of the most common causes of hydraulic hose failure, often resulting from hoses rubbing against machinery surfaces, other hoses, or sharp edges within the operating environment. During installation, it’s crucial to identify areas where hoses may come into contact with abrasive surfaces or each other. Common abrasion points include:
High-Traffic Areas: Where hoses are likely to be handled or impacted during regular operation or maintenance.
Contact with Machine Components: Areas where hoses run close to moving parts, metal edges, or fittings.
Bundled or Parallel Hoses: If multiple hoses are installed in parallel, vibration and movement can cause them to rub against each other, wearing down their outer covers.
To identify these potential abrasion points during installation, inspect routing paths for any sharp edges, tight clearances, or points where hoses touch other components. Adjusting the routing to keep hoses clear of these areas can reduce the risk of abrasion. When avoiding contact is impossible, using abrasion-resistant coverings can help mitigate wear.
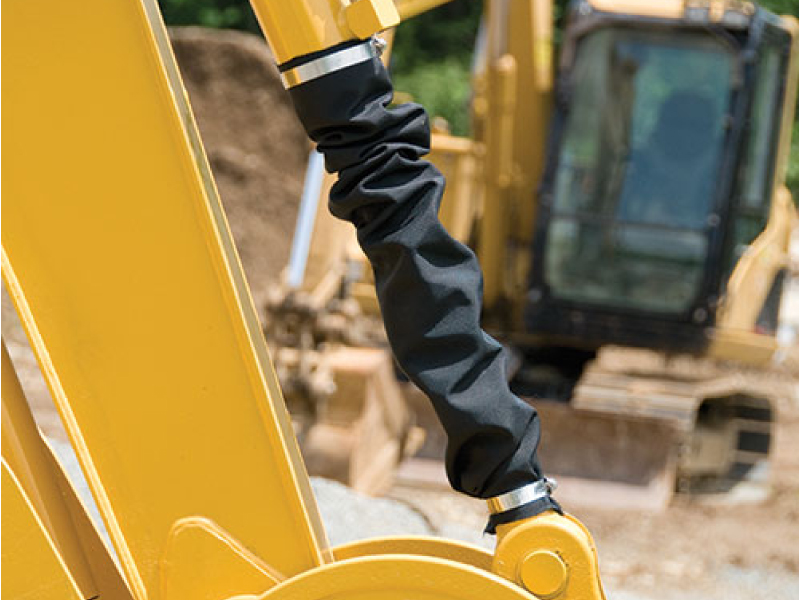
For additional protection, protective sleeves can be added over the hose cover. These sleeves, made from materials like nylon or polyester, offer a flexible yet durable barrier that absorbs much of the wear from abrasives. Sleeves are especially useful in areas where hoses come into contact with sharp or abrasive surfaces or where there is a risk of hoses rubbing against each other.
Impact of Temperature on Hose Performance
Heat and Hose Degradation
High ambient temperatures can have a severe impact on the longevity, flexibility, and reliability of hydraulic hoses. Hydraulic hoses are constructed with an inner tube to carry the pressurized fluid, a reinforcing layer for strength, and an outer cover to protect the hose from external damage. When hoses are consistently exposed to elevated temperatures—whether due to the heated hydraulic fluid, they transport or external factors in their environment—the materials in these layers begin to deteriorate more rapidly than they would under normal operating conditions.
The outer cover, often made from rubber or synthetic materials, is the first line of defense against environmental hazards, including heat. However, prolonged exposure to high temperatures causes these materials to harden, crack, and lose flexibility. Over time, this degradation makes the hose brittle and far more susceptible to leaks or ruptures. The inner tube, which directly carries the fluid, is also at risk; constant exposure to heated hydraulic fluids accelerates the aging of the tube material, increasing its vulnerability to cracking and failure under normal pressures.
Additionally, high temperatures can lead to the deterioration of the hose’s reinforcement layer, which is typically composed of braided or spiral-wound metal or synthetic fibers. This layer is crucial for maintaining the hose’s pressure tolerance and overall structural integrity. As extreme heat weakens this reinforcement, the hose loses its ability to handle its rated pressure, significantly increasing the risk of bursting or leakage. Hoses consistently operating at or above their rated temperature limit experience faster degradation across all layers, leading to a dramatically shortened service life and an increased likelihood of unexpected, catastrophic failures. This type of failure can halt operations, result in costly repairs, and, in some cases, create safety hazards for personnel working nearby.
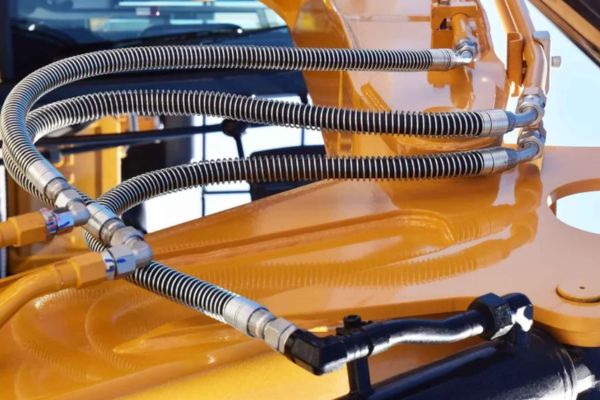

Using Insulation and Protective Sleeves
To combat the negative effects of high temperatures on hydraulic hoses, it is essential to use specialized insulation and protective sleeves, especially in areas exposed to high ambient heat or near hot machine components. Heat-resistant sleeves, commonly made from materials like silicone-coated fiberglass or other heat-tolerant synthetics, provide a protective layer that shields the hose from thermal stress. These sleeves act as a buffer, maintaining a lower temperature within the hose structure and preventing the outer cover from direct heat exposure. By slowing down the rate of heat absorption, these sleeves reduce material degradation and help the hose retain its flexibility and pressure tolerance over a longer period.
Another effective approach is to plan the routing of hoses away from high-temperature components, such as exhaust manifolds, engine blocks, or other heat-generating machinery parts. When possible, position hoses in areas with cooler air circulation to minimize thermal exposure. In instances where rerouting is not feasible, installing heat shields or reflective wraps can provide additional protection. Heat shields work by reflecting radiant heat away from the hose surface, further preventing overheating and reducing the rate of material degradation.
In extremely hot environments, combining these methods—using heat-resistant sleeves, strategic routing, and reflective wraps—can significantly extend hose life and preserve hydraulic system performance. Implementing these thermal protection techniques reduces the frequency of hose replacements, cuts down on unplanned maintenance costs, and ensures a safer, more efficient working environment for hydraulic system operators. By managing temperature exposure effectively, companies can optimize the lifespan of their hoses, maintain consistent system functionality, and avoid the operational risks associated with thermal stress on hydraulic components.
Conclusion
Hydraulic hoses are vital components of any hydraulic system, and their longevity depends on the careful attention given to their installation and upkeep. By prioritizing these best practices, operators can maximize hose performance, protect system integrity, and maintain a safe, productive work environment.
FAQ
Why is proper hydraulic hose routing important?
Proper routing prevents excessive wear, reduces the risk of hose failure, and ensures reliable system performance by minimizing stress on hoses and fittings.
How much slack should I leave in a hydraulic hose?
Leave enough slack to allow for a 2% elongation or 4% contraction under pressure. This prevents tension on fittings and allows for movement without risking hose damage.
What is the minimum bend radius, and why does it matter?
The minimum bend radius is the smallest radius a hose can bend without compromising its structural integrity. Exceeding this radius can damage the hose’s reinforcement layers, reducing its pressure capacity and leading to failure.
Can I mix hoses and fittings from different manufacturers?
It’s best not to mix and match hoses and fittings from different manufacturers, as they may not be compatible, which can lead to leaks or reduce hose life.
How can I protect hoses from heat?
Use heat-resistant sleeves or insulation, and try to route hoses away from hot components to reduce thermal stress and prevent material degradation.
What should I look for during regular hose maintenance?
Check for signs of abrasion, kinks, leaks, hardening, or any visible wear. Ensuring proper clamping and correct alignment will also help prevent damage over time.