Upgrading your valve system by replacing a gate valve with a ball valve can greatly enhance efficiency and performance. Ball valves offer quick operation with a simple 90-degree turn, providing superior flow control and requiring minimal maintenance. They are more durable, compact, and reliable, resulting in fewer repairs and better system efficiency. By switching to ball valves, you ensure faster operation, better sealing, and improved durability, ultimately boosting system reliability and reducing downtime.
What You Need to Know About Gate Valves and Ball Valves
Differences Between Gate Valve and Ball Valve
Understanding the fundamental differences between gate valves and ball valves is key to making an informed decision when it comes to replacing a gate valve with a ball valve. These two types of valves may appear similar at first glance, but their internal mechanisms and applications are quite distinct:
Mechanism of Operation
Gate Valve: A gate valve operates by lifting a gate or wedge out of the flow path. The valve opens and closes by turning a handwheel or actuator multiple times, gradually lifting or lowering the gate. This makes it ideal for fully opening or closing the valve, but not for precise flow control.
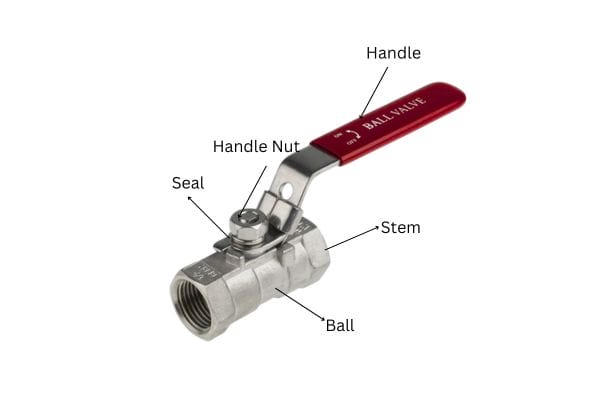
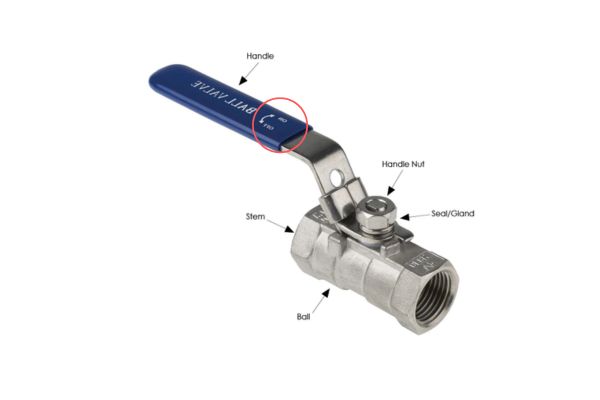
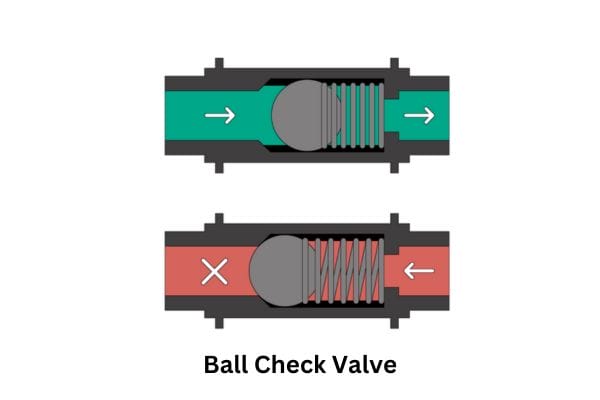
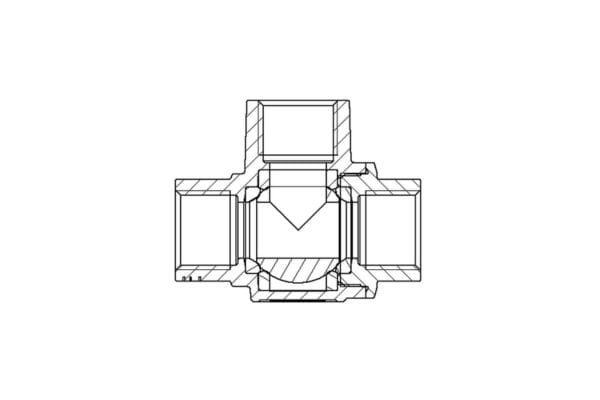
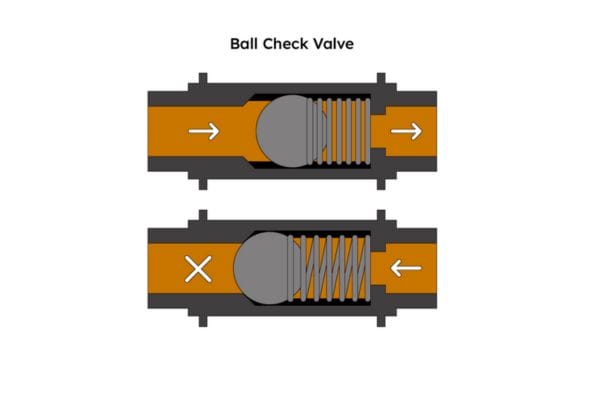
Ball Valve: A ball valve uses a hollow, perforated, and pivoting ball to control the flow of fluid. The ball rotates 90 degrees to either allow or stop the flow. It’s quick to open or close and offers excellent flow control, making it more efficient in applications where frequent adjustments are necessary.
Flow Control
Gate Valve: Typically, gate valves are best suited for applications where the valve is either fully open or fully closed. The gradual opening and closing process makes them less efficient for regulating flow and more prone to wear when partially open.
Ball Valve: Ball valves provide precise control over flow and can be used for both full flow and throttling applications. The quick quarter-turn operation allows for rapid adjustment and shut-off, which is ideal for systems where efficiency and speed are important.
Sealing and Leaks
Gate Valve: Gate valves are more prone to leakage, especially as the gate and seal wear down over time. When the valve is partially open, the seals may not form a perfect seal, leading to potential leaks.
Ball Valve: Ball valves provide a much more reliable seal due to the design of the ball and the seals around it. The ball valve’s seal is robust, and because the ball is only in one of two positions (fully open or fully closed), the likelihood of leaks is significantly lower compared to gate valves.
Maintenance and Longevity
Gate Valve: Gate valves require more maintenance due to their complex components and susceptibility to corrosion and debris buildup. Over time, they can become difficult to operate and prone to failure.
Ball Valve: With fewer moving parts and a simpler design, ball valves are easier to maintain. Their resistance to corrosion and wear means they typically last longer with minimal maintenance.

When and Why to Replace Gate Valve with Ball Valve
Replacing a gate valve with a ball valve is often the right choice when facing several issues or when system requirements change. Here are some scenarios where it’s time to make the switch:
Slow Operation or Difficulty in Adjustments If your gate valve is slow to open and close, or you need more precise flow control, replacing it with a ball valve will offer much faster response times and better control with a quick, 90-degree turn.
Frequent Leaks or Reduced Sealing Performance As gate valves wear over time, their seals can degrade, causing leaks. A ball valve’s design ensures a more secure seal, and its resilience against wear means fewer leaks and better system integrity.
High Maintenance Costs Gate valves require more regular maintenance due to their complex internal components and higher susceptibility to failure. If you’re spending more time and money on maintaining gate valves, switching to a ball valve could reduce downtime and overall maintenance costs.
Improved Flow Control Ball valves are ideal for applications that require precise flow regulation or frequent on/off control. If you need better flow control or are dealing with a system where flow adjustments are crucial, a ball valve offers greater flexibility and efficiency.
Space or Weight Constraints Ball valves are often more compact and lighter than gate valves, which can be advantageous in systems where space or weight limitations are a concern.
Enhanced Durability in Harsh Conditions If your system operates under extreme conditions (e.g., high pressure, temperature, or corrosive environments), ball valves are more resistant to these factors, providing a longer-lasting and more reliable solution.
Signs That Indicate It’s Time to Replace Your Gate Valve
Common Gate Valve Issues: Leaks, Corrosion, and Failure
Gate valves, while reliable for many years, are susceptible to certain issues over time that can affect their performance and your system’s efficiency. Identifying these problems early on can help you determine when to replace your gate valve. Some of the most common gate valve issues include:
Leaks One of the most apparent signs that a gate valve is failing is leakage. As the valve ages, the sealing surfaces may wear down, and the seals or gaskets may no longer form a tight seal, leading to water, gas, or fluid leakage. Leaks can occur around the stem or between the valve body and the bonnet, and even small leaks can escalate into more significant issues over time.
Corrosion Corrosion is a natural consequence of metal components being exposed to moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures. Gate valves, particularly those in harsh environments, are prone to rust and corrosion. Corrosion weakens the valve body and its moving parts, potentially leading to complete failure if not addressed promptly. If you notice visible signs of rust or if the valve starts to seize due to corrosion, it’s a strong indicator that replacement is needed.
Failure to Open or Close Properly A gate valve relies on a gate mechanism that moves up and down to open or close the flow. Over time, the gate may become stuck or difficult to move due to wear, corrosion, or debris buildup. If the valve becomes hard to operate or fails to open or close fully, it can lead to system shutdowns or fluid regulation problems. This can be caused by the valve’s internal components wearing out or becoming obstructed.
How Gate Valve Performance Can Impact Your System
A gate valve’s performance directly impacts the efficiency and reliability of your entire fluid system. Here’s how poor gate valve performance can affect your system:
Flow Restriction and Pressure Drops If the gate valve isn’t functioning properly, it can create flow restrictions even when fully open. This can lead to a reduction in fluid flow, which may cause pressure drops throughout the system. In systems that require precise flow control, this can be especially problematic, as it leads to inefficient operations, energy waste, and potential damage to other components in the system.
Inconsistent Fluid Flow Control Gate valves are typically used for fully open or fully closed applications. However, when they wear out, their ability to maintain a consistent flow is compromised. As the valve becomes harder to operate, partial flow control becomes unreliable, and the fluid may be diverted incorrectly or unevenly. This inconsistency in flow control can have a cascading effect on the system, leading to operational inefficiencies, safety concerns, and potential damage to connected equipment.
Increased Maintenance and Downtime As gate valves start to fail, they require more frequent maintenance, which increases downtime and operational costs. Parts such as the valve stem, packing, and seals may need constant attention or replacement. If the valve continues to fail despite repairs, it may lead to prolonged system shutdowns, which not only affect productivity but also increase labor and material costs.
System Reliability and Safety Risks Leaking or malfunctioning gate valves can lead to hazardous situations, especially in systems dealing with pressurized fluids or gases. If a gate valve fails to close properly, it could cause a system to operate under unsafe conditions, putting both the equipment and personnel at risk. In some cases, if the gate valve fails to open properly, it could prevent proper fluid circulation, causing damage to sensitive components or leading to system failure.

Identifying Signs of Wear and Inefficiency in Gate Valves
As gate valves age, they experience wear and tear that can cause inefficiency or failure. Recognizing the signs early can help you determine if it’s time to replace your gate valve. Look for the following indicators of wear and inefficiency:
Difficulty Operating the Valve If the valve handle or actuator becomes increasingly difficult to turn, this could indicate internal friction or obstruction due to corrosion, debris buildup, or mechanical failure. Difficulty in operating the valve can lead to inconsistent performance or the inability to fully open or close the valve, impacting your system’s operation.
Visible Damage or Wear Inspecting the valve’s external condition is a simple way to check for early signs of damage. Cracks, visible rust, or physical deterioration on the valve body or stem can signal that the valve is no longer functioning at its best. These external signs of damage are often indicative of internal issues, which may be affecting the valve’s performance.
Increased Vibration or Noise If you notice increased vibration or unusual noise during valve operation, this could be a sign that the gate valve is no longer performing smoothly. Irregular operation may indicate that the internal components are damaged or misaligned, which could lead to further damage down the line.
Frequent Leaks or Weeping Leaks, whether from the valve stem, around the bonnet, or from the valve body, are a common sign of wear. Even minor leaks should be addressed, as they can grow worse over time. In some cases, a leaky gate valve can lead to water loss, system contamination, or create a hazardous environment depending on the fluid being transported.
Unusual Pressure Fluctuations If your system experiences fluctuating pressure or difficulty maintaining consistent flow, it may be due to the gate valve not fully closing or opening. Inconsistent pressure can cause stress on other components in the system, leading to inefficiencies or failure in connected equipment.
Choosing the Right Ball Valve for Your System
Factors to Consider: Size, Material, and Pressure Rating
When selecting a ball valve for your system, it’s essential to consider several key factors to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. These factors include size, material, and pressure rating, all of which affect how the valve will function within your piping system.
Size:
Pipe Diameter Compatibility: The size of the ball valve should match the diameter of your pipes to ensure a secure and leak-free connection. If the valve is too small, it can restrict the flow of fluid, whereas a valve that is too large may result in inefficient sealing and excess space inside the valve body.
Flow Requirements: The valve size should also be chosen based on the flow rate requirements of your system. A ball valve that’s too small can create flow restrictions, while a valve that’s too large may be unnecessarily bulky and more costly.
Material:
Corrosion Resistance: Ball valves come in a variety of materials, including stainless steel, brass, PVC, and more. The material you choose will depend on the fluid being controlled and the environmental conditions the valve will be exposed to. For example:
Stainless Steel: Ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, as well as corrosive fluids like acids or saline.
Brass: Common in residential and light commercial applications, suitable for water, oil, and gas.
PVC or CPVC: Suitable for corrosive chemicals and lower pressure systems, often used in industries like water treatment.
Temperature Compatibility: Some materials are better suited for high or low-temperature environments. Ensure the material you choose can handle the expected operating temperature range of your system without degrading.
Pressure Rating:
Match System Pressure: The pressure rating of the ball valve must match or exceed the maximum pressure within your system. Over-pressurizing the valve can lead to leaks, valve failure, or even catastrophic damage.
PN Rating: Most ball valves will have a pressure rating indicated in bar (PN rating), which tells you the maximum pressure the valve can handle at a given temperature.
Temperature vs. Pressure Relationship: It’s important to consider both pressure and temperature, as many valves have different pressure ratings at varying temperatures. Ensure the valve is rated for the highest operating temperature and pressure in your system.
Ball Valve Types and Their Suitability for Different Applications
Ball valves come in several different designs, each suited to specific applications. Here are some common types and where they are typically used:
Standard 2-Way Ball Valve:
Application: This is the most common type of ball valve, used for simple on/off flow control. It has two ports—an inlet and an outlet—and is ideal for applications where fluid flow needs to be completely stopped or allowed through.
Common Uses: Residential plumbing, HVAC systems, water treatment plants, and basic industrial processes.
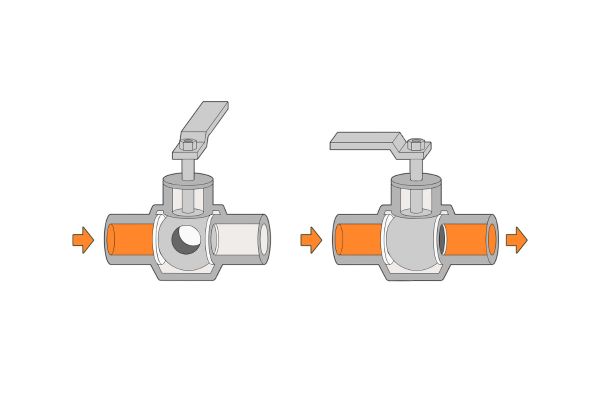
3-Way Ball Valve:
Application: A 3-way ball valve features three ports, typically in a T- or L-shape. This allows for flow diversion or mixing of fluids. It can direct flow between two outlets or mix two fluids together.
Common Uses: Heating and cooling systems, mixing applications, and systems where flow needs to be directed or diverted to multiple paths.
V-Port Ball Valve:
Application: The V-port ball valve has a V-shaped opening in the ball, which allows for precise throttling control. This makes it ideal for applications where you need to regulate or control flow rate, rather than just open or close the valve.
Common Uses: Chemical processing, mixing, or anywhere precise control over the flow is needed, especially in systems requiring modulating control.
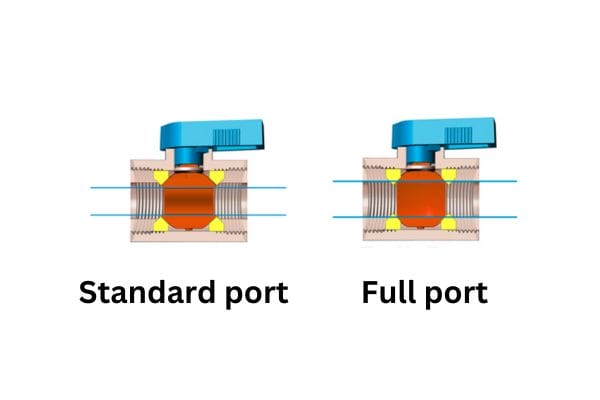
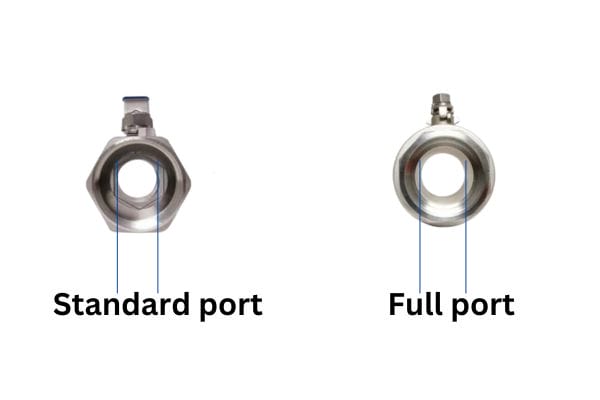
Full-Bore Ball Valve:
Application: A full-bore ball valve has a ball with a hole that matches the diameter of the pipe, allowing for unrestricted flow. This type of valve minimizes pressure drop and resistance when fully open.
Common Uses: High-flow systems, such as water treatment plants, oil and gas pipelines, and other industries requiring high-volume fluid transport.
Trunnion Ball Valve:
Application: Trunnion ball valves are designed for high-pressure and high-flow applications. They have additional supports (trunnions) that help stabilize the ball inside the valve, making them ideal for large pipelines and extreme conditions.
Common Uses: Oil and gas, petrochemical industries, and large industrial systems that handle high-pressure, high-volume fluid flows.
Understanding Valve Compatibility with Existing Pipes and Systems
Ensuring that the ball valve is compatible with your existing piping system is crucial to avoid leakage, poor performance, and unnecessary costs. Here are some key compatibility factors to keep in mind:
Connection Type:
Ball valves come with various connection types, including threaded, flanged, welded, or compression fittings. Ensure that the valve’s connection type matches the connection type of your existing pipes. Using adapters or unions can sometimes solve mismatches, but it’s always best to choose a valve with a matching connection to reduce the risk of leaks or installation errors.
Pressure Class and Standards:
Check the pressure class of the valve and ensure it’s compatible with the pressure rating of your system. For example, valves rated for ANSI class 150 or 300 should match the system’s pressure class to avoid any potential failure or leaks.
Verify that the valve complies with relevant standards for your industry, such as ASME, API, or ISO, ensuring it meets safety and performance criteria.
Pipe Material Compatibility:
The material of the ball valve must be compatible with the material of the piping in your system. For example, using a stainless steel valve in a PVC pipe system might lead to corrosion or poor performance due to differences in material properties. Choose a valve material that matches your pipe’s material for a reliable, long-lasting connection.
Temperature Compatibility:
Verify that the valve can handle the temperature range of the fluid being transported in your system. Some ball valves are rated for higher temperatures, while others are more suitable for low-temperature applications. Installing a valve with an incorrect temperature rating can result in failure, leaks, or reduced service life.
Flow Direction:
Be mindful of the flow direction in your system and check that the ball valve’s flow direction markings are aligned with your system’s flow. Incorrect orientation can lead to inefficiency, wear, or failure of the valve.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Replace Gate Valve with Ball Valve
Shutting Down the System and Relieving Pressure
Before starting any valve replacement procedure, it’s essential to shut down the system properly to ensure both safety and a smooth installation process.
Turn Off the Fluid Supply: Shut off the source of the fluid or gas flowing through the system. This will prevent any accidents or unwanted flow during the replacement.
Isolate the Valve Area: If the valve is part of a larger system, isolate the section of the pipe where the gate valve is located. Use bypass valves or shut-off valves if available to prevent fluid from moving through the section you’re working on.
Relieve Pressure: Ensure all residual pressure in the system is released. Open any valves downstream of the gate valve to vent out any trapped pressure. This step is crucial to avoid any unexpected pressure buildup when removing the old valve.
Drain the Fluid (If Necessary): If the system contains hazardous or corrosive fluids, make sure to drain the fluid from the pipeline or capture it in containers to minimize safety risks and prevent environmental contamination.
Removing the Old Gate Valve: Best Practices
Once the system is safely shut down and pressure has been relieved, proceed with removing the gate valve. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth and safe removal:
Disconnect Power or Actuators: If the gate valve is automated, disconnect any electrical connections, actuators, or pneumatic control systems. Ensure all sources of power to the valve are turned off.
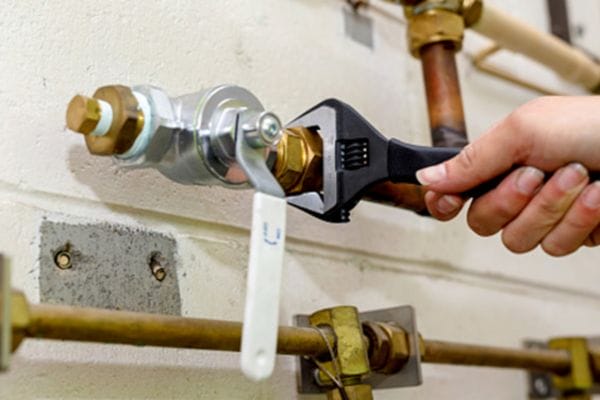
Loosen the Valve Connections: Use a wrench or pipe tool to loosen the nuts or bolts that secure the gate valve to the pipeline. Depending on the valve type (flanged, threaded, or welded), you may need different tools:
Flanged Connections: Loosen and remove the flange bolts.
Threaded Connections: Use a pipe wrench to unscrew the valve from the threads.
Welded Connections: If the valve is welded to the pipe, you’ll need a cutting tool (e.g., saw or grinder) to carefully cut the valve off.
Remove the Valve: Once the connections are detached, carefully remove the gate valve from the pipe. Be mindful of any remaining fluid in the valve, as this could spill when you remove it.
Clean the Pipe Ends: Clean the ends of the pipe where the old valve was connected. Remove any debris, rust, or old sealant to ensure a clean, smooth surface for the new valve installation.
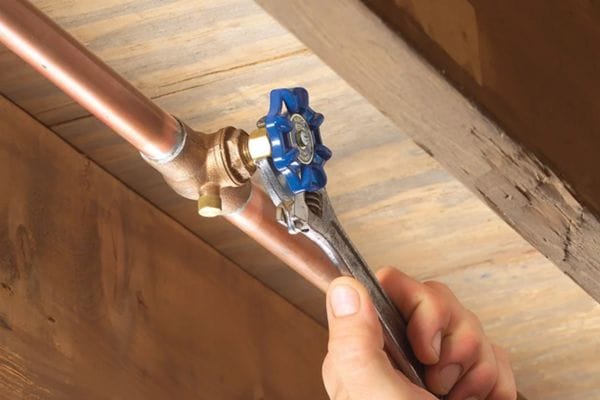

Installing the New Ball Valve: Detailed Instructions
With the old gate valve removed, it’s time to install the new ball valve. Here’s how to do it step-by-step:
Choose the Right Ball Valve: Ensure that the ball valve is the right size, material, and pressure rating for your system. The valve should match the pipe diameter and material (e.g., stainless steel, brass, PVC), and be able to handle the pressure and flow rates of your application.
Check Flow Direction Markings: Before installing, check the flow direction arrow on the ball valve to ensure it aligns with your system’s flow. Ball valves typically have an arrow indicating the correct flow direction, which is critical for proper operation.
Apply Thread Sealant (if applicable): If the new ball valve has threaded connections, apply an appropriate sealant (e.g., PTFE tape) to the threads on the pipe. Be sure to apply it in the direction of the threads to avoid contamination and ensure a proper seal.
Align the Ball Valve with the Pipe: Carefully position the ball valve between the two pipe ends, making sure it is aligned correctly for a secure fit. Ensure the valve handle is easily accessible for operation.
Connect the Valve to the Pipe:
Flanged Connections: Place the flanges of the valve against the pipe flanges and bolt them securely. Tighten the bolts in a criss-cross pattern to ensure even pressure distribution.
Threaded Connections: Screw the ball valve onto the threaded pipe ends, using a pipe wrench to tighten it securely. Be careful not to over-tighten, as this can damage the valve or threads.
Welded Connections: If the ball valve is welded into place, use the appropriate welding equipment to join the valve to the pipe. Make sure the welds are secure and meet any applicable standards.
Check Valve Orientation: Verify that the ball valve is oriented correctly, with the handle or actuator in the right position for operation. The valve should be perpendicular to the flow direction when closed and parallel when open.
Checking for Leaks and Verifying Valve Function
After installing the ball valve, it’s essential to test the system to ensure everything is working properly and there are no leaks.
Re-pressurize the System: Slowly bring the system back online, turning on the fluid supply and allowing pressure to build up gradually. This helps prevent sudden pressure spikes that could damage the system.
Inspect for Leaks: Carefully check all valve connections (flanged, threaded, or welded) for leaks. Use a flashlight to inspect hidden or hard-to-see areas. If any leaks are detected, tighten the connections or use additional sealant as necessary to resolve the issue.
Test Valve Operation: Open and close the ball valve several times to ensure smooth operation. The valve should open and close with a simple 90-degree turn, and the handle or actuator should operate freely without resistance.
Verify Flow Control: If applicable, test the valve for proper flow control. Ensure that fluid is flowing properly through the system, and that the ball valve is accurately regulating the flow when adjusted.
Final Inspection: Once you’ve verified that the ball valve is functioning correctly and there are no leaks, do a final check of the system. Ensure that all other components are properly sealed and operational before resuming full system use.
Troubleshooting Common Issues During Valve Replacement
What to Do if the New Ball Valve Isn’t Fitting Properly
Sometimes, during the installation of a new ball valve, you may encounter situations where the valve doesn’t fit as expected. Here’s what to do if you run into these issues:
Check for Compatibility Ensure that the new ball valve matches the size and connection type of your existing piping. A mismatch in the pipe diameter or connection type (e.g., threaded vs. flanged) could prevent the valve from fitting correctly. If there’s a mismatch, you may need to get an adapter or a valve that suits your pipe’s specifications.
Verify the Pipe End Condition Sometimes, the issue lies with the pipe ends themselves. Check if the ends of the pipe are clean, smooth, and free from any damage or debris. Rough or damaged pipe ends may prevent the valve from sealing properly. You may need to clean or recondition the pipe ends using a pipe reamer or a wire brush.
Use the Right Gaskets or Seals When installing a flanged ball valve, ensure the correct gasket or seal is used between the valve and the pipe. If you’re using a threaded connection, check the sealant or PTFE tape for proper application. If necessary, replace worn gaskets or seals that might be preventing a proper fit.
Check for Valve Orientation Ensure that the valve is oriented correctly according to the system’s flow direction markings. Installing the valve backward can cause misalignment and prevent the valve from fitting correctly. Check for the flow direction arrow and adjust accordingly.
Verify the Valve Type Sometimes, the valve type may not be suitable for the application. For instance, if the system requires a V-port ball valve for throttling, but a standard 2-way valve is installed, you might face issues with system pressure or flow control. Confirm that you are using the right type of valve for the specific needs of your system.
Solving Common Leak Problems
Leaks can occur during or after the installation of a ball valve, but these are often solvable with some troubleshooting. Here are some common causes of leaks and how to fix them:
Leaking at the Threads (Threaded Connections)
Cause: A common cause of leaks at threaded connections is improper application of thread sealant or PTFE tape.
Solution: Remove the valve and check the threads. If PTFE tape or thread sealant wasn’t applied correctly, clean the threads and reapply the sealant. Make sure to wind the tape in the correct direction (clockwise) so that it doesn’t unravel when tightening the valve. Then, reattach the valve and tighten it properly.
Leaking at the Flanges (Flanged Connections)
Cause: Leaks at flanged connections are typically caused by either improperly tightened bolts or damaged gaskets.
Solution: Check the flange bolts to ensure they are tightened evenly in a criss-cross pattern to ensure uniform pressure. If the gasket is damaged or worn, replace it with a new one, making sure it’s compatible with both the valve and the pipe material. Ensure that the gaskets are seated properly before tightening.
Leaking at the Valve Stem (Stem Seal Leakage)
Cause: A worn or improperly installed stem seal can cause leaks around the valve stem, especially when the valve is in the open or closed position.
Solution: Inspect the valve stem packing for any visible damage or wear. If the packing is damaged or worn out, it will need to be replaced. Some ball valves also allow you to tighten the packing nut to reduce stem leaks. Be careful not to over-tighten, as this could lead to difficulty in valve operation.
Leaks Between the Valve and the Pipe (Body-to-Pipe Leak)
Cause: Leaks at the junction between the valve and the pipe are typically caused by misalignment, insufficient tightening, or faulty seals.
Solution: Double-check that the valve is properly aligned with the pipe and that all connections are secure. Re-tighten the bolts or nuts (but avoid over-tightening). If the problem persists, remove the valve and inspect the seals or gaskets for damage. Replace any worn seals and apply new sealant if necessary.
Fixing Valve Handle or Actuator Issues
If you’re having trouble with the valve handle or actuator after installation, it could be due to several reasons. Here’s how to resolve common issues with the handle or actuator:
Hard-to-Turn Handle (Manual Ball Valve)
Cause: If the valve handle is difficult to turn, it could be due to excessive friction, internal component misalignment, or a faulty stem seal.
Solution: First, check the valve to ensure it’s not seized or obstructed by debris or foreign particles. You can try loosening the packing nut or stem nut to reduce friction around the stem. If the handle remains stiff after making these adjustments, it could indicate an issue with internal parts, and the valve might need to be replaced.
Loose or Wobbly Handle
Cause: A loose or wobbly handle is usually the result of a loose nut or a worn-out connection between the handle and the valve stem.
Solution: Tighten the handle nut or reattach the handle if it’s come loose from the stem. If the connection between the handle and stem is worn, you may need to replace the handle or stem assembly. Some ball valves have adjustable stems or quick-release handles that can be tightened or replaced easily.
Actuator Malfunctions (Automated Ball Valve)
Cause: Issues with an actuator, such as failure to open or close, can be caused by electrical or pneumatic malfunctions, improper wiring, or lack of power.
Solution: If the actuator isn’t functioning, check the power source and verify that the electrical connections are secure. For pneumatic actuators, check the air pressure and ensure the lines are not clogged. If the actuator still doesn’t function, you may need to troubleshoot or replace the actuator’s components (e.g., solenoid valve, motor, or pneumatic components).
Misalignment of Actuator with Valve Stem
Cause: In automated systems, the actuator may become misaligned with the valve stem, preventing the valve from opening or closing fully.
Solution: Re-align the actuator with the valve stem. This may involve adjusting the actuator mounting bracket or reattaching the actuator to ensure it connects properly with the valve stem. After adjusting, verify that the actuator moves the valve ball smoothly through its full range of motion.
Conclusion
By switching to ball valves, you address common issues like slow operation and frequent leaks, ensuring smoother operations, fewer repairs, and greater reliability over time. Don’t wait for valve failure—take proactive steps to improve your system’s efficiency and longevity with a reliable, easy-to-maintain ball valve solution.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a gate valve and a ball valve?
A gate valve requires multiple turns to open or close, while a ball valve uses a simple 90-degree turn for quick and efficient flow control.
Why should I replace my gate valve with a ball valve?
Ball valves offer faster operation, superior sealing, less maintenance, and are more durable, resulting in a more efficient and reliable system.
Are ball valves easy to maintain?
Yes, ball valves have a simple design, making them easy to maintain and less prone to common issues like leaks or corrosion.
How do ball valves improve system efficiency?
Ball valves provide smoother, uninterrupted flow and reduce energy consumption, leading to better system performance and lower operational costs.
Can ball valves handle high-pressure or corrosive environments?
Yes, ball valves are designed to withstand high pressure and harsh environments, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
When should I consider upgrading to ball valves?
If you’re experiencing slow operation, frequent leaks, or high maintenance costs with gate valves, upgrading to ball valves can solve these issues and improve overall system performance.