How to Seal Hydraulic Fittings?
It is critical for hydraulic systems and for operators to seal hydraulic fittings properly. This is because if a fitting is incorrectly sealed, it may cause damage to the fitting, system failure, and even injury to personnel.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Hydraulic systems are an integral part of all types of industrial machinery and hydraulic equipment. They can only function properly if they are properly sealed. Proper sealing ensures that hydraulic fluid remains in the system, maintains system pressure, and prevents failures or leaks from occurring. Moreover, proper sealing is what prevents external contamination from affecting the operation of the hydraulic system.
To properly install hydraulic fittings, you need to understand how to seal hydraulic fittings.
Why fittings leak
Typically, hydraulic fittings leak due to incorrect installation, excessive pressure, thread damage, vibration, material incompatibility, and seal damage. All of these reasons may lead to leaking fittings, then cause damage to the hydraulic system and have an impact on your machinery, time, and economy. In this article, Topa will focus on how fittings are sealed and how to seal them to prevent leaks properly, please continue to read!
Sealing Methods
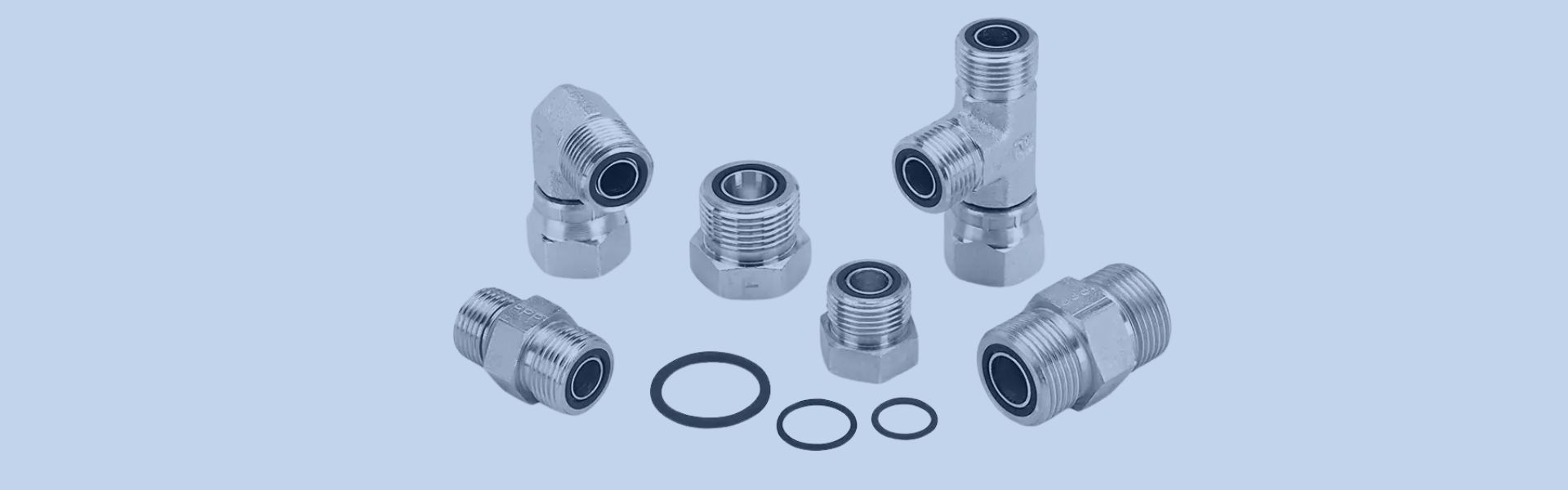
Although the specific structure of the various sealing forms is different, the sealing principle is that the metal surface or seals (such as O-rings, ED seals, gaskets, combination gaskets, etc.) and the metal surface between the seals are squeezed to form a sealing surface to stop the hydraulic oil from spilling.
Flat Face Seal
Flat face seals are classified as E-type port end seals, A-type port end seals, and O-ring face seals.
E-type port end seal
The E-type port end sea is a metric fine thread with an annular groove structure. The metric fine threads have good self-locking properties and are highly resistant to vibration and loosening. The groove structure requires the installation of packing seals, which can be made of fluoroelastomer or nitrile rubber. This method ensures that the straight threaded fitting forms a seal and reduces the risk of leakage.

A-type port end seal
Type A port end seal has a metric fine thread or a British standard pipe taper(BSPT)thread on the male end and requires a gasket or a combination gasket. The BSPT threads are tapered, similar to NPT threads, but they have different pitches, so there is a slight difference in the sealing method.

O-ring face seal
The O-ring face seal(ORFS)has a groove at the top of the fitting thread end that allows the O-ring to be installed. When the fittings are tightened, the O-ring and the top of the other fitting will fit together tightly to form a seal and prevent leakage.
Tapered Face Seals
Tapered seals are divided into flare-type seals, 24° tapered seals, 30° tapered seals, and compression seals.
| 24° internal chamfer | DIN/Metric | ||
| 30° internal chamfer | BSPP | NPTF/NPSM | |
| 30° external flare | Komastu | JIS | |
| 37° external flare | JIC | Metric/GB | |
| 45° external flare | SAE 45° | AN 45° | |
| Flat | ORFS/ORB | Metric | BSPT |
Flared face seal
Flare face is also called chamfer or flare. The raised tapered face of the male thread is the flare seat, and the recessed face of the female thread is the inverted flare. When female and male threads are used together, the contact surfaces of the two will fit tightly, creating a hard metal-to-metal seal. Hydraulic fittings commonly have 37° tapered cone faces and 45° tapered faces, and the internal and external threads of these fittings can be installed to form a flared face seal.

24° tapered seal
The 24° taper seal is a composite seal. It is a combination of a metal-to-metal hard seal and a metal face with an O-ring elastic seal. The fitting end is a metric fine thread with a 24° flare (seal bevel angle). This sealing structure is the German standard and is suitable for components with strict requirements for pressure-resistance capacity and sealing capability. This tarped seal can withstand different levels of pressure. Depending on the pressure-resistance capacity, these fittings are classified as light or heavy-duty.

30° cone seal
The 30° tapered seal has a metric fine thread or British pipe thread with a groove on the male end and a metric fine thread with a 30° taper on the female end, which requires an O-ring. This sealing structure is mostly used for the connection between the valve body and connector, and the hydraulic system pressure measuring port.

Compression seal
The external thread of the compression seal is a 24° female taper and the internal thread is also a 24° male taper, and the two are clamped to each other by means of a ferrule. There are also one-piece and two-piece ferrule fittings, with one and two ferrules respectively. This structure is the same as the 24° cone (compound seal) internal cone, and the two internal cone fittings can be used interchangeably.

Other Sealing Methods
Teflon Tape
Teflon tape is made of Polytetrafluoroethylene film and is commonly white. This tape is wrapped clockwise around the male threads of the hydraulic fitting and then installed together with the female threads. However, Teflon tape is only suitable for some hydraulic systems. If Teflon tape is used in the wrong place, it is hard to form a seal and may even cause pieces of tape to contaminate the hydraulic fluid.

Thread Sealants
Liquid sealants can be applied to the metal surface of the fitting to fill in scratches. And defects on the fitting surface, preventing displacement and leakage. Thread sealants can be used on all-metal fittings to improve the sealability of the fitting.
Sealants are not normally supplied with metal fittings, except for DOT air brake fittings, so you should ask the manufacturer in advance before using a sealant.

How to Seal Hydraulic Fittings
All fittings only need to be installed correctly following the steps to ensure a seal.
First, clean the fitting surface
It would help if you made sure that the fitting surface and the installation area are clean and that there are no contaminants affecting the sealing effect.
Second, inspect the fitting
You need to check the fitting for damage. Then replace it with a new one immediately if there is any damage.
Then, choose the sealant
Generally, metal-to-metal sealed and O-ring sealed fittings do not require additional sealant. However, if you need to use sealant, choose the right sealant and use it with your fitting.
Next, install the fitting
When installing the fittings, either by hand or with the help of tools, make sure that the fittings are installed in place. But don’t install it too tightly, as this may cause the fitting to deform.
Finally, check carefully
The last step is also the most important one, you need to carefully check whether the installation is in place and whether it produces leaks. If you find any problems with the fitting seal, reinstall it again.
Conclusion
When selecting various sealing forms of fittings, be sure to consider the pressure, temperature, and compatibility of the environment in which they will be used. Regardless of the sealing form of the fitting, you must install the hydraulic fitting according to professional standards to ensure that the sealing will not fail and to ensure the safety of the hydraulic system.
FAQ
Which seal type works best?
Use O-rings (NBR/FKM material) for dynamic connections and Teflon tape/paste for tapered threads (NPT/BSPT). Match seal hardness (70-90 Shore A) to pressure.
How to prevent overtightening?
Follow torque specs (e.g., 1/2″ JIC = 85-100 Nm) – overtightening deforms sealing surfaces by 0.1mm can cause leaks.
Should I reuse seals?
Never reuse O-rings/seal washers – 95% of reinstallation leaks come from compromised seals.
How to seal parallel threads?
Use bonded seals (Dowty washers) or sealing collars for BSPP/SAE straight threads (ISO 8434-2 standard).
Why do flared fittings leak?
Clean 37° JIC/45° SAE flare surfaces with lint-free cloth – microscopic debris causes 60% of flare connection failures.
When to use thread locker?
Apply anaerobic sealant (Loctite 545) only on dry male threads for vibration-prone NPT/BSPT connections – avoid on flared/O-ring fittings.
Topa Blog
Find out more about Topa Blog and learn more about specialized hydraulic fittings.