Whether controlling the flow of water in a home or managing the flow of oil in a manufacturing plant, the right valve ensures optimal performance, safety, and efficiency. When it comes to choosing a valve for your system, one of the most common decisions you’ll face is selecting between ball valves and butterfly valves.
Overview of Ball Valves
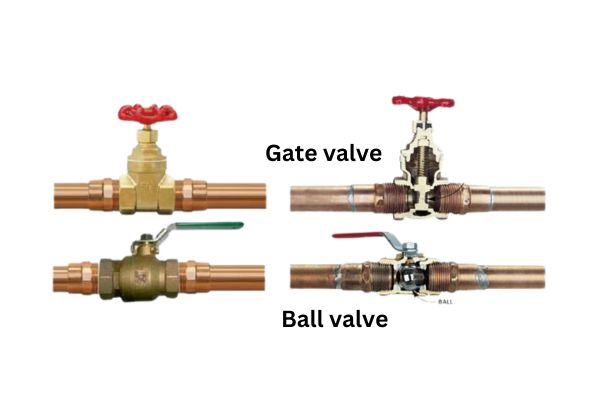
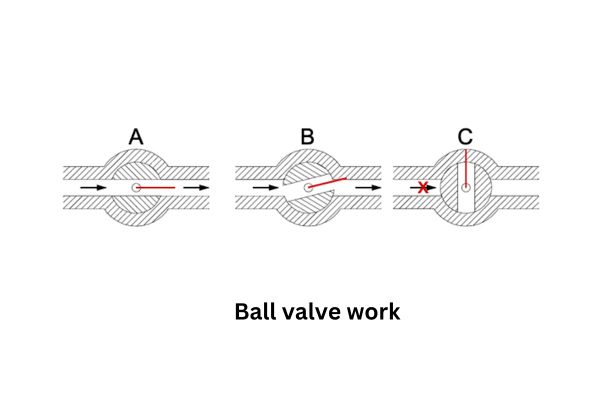
A ball valve is a valve designed primarily for on/off control of fluid flow. This type of valve uses a spherical ball with a hole (known as a bore or port) through the center, which rotates within the valve body to either allow fluid to pass through or block it entirely. When the hole aligns with the inlet and outlet ports, fluid flows freely; when it is rotated 90 degrees, the flow is completely shut off. Ball valves are known for their quick and reliable shutoff capabilities, making them essential in applications where stopping or starting flow quickly is crucial.
Basic Construction
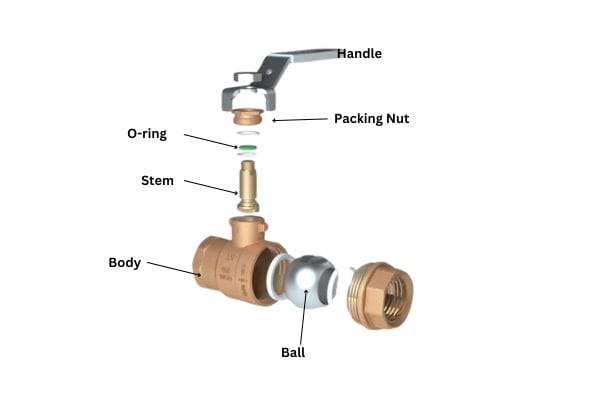
The ball valve’s construction includes several key components that work together to provide durable and efficient fluid control:
Valve Body: This outer shell houses the ball and other components, providing structural integrity.
Ball: The spherical core with a hole through the center controls the flow. The ball is usually made of stainless steel or other durable materials to withstand pressure and corrosion.
Seats: Positioned around the ball, these sealing rings ensure a tight shutoff when the valve is closed, minimizing leakage.
Stem: This component connects the ball to the actuator or handle, enabling rotation to open or close the valve.
Handle or Actuator: A handle (for manual operation) or actuator (for automated systems) is used to rotate the stem, which in turn rotates the ball.
This design allows for quick shutoff and minimal leakage, as the ball forms a tight seal against the seats when closed.

Types of Ball Valves
Ball valves come in several types, each suited for specific applications based on pressure requirements, flow control needs, and environmental factors.
Floating Ball Valve:
In a floating ball valve, the ball is not fixed but instead “floats” between two seats. Fluid pressure on the upstream side pushes the ball against the downstream seat, creating a seal when the valve is closed.
These valves are generally best suited for low- to medium-pressure applications and are commonly found in systems that require reliable shutoff but do not operate at very high pressures.
Trunnion-Mounted Ball Valve:
Unlike floating ball valves, trunnion-mounted ball valves have additional support at the top and bottom of the ball, stabilizing it within the valve body. These trunnions (pivot points) reduce the pressure load on the ball and seat, making the valve suitable for high-pressure applications.
Trunnion-mounted ball valves are typically used in larger pipeline systems, such as those in the oil and gas industry, where high pressures and larger valve sizes require a more stable design.
V-Port Ball Valve:
V-port ball valves have a V-shaped notch in the ball, allowing for more precise control of flow rate. As the valve opens, the flow through the V-shaped opening gradually increases, providing better throttling control than standard ball valves.
These valves are ideal for applications where flow needs to be modulated rather than simply turned on or off. They are used in industrial processes requiring precise control over fluid flow.
Working Principle
The ball valve operates by rotating the ball within the valve body to open or close the flow path. When the handle or actuator is turned 90 degrees, the ball rotates so that the hole aligns with the inlet and outlet ports, allowing fluid to pass through. This quick, quarter-turn action makes ball valves efficient for applications where fast on/off control is essential.
For applications requiring throttling, V-port ball valves allow for partial rotation, where the V-shaped notch in the ball controls the flow more precisely. However, standard ball valves are not typically recommended for throttling, as they lack the gradual control needed for fine adjustments.
Applications
Ball valves are versatile and used across numerous industries due to their robust design and ease of use. Common applications include:
Natural Gas Pipelines: Ball valves are often used in gas pipelines for their reliability and ability to handle high pressures. The quick shutoff capability is crucial for safety in gas applications.
Water Systems: In water treatment and distribution, ball valves control flow and provide shutoff for maintenance, repair, and isolation purposes.
Industrial Processes: Ball valves are widely used in manufacturing plants to control fluids, gases, and chemicals within systems, especially where high reliability and durability are required.
HVAC Systems: Ball valves are employed in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to regulate water flow or refrigerants, providing efficient control for temperature regulation.
Advantages of Ball Valves
Ball valves are favored for several reasons that make them ideal in various demanding applications:
Quick Shutoff: The quarter-turn operation allows for rapid and reliable shutoff, essential for emergency situations.
High Reliability: With fewer moving parts and a simple design, ball valves are durable and require minimal maintenance, reducing operational costs over time.
Minimal Leakage: The tight seal formed by the ball and seats minimizes leakage, ensuring efficient operation and preventing fluid loss.
Suitable for High-Pressure Applications: Trunnion-mounted ball valves, in particular, can withstand high pressures, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications like oil and gas pipelines.
Limitations of Ball Valves
Despite their many advantages, ball valves also have some limitations:
Throttling Limitations: Standard ball valves are not designed for throttling and may not provide precise control over flow rate. V-port ball valves offer improved throttling, but they are still limited compared to specialized throttling valves like globe valves.
Larger Size and Higher Cost: Ball valves, especially in larger diameters, tend to be bulkier and more expensive than other valve types, such as butterfly valves. This can make them less suitable for applications where space and budget are major constraints.
Overview of Butterfly Valves
A butterfly valve is a flow control device widely used to regulate or isolate fluid flow in various industrial and residential applications. It uses a flat, rotating disc mounted on a shaft, which pivots within the valve body to either allow or restrict flow. Butterfly valves are known for their compact design and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for large-diameter pipelines and applications where space and budget are primary considerations.
The core function of a butterfly valve is to regulate flow through a relatively simple mechanism. When the disc is fully rotated to align with the pipe, it allows fluid to flow freely; when turned perpendicular to the flow, it blocks it. Butterfly valves are often preferred for their ease of installation, quick operation, and efficiency in controlling moderate to large fluid flows.
Basic Construction
A butterfly valve has three primary components:
Valve Body: This outer casing houses the internal components and provides structural support for the valve. It is designed to fit between two pipe flanges in the system.
Disc: The disc, also called the vane, is the central component responsible for regulating flow. When rotated, the disc either allows fluid to pass through or blocks it.
Shaft: The shaft connects the disc to the actuator or handle, enabling the rotation needed to open or close the valve.
This straightforward design reduces the number of moving parts and makes butterfly valves easier to maintain compared to other valves with more complex constructions.

Types of Butterfly Valves
Several types of butterfly valves are available, each designed for specific applications based on factors like installation requirements, pressure, and flow control needs:
Wafer Type Butterfly Valve:
Wafer-type butterfly valves are designed to fit snugly between two pipe flanges without requiring additional support bolts. They rely on the surrounding pipeline for stability and are often held in place by flange bolts.
This type of valve is commonly used where a simple, lightweight design is needed and is ideal for systems with limited space. However, wafer valves cannot isolate the downstream side of the system, which can be a limitation in certain applications.
Lug Type Butterfly Valve:
Lug-type butterfly valves feature threaded lugs around the valve body, allowing it to be bolted directly to flanges on either side. This design enables one side of the pipeline to be disconnected while maintaining a seal on the other side, allowing for more versatile maintenance.
Lug valves are frequently used in systems where sections of the pipeline need to be isolated, offering a secure and stable connection that makes them suitable for moderate-pressure applications.
Flanged Type Butterfly Valve:
Flanged butterfly valves have flanges on either side of the valve body, which bolt directly to flanged pipes, providing a secure and tight seal. This type is ideal for larger piping systems, as it offers increased stability and leak resistance.
Flanged butterfly valves are commonly used in large-scale water, wastewater, and industrial systems where a reliable, sturdy connection is essential.
High-Performance Butterfly Valve:
High-performance butterfly valves are specifically designed to handle high-pressure and high-temperature applications. They often feature special materials like metal seats and reinforced disc designs, making them capable of withstanding extreme conditions.
These valves are ideal for demanding applications, such as in the oil and gas industry, where durability and resilience are critical.
Working Principle
The operation of a butterfly valve is straightforward and relies on the rotation of the disc to control fluid flow. When the disc is rotated so that it is aligned with the flow direction, fluid passes through with minimal obstruction. When the disc is turned perpendicular to the flow path, it blocks the fluid, effectively stopping the flow.
This design differs from ball valves, which use a spherical ball to control flow. Unlike ball valves, butterfly valves require only a quarter turn (90 degrees) to move from fully open to fully closed, enabling fast operation. However, while butterfly valves can be used for throttling, they generally lack the precise flow control offered by specialized throttling valves.

Applications
Butterfly valves are versatile and found in various applications where space efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and moderate flow control are priorities. Common uses include:
Water Treatment: Butterfly valves are widely used in water treatment plants for their ease of installation, low cost, and ability to handle large volumes of water.
HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, butterfly valves regulate water and air flow efficiently.
Large Pipelines: For large-scale pipeline systems in industries such as chemical processing, power generation, and wastewater treatment, butterfly valves offer a compact and effective solution for flow control.
Industrial Applications: Butterfly valves are also common in many industrial processes, especially where space and weight considerations are crucial, as in certain marine and automotive applications.
Advantages of Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves are known for several distinct advantages:
Space-Saving Design: Butterfly valves are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for installations where space is constrained.
Cost-Effective: Compared to other types of valves, butterfly valves are generally more affordable, especially for large systems. Their simple design also reduces maintenance costs.
Suitable for Moderate to Large Flow Systems: Butterfly valves are efficient at handling high flow rates, making them suitable for applications that require large volumes of fluid movement with minimal pressure drop.
Limitations of Butterfly Valves
Despite their advantages, butterfly valves have some limitations:
Higher Leakage Potential: Butterfly valves, particularly wafer and lug types, may have a higher potential for leakage than ball valves. This can be a concern in systems where zero leakage is critical.
Less Precise Throttling Control: While butterfly valves can be used for throttling, they do not offer the same level of precise flow control as valves specifically designed for modulation, like globe or V-port ball valves. The disc’s design creates turbulence, which can limit fine control.
Performance Comparison: Ball Valves vs Butterfly Valves
Flow Control
Ball Valves: Ball valves are primarily designed for on/off control. The valve’s ball has a single hole or port through the center, which allows fluid to pass when aligned with the inlet and outlet. A quick 90-degree rotation of the ball provides complete shutoff, making ball valves highly effective in applications requiring quick isolation. However, throttling capabilities are limited in standard ball valves, as they are not optimized for partial flow adjustments. Attempts to throttle with a ball valve can lead to wear on the valve seats and reduce the lifespan of the valve.
While V-port ball valves offer some throttling functionality by allowing the ball to rotate partially, they still lack the precision and gradual control of valves designed specifically for throttling. This makes ball valves ideal for systems that prioritize fast, reliable shutoff over precise flow modulation.
Butterfly Valves: Butterfly valves, in contrast, are well-suited for flow modulation. Their disc-shaped design allows for incremental opening and closing, which provides better control over fluid flow than ball valves. The disc’s position can be adjusted to allow more or less fluid through, making butterfly valves effective in applications that require throttling. As a result, butterfly valves are commonly used in large systems where continuous flow adjustments are necessary, such as in water treatment plants and HVAC systems.
However, butterfly valves may not offer as tight shutoff as ball valves. They can still achieve a reasonable level of flow control and are preferred when systems require large flow capacities with moderate throttling.
Pressure and Temperature Handling
Ball Valves: Ball valves excel in high-pressure applications due to their design, which includes strong seals and fewer moving parts. Trunnion-mounted ball valves, in particular, are designed to handle high pressures by stabilizing the ball with trunnion supports at the top and bottom. This added stability distributes pressure more evenly, making them suitable for systems with extreme pressure levels, such as natural gas pipelines or oil refineries.
In terms of temperature, ball valves can generally handle a broad range. However, the specific tolerance depends on the valve material. Stainless steel and metal-seated ball valves can endure higher temperatures, whereas plastic or rubber-seated options are suitable only for low-temperature applications.
Butterfly Valves: Butterfly valves are typically used in moderate-pressure systems but can handle high pressures when designed as high-performance butterfly valves. These valves use reinforced discs and specialized materials like metal seats to withstand higher pressures and temperatures. High-performance butterfly valves are often used in industrial applications, including power plants and oil refineries, where both pressure and temperature resistance are necessary.
However, standard butterfly valves are not typically used in extreme conditions. While they are effective at handling moderate pressures and temperatures, their performance can decline in applications that involve sudden changes in pressure or temperature. In general, butterfly valves provide a cost-effective solution for moderate pressure and temperature environments.

Sealing and Leakage
Ball Valves: One of the significant advantages of ball valves is their ability to create a tight seal, which minimizes leakage. When the ball is rotated into the closed position, it presses against the valve seats, forming a tight seal that effectively prevents fluid from passing through. This characteristic is crucial in applications requiring zero leakage, such as in chemical processing or high-pressure pipelines. Additionally, ball valves are less prone to leakage even after extended use, which enhances their reliability in long-term operations.
However, the effectiveness of the seal depends on the valve’s design and material. For example, soft-seated ball valves (using materials like PTFE) offer excellent sealing for low to moderate pressure but may be less effective in high-temperature applications. Metal-seated ball valves, while more durable in extreme temperatures, may allow minimal leakage when compared to soft-seated options.
Butterfly Valves: Butterfly valves are generally more prone to higher leakage potential compared to ball valves, especially in larger diameters. The disc, when turned to the closed position, may not create a seal as tight as a ball valve, particularly in standard models. This is due to the disc’s position within the flow path, which may not always fully block fluid when high pressure is exerted on the downstream side.
While high-performance butterfly valves improve sealing capabilities by incorporating stronger materials and tighter seats, they still may not achieve the same leak-tight seal as ball valves. For applications where even minimal leakage is unacceptable, ball valves would generally be a better choice.
Flow Efficiency
Ball Valves: Ball valves offer excellent flow efficiency with minimal pressure drop when fully open. The straight-through design of the ball, when aligned with the flow, allows fluid to pass with very little resistance. This is especially important in systems where maintaining flow rate and pressure consistency is essential, as minimal resistance leads to reduced energy consumption and better overall efficiency. Ball valves are often chosen for high-flow applications where a smooth and unrestricted passage is necessary.
However, when partially open, ball valves can create turbulent flow due to the shape of the ball. This turbulence can lead to wear on the valve components and may reduce flow efficiency in throttling applications. As a result, ball valves are best suited for applications requiring fully open or fully closed positions rather than partially open positions.
Butterfly Valves: Butterfly valves are also efficient in terms of flow rate and pressure drop, but their performance varies based on the valve’s position and the fluid characteristics. When fully open, butterfly valves have a low-pressure drop similar to ball valves, as the thin disc provides minimal obstruction to flow. This makes them effective in large piping systems where energy efficiency is important.
In throttling applications, butterfly valves maintain better flow efficiency than ball valves due to their streamlined design. However, the disc remains in the flow path even when the valve is fully open, which can create some resistance, especially in high-flow situations. Despite this, butterfly valves are generally more energy-efficient than ball valves in applications requiring continuous flow regulation.
Conclusion
When choosing between ball and butterfly valves, consider the specific needs of your system. If your application requires a tight seal, high-pressure handling, and quick shutoff, a ball valve is likely the better choice. For moderate pressure systems where space efficiency and cost-effectiveness are priorities, especially in large-diameter pipelines, butterfly valves may be ideal.
FAQ
What’s the main difference between ball valves and butterfly valves?
Ball valves provide tight on/off control with minimal leakage, while butterfly valves offer better flow modulation and are more compact, making them ideal for large systems.
Which valve type is better for high-pressure applications?
Ball valves are generally better for high-pressure applications due to their robust sealing capabilities, especially trunnion-mounted ball valves.
Can butterfly valves handle throttling applications?
Yes, butterfly valves are suitable for throttling and offer good flow modulation, especially in large systems, though they may be less precise than specialized throttling valves.
Are ball valves more leak-proof than butterfly valves?
Yes, ball valves provide tighter sealing and are typically more effective at minimizing leakage than butterfly valves.
Which valve is more cost-effective?
Butterfly valves are generally more cost-effective, especially in larger sizes, making them ideal for budget-sensitive, large-scale applications.
How do I choose the right valve type for my system?
Consider factors like pressure, space, flow control needs, and budget.