Thread galling is a type of wear that occurs when two metal surfaces, particularly those with fine threads, adhere to each other during movement or assembly. This phenomenon is primarily caused by friction and heat, leading to the transfer of material between the surfaces. This damage can compromise the integrity of threaded fittings. Commonly seen in stainless steel applications, thread galling can significantly impact the performance and longevity of hydraulic systems.
What is Thread Galling?
A. Explanation of the Phenomenon
Thread galling occurs when two metal surfaces, particularly those that are threaded, come into contact and experience excessive friction. This friction generates heat, which can cause localized melting and adhesion between the surfaces. As a result, material from one thread may transfer to the other, leading to rough spots, deformation, or even complete failure of the threads. This phenomenon is especially problematic in applications involving tight tolerances, where even minor wear can compromise functionality.
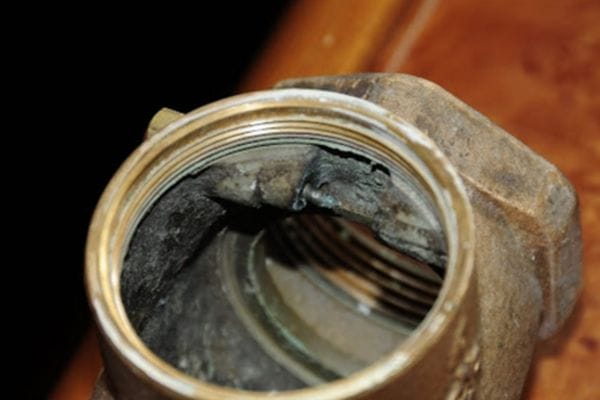
Galling is often characterized by visible signs such as scoring, pitting, or material loss, which can manifest as grooves or rough surfaces on the threads. It can occur during assembly, disassembly, or even during the operation of a hydraulic system, significantly affecting the reliability and safety of the components involved.

B. Mechanisms Behind Thread Galling
The mechanisms of thread galling are primarily attributed to two factors: material properties and mechanical conditions. When metals with similar properties come into contact, especially under high load and inadequate lubrication, the likelihood of galling increases.
Friction and Heat Generation: As the surfaces slide against each other, friction generates heat, which can soften the material at the contact points. This softening reduces the material’s resistance to adhesion, leading to galling.
Mechanical Interlocking: The microscopic surface textures of metals can create points of interlocking. Under sufficient pressure, these points can fuse together, further promoting the transfer of material from one surface to another.
Environmental Factors: Factors such as contamination, corrosion, and the presence of foreign particles can exacerbate galling. When contaminants enter the threaded interface, they can create additional wear and tear, accelerating the galling process.
Stress Concentration: High-stress areas in threaded joints, especially in tapered threads like NPT (National Pipe Thread), are more susceptible to galling. The geometry of these threads can concentrate stress, increasing the likelihood of adhesion and material transfer.
C. Common Materials Affected
Thread galling is predominantly observed in certain materials, with stainless steel being the most commonly affected. Its popularity in hydraulic systems stems from its corrosion resistance and strength. However, specific grades of stainless steel, particularly austenitic types like 304 and 316, are more prone to galling due to their ductility and work-hardening properties.
Other materials that can experience galling include:
Aluminum: While lighter and often used in hydraulic applications, aluminum can gall easily due to its softness compared to steel.
Bronze: This material, often used in marine applications, can also be susceptible to galling under certain conditions, especially in threaded joints.
Nickel-Based Alloys: Although these materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, they can also suffer from galling, particularly in high-load applications.
Risks Associated with Thread Galling
A. Impact on Fitting Integrity and Performance
Thread galling poses significant risks to the integrity and performance of hydraulic fittings. As galling damages the threads, it can lead to several issues that compromise the effectiveness of the hydraulic system:
Loss of Sealing Capability: Damaged threads can disrupt the tight fit required for effective sealing. This can result in leaks, which not only reduce system efficiency but can also lead to fluid loss and contamination.
Increased Friction: Galling creates rough surfaces that increase friction between threaded components. This heightened friction can result in higher torque requirements for assembly and disassembly, complicating maintenance and increasing the risk of further damage.
Thread Deformation: As galling progresses, it can cause threads to deform, rendering them unusable. Deformed threads may no longer fit properly with mating components, necessitating costly replacements or repairs.
Compromised Load-Bearing Capacity: The structural integrity of fittings is crucial for their ability to withstand operational pressures. Galling can weaken the threads, reducing the load-bearing capacity and increasing the likelihood of catastrophic failure under stress.
B. Long-term Implications for Hydraulic Systems
The long-term implications of thread galling extend beyond immediate damage to fittings. Over time, the cumulative effects can lead to severe operational challenges:
Increased Downtime: Frequent leaks or failures due to galling necessitate regular maintenance, leading to increased downtime for repairs. This downtime can disrupt operations, particularly in critical applications where hydraulic systems play a vital role.
Higher Maintenance Costs: The need for frequent repairs and replacements contributes to rising maintenance costs. Organizations may incur significant expenses in labor and replacement parts, impacting their overall budget and operational efficiency.
System Reliability Issues: As galling worsens, the reliability of the hydraulic system diminishes. Operators may face unexpected failures, leading to safety concerns and potential hazards, particularly in high-stakes environments like manufacturing and construction.
Impact on System Performance: The overall performance of the hydraulic system can be compromised due to inefficient fluid flow and pressure loss. This can affect productivity and lead to suboptimal functioning of hydraulic machinery.
Identifying Thread Galling
A. Symptoms and Signs of Galling
Identifying thread galling early is crucial for preventing further damage to hydraulic systems. The symptoms and signs of galling can vary, but common indicators include:
Visible Damage: Look for noticeable scoring, scratches, or gouges on the threaded surfaces. These physical signs can indicate material transfer and degradation of the threads.
Thread Deformation: Galling can cause threads to become distorted or misaligned. If the threads appear flattened or uneven, this could signal the onset of galling.
Increased Torque Requirements: If assembly or disassembly requires significantly more force than usual, it may indicate that galling has occurred. Higher friction levels resulting from damaged threads can lead to this phenomenon.
Fluid Leaks: One of the most critical signs of galling is the presence of fluid leaks. If a fitting that previously sealed well starts to leak, galling may have compromised its integrity.
Difficulties in Assembly: If components are challenging to thread together or become stuck, this may be due to galling. This is especially true if the issue arises after previous successful assemblies.
B. Tools and Methods for Inspection
Various tools and methods can assist in the inspection for thread galling, enabling early detection and remediation:
Visual Inspection: A simple yet effective method, visual inspection can reveal obvious signs of damage. Use magnifying glasses or borescopes for better visibility of threaded areas.
Calipers and Micrometers: Precision measuring tools like calipers and micrometers can assess thread dimensions. Any significant deviations from standard measurements may indicate galling.
Torque Wrenches: Utilizing a calibrated torque wrench can help determine if increased resistance is present during assembly. Monitoring torque values can identify abnormal behavior associated with galling.
Thread Gauges: These gauges can assess the integrity of threads by checking for wear or deformation. They can help identify whether the threads meet specification standards.
Ultrasonic Testing: For critical applications, ultrasonic testing can detect internal flaws and material integrity issues without disassembling components. This non-destructive testing method can be invaluable for identifying potential problems before they lead to failure.
Dye Penetrant Testing: This method involves applying a penetrant dye to the surface of the threads. After a period, a developer is applied, which highlights cracks or defects, helping to identify areas affected by galling.

C. Comparison with Other Forms of Thread Damage
While thread galling is a specific form of damage, it can be confused with other types of thread issues. Understanding the differences is essential for accurate diagnosis:
Thread Wear: Unlike galling, which involves material transfer between surfaces, thread wear is typically due to abrasion over time. Wear can manifest as smooth, rounded edges rather than the rough, torn appearance associated with galling.
Thread Stripping: Stripping occurs when threads are stripped away entirely, often due to excessive force or torque. This results in a loss of engagement rather than the material transfer seen in galling.
Corrosion: Corroded threads may appear pitted or rough due to chemical reactions rather than mechanical wear. Corrosion can lead to thread weakening, but it is distinct from the physical adhesion and transfer characteristic of galling.
Cross-Threading: This occurs when threads are misaligned during assembly, leading to damaged threads. The result is usually visible misalignment and deformation, but it does not involve the material transfer seen in galling.
Prevention Strategies
A. Proper Torque Application and Guidelines
Proper torque application is critical in preventing thread galling, as excessive or inadequate torque can lead to various issues. Following established guidelines can help ensure optimal performance:
Torque Specifications: Always adhere to manufacturer-recommended torque specifications for threaded connections. These specifications are designed to achieve the right balance of tightness without over-stressing the materials involved.
Use of Torque Wrenches: Employ calibrated torque wrenches to apply consistent and precise torque. Digital torque wrenches can provide real-time feedback, reducing the likelihood of human error.
Incremental Tightening: For larger assemblies, apply torque in increments. This allows for an even distribution of pressure across all threads, minimizing the risk of galling.
Regular Calibration: Regularly calibrate torque wrenches to ensure accuracy. Miscalibrated tools can lead to incorrect torque application, increasing the chances of galling.
Training and Best Practices: Train technicians on the importance of proper torque application. Implementing best practices in assembly can significantly reduce the risk of thread galling.
B. Importance of Alignment During Assembly
Proper alignment during the assembly of threaded components is crucial to prevent galling:
Thread Engagement: Misalignment can lead to improper thread engagement, which increases friction and stress on the threads. Ensure components are aligned accurately to facilitate smooth engagement.
Use of Alignment Tools: Employ alignment tools such as guide pins or jigs to ensure proper positioning of components before tightening. This can help prevent misalignment and the subsequent risk of galling.
Visual Checks: Conduct visual inspections during assembly to confirm that components are aligned correctly. Any visible misalignment should be addressed before proceeding to avoid undue stress on the threads.
Gentle Hand Tightening: Initially hand-tighten fittings to ensure proper alignment before using tools. This helps avoid misalignment and excessive friction during the final tightening phase.
C. Selecting Compatible Materials and Coatings
Choosing the right materials and coatings can play a significant role in preventing thread galling:
Material Compatibility: Select materials that are less likely to gall when in contact. For example, pairing stainless steel with brass or using gall-resistant alloys can reduce the risk of galling.
Surface Treatments: Coatings such as nickel plating or anodizing can improve the wear resistance of threaded components, minimizing the likelihood of galling. These treatments can provide a smoother surface, reducing friction during assembly.
Material Selection: Consider using materials specifically designed for high-stress applications. Alloys that incorporate elements like molybdenum or tungsten can enhance resistance to galling.
Testing for Galling Resistance: Before selecting materials, conduct tests to evaluate their galling resistance under expected operational conditions. This proactive approach can help ensure long-term reliability.
D. Use of Lubricants and Thread Sealants
Lubricants and thread sealants are essential tools in the prevention of thread galling:
Thread Lubricants: Apply appropriate thread lubricants to reduce friction during assembly. Lubricants create a film that minimizes direct metal-to-metal contact, decreasing the chances of galling.
Selection of Lubricants: Choose lubricants compatible with the fluids used in the hydraulic system. Ensure that the lubricant can withstand the operational temperature and pressure conditions.
Thread Sealants: Use thread sealants to enhance sealing and reduce the potential for leaks. Sealants can also provide a buffer against friction, further minimizing galling risks.
Application Techniques: Apply lubricants and sealants uniformly across the threads to ensure even coverage. Inconsistent application can lead to localized high-friction areas, increasing the likelihood of galling.
Regular Maintenance: Incorporate regular checks and maintenance of lubricants and sealants within the maintenance schedule. Over time, lubricants can degrade, so it’s essential to ensure they are replenished as needed.
Remedies for Existing Galling Issues
A. Repair Techniques for Damaged Threads
When thread galling occurs, prompt and effective repair is essential to restore the integrity of the fittings:
Cleaning the Threads: Start by thoroughly cleaning the affected threads to remove any debris, metal shavings, or lubricant residue. Use a wire brush or thread cleaning tool to ensure that the threads are clear of contaminants.
Re-Tapping: For minor galling, re-tapping the threads with a tap of the same size can help restore functionality. This technique involves carefully cutting new threads into the damaged area, effectively smoothing out rough spots. It’s important to ensure that the tap is aligned correctly to avoid further misalignment.
Heli-Coil Inserts: If the damage is more severe, consider using Heli-Coil inserts. These inserts can provide a new threaded surface within the existing hole, allowing for the re-establishment of secure connections. Proper installation of Heli-Coils requires careful drilling and tapping to accommodate the insert.
Welding or Brazing: In cases where threads are extensively damaged, welding or brazing may be necessary to build up the damaged area. Once the area has been repaired, it can be re-threaded to restore its original functionality. This technique is typically more labor-intensive and requires skilled workmanship.
Professional Services: For critical components, it may be prudent to engage professional repair services that specialize in hydraulic fittings. These experts can assess the damage and recommend appropriate repair solutions.
B. When to Replace Fittings vs. Repair
Determining whether to repair or replace damaged fittings depends on several factors:
The extent of Damage: If the galling is superficial and limited to a small area, repair techniques such as re-tapping or using inserts may be sufficient. However, if the damage is widespread, replacing the fitting may be more effective.
Safety Considerations: In high-stakes applications, the integrity of hydraulic fittings is paramount. If there’s any doubt about the safety of a repaired fitting, replacement is the safer option. Always prioritize safety over cost savings.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluate the costs associated with repair versus replacement. Sometimes, the expense of repairs, particularly when factoring in labor and downtime, can exceed the cost of a new fitting. A thorough cost analysis can guide the decision-making process.
Long-Term Reliability: Consider the long-term reliability of repaired versus new fittings. If the fitting is crucial to system performance and safety, investing in a replacement may be more prudent to avoid future issues.
Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding repairs. Some manufacturers may recommend against repairing specific components due to safety or performance concerns.
C. Best Practices for Future Prevention
To mitigate the recurrence of thread galling, it’s essential to implement best practices:
Regular Maintenance: Establish a routine maintenance schedule that includes inspections of threaded connections. Early detection of wear or damage can prevent more severe issues down the line.
Documentation of Issues: Maintain records of any galling incidents, repairs made, and conditions under which they occurred. This documentation can help identify patterns and inform future prevention strategies.
Training and Awareness: Train personnel on the importance of proper assembly techniques and the risks associated with thread galling. Creating awareness can help ensure adherence to best practices.
Material Selection Reviews: Regularly review the materials used in threaded connections. Ensure that the selected materials are appropriate for the operational environment and are less prone to galling.
Conclusion
The potential for thread galling emphasizes the need for continuous education and improvement within the industry. With advancements in materials and technologies, professionals have access to better solutions to mitigate the risks associated with galling. This is not only a matter of operational efficiency but also of adhering to safety standards and best practices that protect personnel and assets.
FAQ
What is thread galling?
Thread galling is a form of wear that occurs when two metal surfaces in contact cause material transfer, leading to thread damage and potential failure in hydraulic systems.
What are the common signs of thread galling?
Signs of thread galling include visible scoring or scratches on threads, increased torque requirements during assembly, fluid leaks, and thread deformation.
How can I prevent thread galling?
Prevention strategies include proper torque application, ensuring alignment during assembly, selecting compatible materials, and using lubricants or thread sealants.
When should I repair or replace a fitting affected by galling?
Repair minor damage through re-tapping or inserts, but consider replacement if the damage is extensive or if safety is a concern.
What tools are useful for inspecting thread galling?
Useful tools include visual inspection aids, calipers, thread gauges, torque wrenches, and ultrasonic testing equipment.
Why is addressing thread galling important?
Addressing thread galling is crucial for maintaining the integrity, safety, and efficiency of hydraulic systems, preventing costly downtime, and ensuring reliable operation.