Hydraulic Fittings Types: The Ultimate Guide
Table of Contents
Introduction
The core advantage of hydraulic systems lies in their ability to provide high power density and variable force and motion control. Hydraulic fittings are critical components within hydraulic systems, serving as connectors between hoses, tubes, and other components. Understanding the different types of hydraulic fittings is crucial for ensuring system integrity, performance, and safety. Incorrect fitting selection or installation can lead to leaks, system failures, and potential safety hazards. Therefore, a comprehensive knowledge of hydraulic fittings helps in maintaining the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of hydraulic systems.
What are Common Hydraulic Fittings Types?
Common hydraulic fittings types include threaded fittings (NPT, BSP, JIC, SAE), flare fittings (37-degree and 45-degree), O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings, quick connect fittings, compression fittings, and crimp fittings. Each type serves specific purposes, such as ensuring secure connections, preventing leaks, and facilitating easy assembly and disassembly. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right fitting for your hydraulic system, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Main Types of Hydraulic Fittings
Threaded Fittings and Hose Fittings
Threaded Fittings:
Threaded fittings are characterized by their external and internal threads, which allow them to be screwed together with corresponding threaded components. These fittings are commonly made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, and brass, and are often used in stationary hydraulic systems for their strong and secure connections. They are typically utilized in applications where the components need to be disassembled and reassembled for maintenance or repairs.
Hose Fittings:
Hose fittings connect flexible hydraulic hoses to various system components. These fittings usually have a barb or a ferrule that grips the hose securely. They are designed to absorb movement and vibration, making them ideal for mobile applications where flexibility is crucial. Hose fittings are often made from materials like brass, stainless steel, and other durable metals, ensuring they can withstand high-pressure environments and frequent movement.
Flare Fittings
Features and Use
Flare fittings are designed with a flared end that connects to a corresponding fitting, creating a tight, leak-proof seal. The flared end typically forms a conical shape, allowing the tubing to sit securely against the fitting. This design is particularly effective in high-pressure applications, where maintaining a robust seal is critical.
Types
37-degree Flare: The flared end forms a 37-degree angle.
Uses: Ideal for high-pressure hydraulic systems and compatible with JIC (Joint Industry Council) standards. Commonly used in industrial and military applications for their durability and reliability.
45-degree Flare: The flared end forms a 45-degree angle.
Uses: Frequently found in automotive and refrigeration applications. These fittings are suited for systems where the pressures are generally lower compared to those requiring 37-degree flare fittings. They are widely used in automotive fuel lines and refrigeration systems.
Tee and Cross Fittings
Tee Fittings:
Tee fittings have a T-shaped design with three openings: one inlet and two outlets. This configuration allows them to split a single flow into two separate flows or combine two flows into one. They are commonly used in hydraulic systems to branch off lines to different components or systems.
Cross Fittings:
Cross fittings feature a cross-shaped design with four openings: one inlet and three outlets. They are used in more complex hydraulic systems where multiple branching or merging of fluid lines is required. These fittings are essential for distributing fluid in multiple directions from a single source.
Flange Fittings
Flanged Hose Fittings:
Flanged hose fittings typically have a hose end on one end to securely attach to a hose and a flat end on the other end to install an O-ring. Flanges provide a stable connection and are ideal for high-pressure applications that require a firm and reliable seal.
Flange Connectors:
Flange connectors utilize a similar flat circular design with bolt holes, but are used to connect pipes or other components in hydraulic systems. They provide a strong, stable connection that ensures system integrity at high pressures.
Pressure range:
- 3000psi/Code 61: For medium pressure applications, providing a safe and reliable connection.
- 6000psi/Code 62: Designed for high pressure systems to ensure durability and leak-proof performance.
- 9000psi: For use in ultra-high pressure environments, providing superior strength and reliability for critical applications.
Compression Fittings
Components of the Compression Fitting
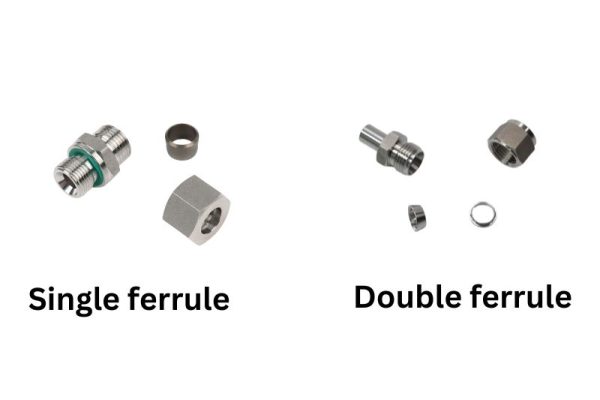
Compression fittings are composed of three primary parts: the body, the nut, and the ferrule(s).
- The Body: The body is the main structure of the fitting, featuring an inlet for the pipe or tube. It provides the foundation for the connection and typically includes internal threading to accommodate the nut.
- The Nut: The nut fits over the pipe and threads onto the body. As it tightens, it forces the ferrule(s) into the body, compressing them around the pipe. This action ensures a tight, leak-proof connection. The nut is usually hexagonal, allowing for easy tightening with a standard wrench.
- The Ferrule(s): Ferrules are ring-like components placed between the body and the nut. Depending on the type of fitting, there may be one (single ferrule) or two (double ferrule). When the nut is tightened, the ferrule(s) are compressed between the nut and the body, creating a seal by gripping the pipe. Ferrules are typically made from metal, such as brass or stainless steel, for durability and effective sealing.
Characteristics
Compression fittings are valued for their ability to create a reliable, leak-proof seal without the need for soldering or welding. They are used in various applications, including hydraulic, pneumatic, and plumbing systems, where ease of installation and maintenance is critical. Their design allows for the connection and disconnection of pipes and tubes without damaging the components, making them reusable and versatile.
Types
Single Ferrule:
- Characteristics: Single ferrule fittings have a simple design and are easy to install. They consist of one ferrule that compresses around the pipe as the nut is tightened.
- Uses: These fittings are suitable for low to medium-pressure applications where ease of installation is prioritized. Commonly used in household plumbing, low-pressure hydraulic systems, and basic pneumatic applications.
Double Ferrule:
- Characteristics: Double ferrule fittings provide a better seal with two ferrules, one in front and one in back. This design offers more secure connections by distributing the compressive force more evenly around the pipe.
- Uses: These fittings are more suitable for high-pressure applications, providing enhanced reliability and leak prevention. They are commonly found in high-pressure hydraulic systems, critical pneumatic systems, and in industries where safety and precision are crucial, such as chemical processing and oil and gas.
To install a compression fitting
Insert the Pipe: Insert the pipe into the fitting body until it reaches the internal stop.
Add the Ferrule(s): Place the ferrule(s) onto the pipe.
Tighten the Nut: Thread the nut onto the body and begin tightening. As the nut is tightened, the ferrule(s) are compressed between the nut and the fitting body, creating a tight, leak-proof seal.
Ensure Proper Compression: For double ferrule fittings, the rear ferrule helps the front ferrule to form a tighter seal by gripping the pipe and preventing movement.
Proper installation is critical to ensuring the integrity and efficiency of the connection. Over-tightening can damage the ferrules or pipe, while under-tightening can result in leaks. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for the best results.
Crimp Fittings
Crimp fittings are designed with a fitting body and a cylindrical metal sleeve that fits over the end of a hose. The sleeve, when crimped, ensures a permanent and secure connection. The fittings are typically made from durable metals like steel or brass, providing robustness and reliability for high-pressure applications.
Crimping Process
- Insert the Hose: Insert the end of the hose into the fitting body until it reaches the internal stop.
- Position the Sleeve: Slide the metal sleeve over the end of the hose.
- Crimp the Sleeve: Use a hydraulic crimping machine to compress the sleeve uniformly around the hose.
Reusable Hydraulic Hose Fitting
Components
Reusable fittings are designed to increase the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of hydraulic systems. These fittings consist of three main components:
Fitting Body: This section has a threaded end on one section and a hose end on the other, which is also threaded and can be fitted with a sleeve. It is usually made of durable metal to ensure longevity and resistance to high pressure.
Sleeve: The sleeve contains the threads and can be installed with the fitting body.
Typical Applications:
- Maintenance and Repair: In industries where hoses are frequently replaced or adjusted, such as maintenance workshops and service centers, reusable fittings offer a practical solution.
- Agriculture: Agricultural equipment, such as tractors and irrigation systems, often require hose adjustments. Reusable fittings allow for quick and easy replacements, ensuring minimal downtime.
- Construction: Construction machinery that operates in harsh environments can benefit from the versatility of reusable fittings, making it easier to manage hose replacements on-site.
Specialized Hydraulic Fittings
Swivel Fittings
Appearance:
Swivel fittings are characterized by their ability to rotate along one or more axes. They typically consist of two main parts: a rotating joint and a fixed part that connects to the hose or system. The rotating joint allows for 360-degree movement, making it easier to manage hose orientation and alignment.
Usage:
Swivel fittings are used in applications where hoses need to rotate or move frequently without causing kinks or stress on the connection points. They are commonly found in machinery and equipment that require dynamic movements, such as robotics, automotive applications, and heavy machinery.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Flexibility: Allows for greater movement and adjustment of hoses.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Minimizes the risk of hose damage due to twisting or bending.
- Improved Hose Life: Extends the lifespan of hoses by preventing kinks and stress at connection points.
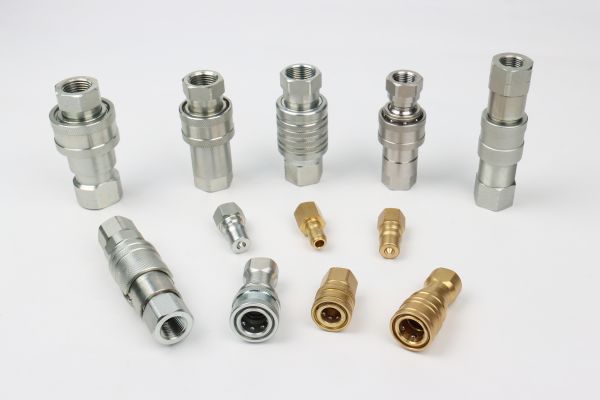
Quick Connections
Quick connections are designed for fast and easy connection and disconnection of hydraulic lines. They typically consist of a male and a female part that snap together securely without the need for tools.
Function:
Quick connections are used to simplify the process of connecting and disconnecting hydraulic hoses, especially in applications where frequent changes are necessary. They are ideal for use in mobile equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial settings.
Different Types of Hydraulic Quick Couplers
Push-to-Connect Couplers
These couplers allow for a quick and straightforward connection by simply pushing the two halves together. They typically have an automatic locking mechanism that ensures a secure connection.
Threaded Couplers
These couplers use threads to connect and secure the two halves. They provide a robust and leak-proof connection, suitable for high-pressure applications.
Flat Face Couplers
Designed with a flat face to minimize fluid loss during disconnection and to prevent the introduction of air and contaminants into the hydraulic system.
Ball Valve Couplers
Utilize a ball valve mechanism for quick and easy connection and disconnection. They are designed to withstand high pressures and provide a secure seal.
Bayonet Couplers
These couplers use a bayonet locking mechanism, similar to those found in electrical connectors, which requires a push-and-twist motion to lock.
Wing Nut Couplers
Feature wing nut-style handles that allow for easy manual tightening and loosening. They provide a secure connection without the need for additional tools.
Dry Break Couplers
Designed to prevent any fluid loss during disconnection. They feature a sealing mechanism that closes off the flow of fluid before the coupler is fully disconnected.
High-Flow Couplers
Engineered to handle high flow rates with minimal pressure drop. They often have larger internal diameters to accommodate the increased flow.
Dust Cap and Plug Couplers
Include dust caps and plugs to protect the coupler ends when not in use, preventing dirt and debris from contaminating the hydraulic system.
Bulkhead Fittings
Bulkhead fittings are specialized components designed to create a secure passage for hoses or pipes through walls, panels, or bulkheads. They typically feature a threaded body that allows for easy and secure installation.
Key Characteristics:
- Threaded Body: The threaded design enables easy mounting and secure fastening through walls or panels.
- Dual-Sided Connection: Provides connection points on both sides of the wall or panel, facilitating fluid transfer through enclosed systems.
- Durable Materials: Usually made from robust metals like brass, stainless steel, or plastic, ensuring long-lasting performance and resistance to corrosion.
Banjo Fitting
Banjo fittings are distinguished by their unique round, banjo-like shape. They consist of two main components:
Hollow Bolt: This component allows fluid to pass through its center.
Spherical Union: Attached to the hollow bolt, this part enables rotation and connection to the hose or other components, facilitating fluid flow even in tight or confined spaces.
Functions
Banjo fittings are primarily used to connect hoses to system components in areas where space is limited and conventional fittings are impractical. Their design allows for rotation and flexibility, making them ideal for complex hydraulic and fuel systems.
Common Applications:
- Fuel Systems: Used to ensure secure and leak-proof connections in fuel lines.
- Braking Systems: Essential in automotive and motorcycle braking systems for their ability to fit into tight spaces and provide reliable fluid transfer.
- Hydraulic Lines: Utilized in various hydraulic systems to connect hoses in confined areas while maintaining fluid integrity and pressure.
Types
Single Banjo: Features one fluid passage.
- Use Case: Typically used in systems where a single line needs to be connected, such as in standard fuel or brake line applications.
Double Banjo: Features two fluid passages.
- Use Case: Ideal for applications where multiple lines need to be connected simultaneously, such as complex hydraulic systems or dual fuel setups.
Grease Fitting
Grease fittings, also known as Zerk fittings, are small, standardized components used to facilitate the injection of lubricants into mechanical systems. They typically feature a ball check valve that allows grease to enter but prevents contaminants from escaping.
Key Characteristics:
- Ball Check Valve: Prevents backflow and contamination, ensuring that only clean grease enters the system.
- Standardized Size: Typically follow industry standards for thread size and shape, making them compatible with most grease guns.
- Material: Commonly made from durable metals such as steel or brass to withstand high pressures and resist corrosion.
Function
Grease fittings serve the critical function of maintaining the lubrication of moving parts within machinery and mechanical systems. Proper lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and prolongs the lifespan of components.
- Lubrication Point: Provides an access point for grease guns to inject lubricant directly into bearings, joints, and other moving parts.
- Contamination Prevention: The ball check valve design ensures that dirt and debris do not enter the lubrication system, maintaining the integrity of the lubricant and the components it protects.
- Ease of Maintenance: Facilitates regular maintenance and lubrication, making it easier to keep machinery operating smoothly and efficiently.
Classification
- Straight Grease Fittings: Feature a straight design for direct access.
- Angled Grease Fittings: Come in various angles, such as 45 degrees or 90 degrees.
- Flush Grease Fittings: Sit flush with the surface, providing a low-profile connection.
- Button Head Grease Fittings: Have a larger head designed for high-volume grease delivery.
- Drive-Type Grease Fittings: Driven into place rather than threaded, providing a secure fit without the need for threading.
Test Fitting
Test fittings are specialized components designed to facilitate the monitoring and testing of hydraulic systems. They typically feature ports or valves that allow for the connection of diagnostic equipment, such as pressure gauges or sensors, without disrupting the system’s operation.
Key Characteristics:
- Pressure Port: Provides an access point for measuring system pressure.
- Sealing Mechanism: Ensures a leak-proof connection when diagnostic tools are attached.
- Durability: Constructed from high-quality materials like stainless steel or brass to withstand high pressures and harsh environments.
- Compatibility: Designed to work with a range of diagnostic tools and sensors, adhering to industry standards for thread sizes and connection types.
Function
The primary function of test fittings is to accurately measure and monitor hydraulic system parameters, such as pressure and flow, without disassembling or disrupting the system.
- Pressure Monitoring: Allows for real-time measurement of system pressure, aiding in diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- System Testing: Facilitates the testing of hydraulic circuits and components to ensure they are operating within specified parameters.
- Maintenance: Provides an easy access point for routine system checks, helping to prevent failures and extend the lifespan of the system.
Choosing the Right Hydraulic Fitting
Factors to Consider
When selecting hydraulic fittings, several crucial factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the hydraulic system. These factors include pressure ratings, temperature compatibility, fluid compatibility, and application requirements.
Pressure Ratings:
- Consideration: Ensure the fitting can withstand the maximum operating pressure of the hydraulic system. Different fittings are rated for different pressure ranges.
- Importance: Using a fitting with an insufficient pressure rating can lead to failures, leaks, and potential system damage.
Temperature Compatibility:
- Consideration: Choose fittings that can operate effectively within the temperature range of the system’s environment and the fluid being used.
- Importance: Fittings that cannot handle extreme temperatures (either high or low) may degrade, causing leaks or failures.
Fluid Compatibility:
- Consideration: Ensure that the fitting material is compatible with the hydraulic fluid to prevent corrosion, swelling, or deterioration.
- Importance: Incompatible materials can lead to chemical reactions that weaken the fitting, resulting in leaks or system contamination.
Application Requirements:
- Consideration: Assess the specific needs of the application, including space constraints, movement, and environmental conditions (such as exposure to chemicals or harsh environments).
- Importance: Selecting fittings that match the application’s demands ensures the reliability and efficiency of the hydraulic system.
Compatibility with Hydraulic Hoses

Ensuring compatibility between hydraulic fittings and hoses is vital for maintaining system integrity and performance.
Matching Fittings with Hoses:
- Consideration: Use fittings that are designed to work with the specific type and size of hose in your system. Check manufacturer specifications for compatibility.
- Importance: Properly matched fittings and hoses prevent leaks, maintain pressure, and ensure a secure connection.
Importance of Correct Sizing:
- Consideration: Accurate sizing of fittings and hoses is essential to avoid issues such as leaks or reduced flow rates. Measure both the internal and external dimensions as specified by the manufacturer.
- Importance: Incorrect sizing can lead to fitting failures, inefficient system performance, and potential safety hazards.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes in the selection and installation of hydraulic fittings can save time, and money, and prevent system failures.
Misidentification of Threads:
- Mistake: Using the wrong thread type (e.g., NPT, BSP, JIC) can cause improper connections.
- Solution: Verify thread type using thread gauges and refer to manufacturer specifications to ensure correct identification.
Over-tightening or Under-tightening:
- Mistake: Over-tightening can damage threads and fittings, while under-tightening can result in leaks.
- Solution: Follow manufacturer torque specifications to achieve the correct tightness, using appropriate tools to avoid over or under-tightening.
Ignoring Material Compatibility:
- Mistake: Using fittings made from incompatible materials can lead to corrosion or degradation when exposed to certain fluids or environmental conditions.
- Solution: Check the chemical compatibility of fitting materials with the hydraulic fluid and environmental factors. Consult material compatibility charts and manufacturer recommendations.
Conclusion
In this guide, we covered the various types of hydraulic fittings. Each type has unique features, applications, and advantages, essential for maintaining system integrity and performance. By understanding the characteristics and uses of each fitting type, you can make informed decisions and enhance the reliability of your hydraulic systems. Apply this knowledge to optimize your hydraulic systems and ensure their safe and efficient operation.
FAQ
What are the most common types of hydraulic fittings?
The most common types of hydraulic fittings include crimp fittings, reusable fittings, quick-connect couplers, swivel fittings, banjo fittings, and bulkhead fittings.
What is the difference between crimp fittings and reusable fittings?
Crimp fittings provide a permanent connection using a crimping tool to secure the hose, while reusable fittings can be detached and reattached to new hoses, making them ideal for frequent hose changes.
What are quick-connect couplers used for?
Quick-connect couplers are designed for fast and easy connection and disconnection of hydraulic lines, commonly used in applications where frequent hose changes are required, such as in agricultural machinery and mobile equipment.
How do swivel fittings benefit hydraulic systems?
Swivel fittings allow for 360-degree rotation, reducing hose stress and preventing kinks, which enhances the flexibility and longevity of hydraulic hoses in systems with dynamic movements.
What is the purpose of a banjo fitting in hydraulic systems?
Banjo fittings are used to connect hoses to components in tight spaces, allowing fluid to pass through the fitting while enabling rotation, commonly found in fuel systems and braking systems.
Why are bulkhead fittings important in hydraulic applications?
Bulkhead fittings provide a secure connection point through walls or panels, ensuring a stable and leak-proof connection for hoses or pipes in tanks, reservoirs, and other enclosed systems.