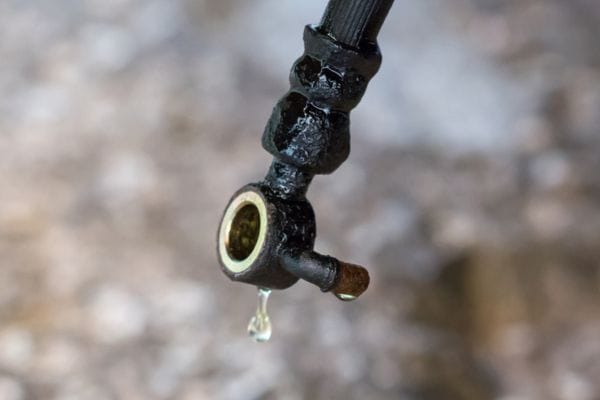
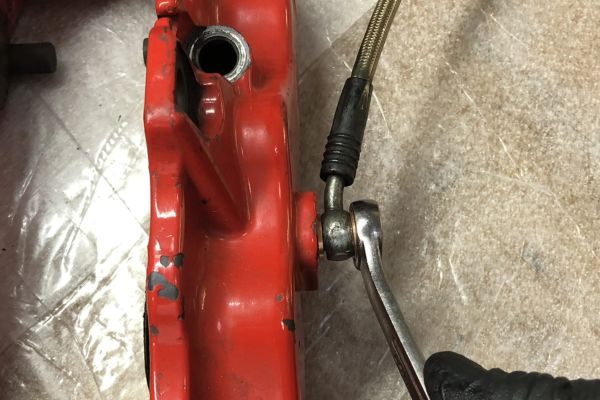
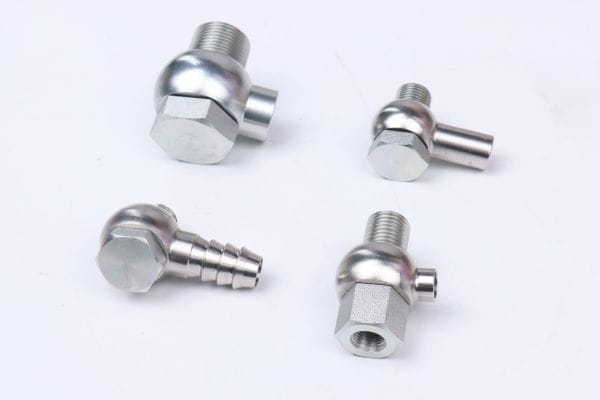
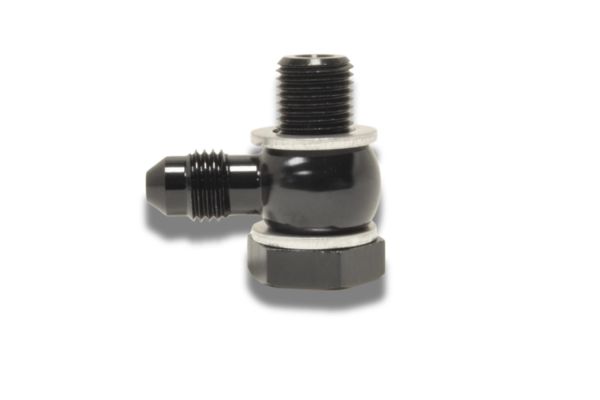
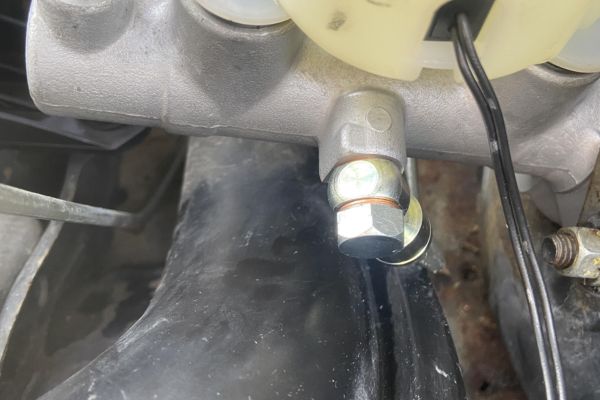
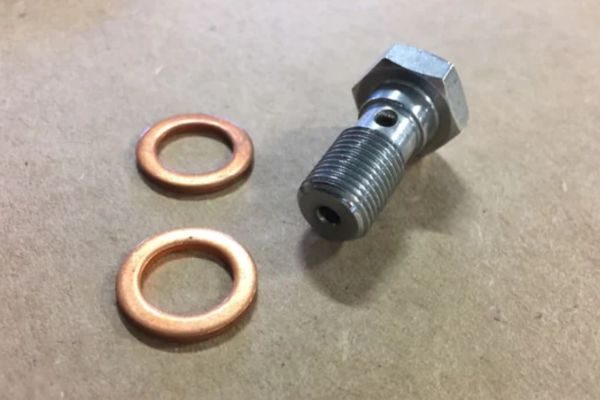
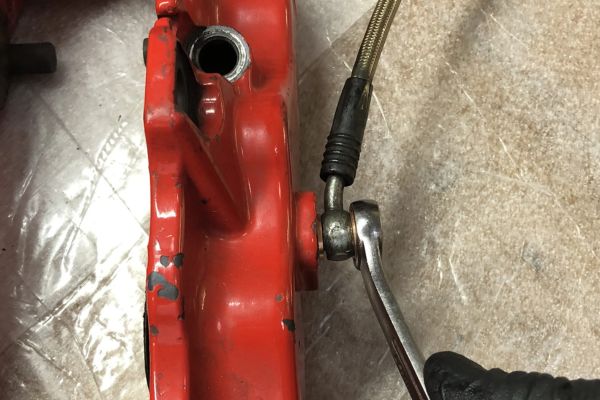
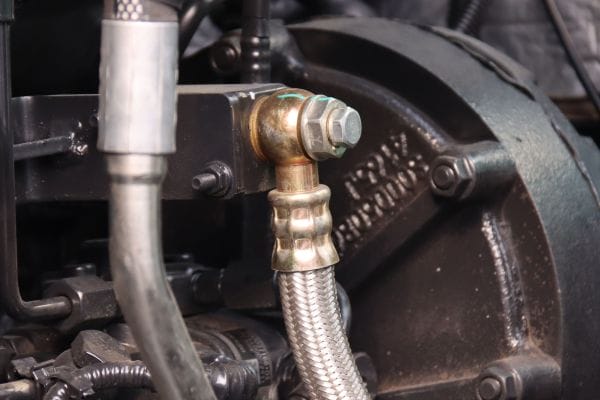
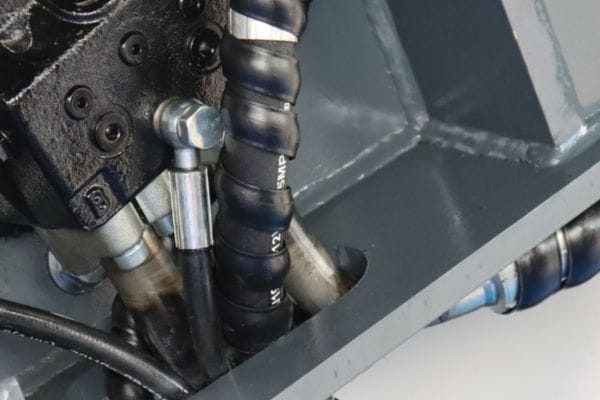
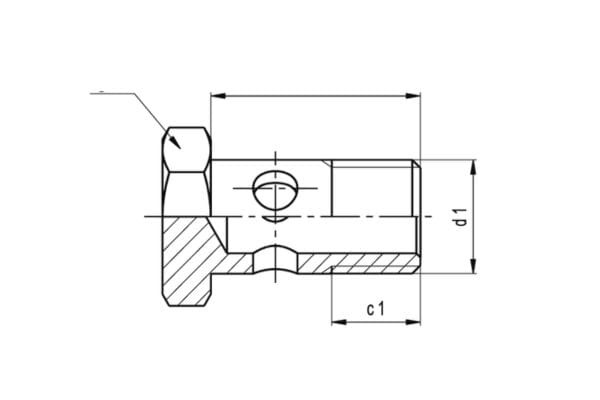
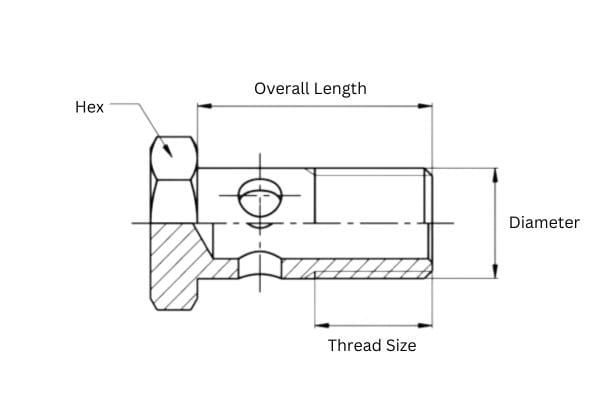
The purpose of the banjo fitting is to create a secure, leak-proof connection between hydraulic hoses and the equipment they’re attached to. It allows hydraulic fluid to flow from one part of the system to another while preventing spills or leaks. The banjo fitting’s design also enables tight, compact installations in areas with limited space, making it especially useful in complex machinery.
Key Components of a Hydraulic Hose Banjo Fitting
Understanding the banjo fitting structure
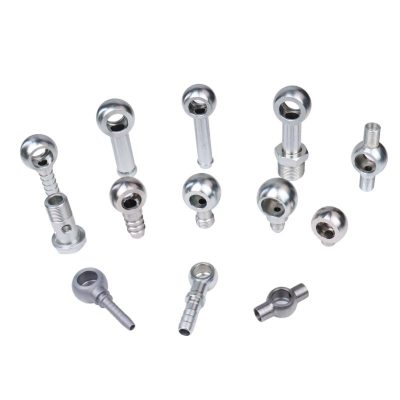
A hydraulic hose banjo fitting is a unique type of connector used in hydraulic systems. The fitting typically has a flat, circular design with a hole in the middle to allow hydraulic fluid to flow through. This structure is what gives it the “banjo” shape, which is similar to the body of a musical instrument. The fitting usually consists of three main parts:
Body: The main part of the banjo fitting, typically made of stainless steel, brass, or aluminum, that houses the hydraulic fluid passage.
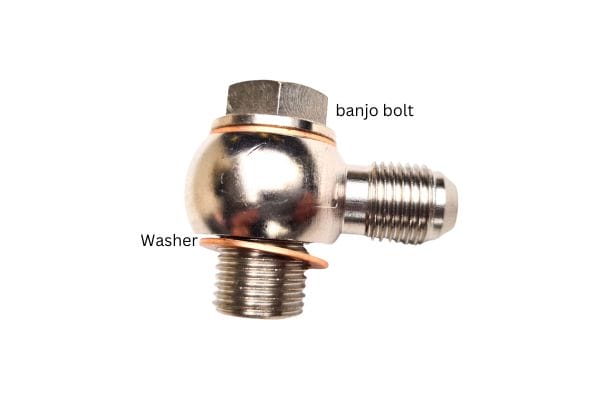
Bolt: A bolt runs through the center of the fitting, securing it to the connected components. It ensures a tight, leak-free seal when tightened to the correct torque specifications.
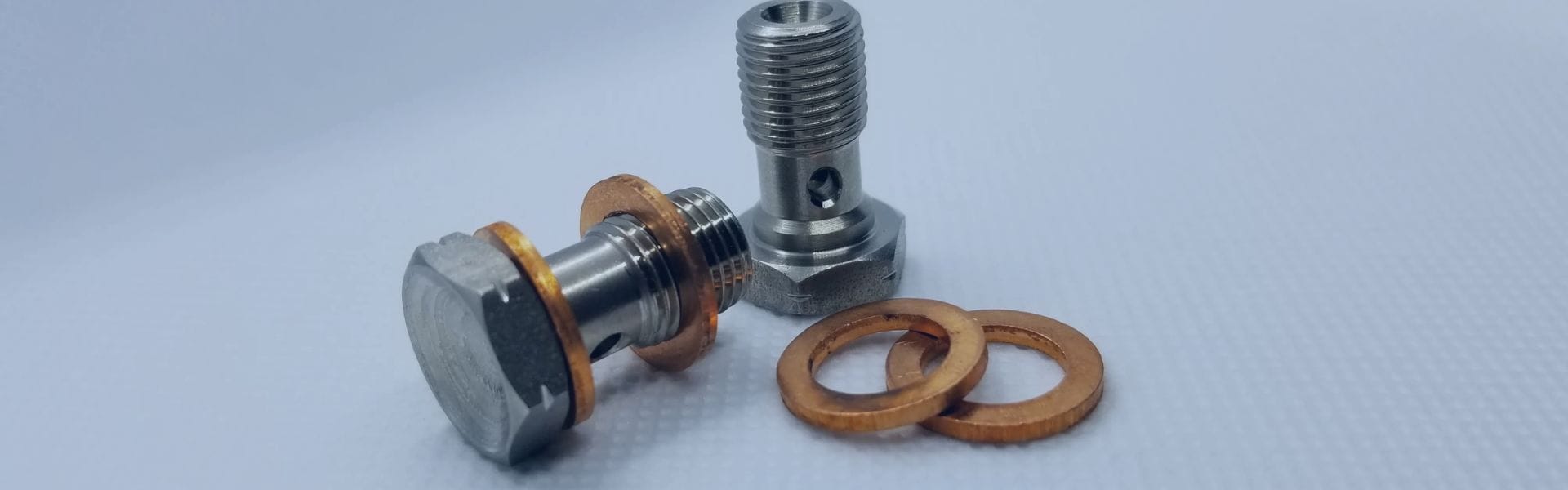
Sealing surfaces: The sealing surfaces, typically located on the fitting and the mating part (like a hydraulic flange or the hose itself), are critical for preventing fluid leaks. These surfaces may have an O-ring or a flat washer to help ensure a tight, secure seal.
This structure allows the banjo fitting to connect hoses and other hydraulic components even in tight spaces, where a traditional straight fitting may be difficult to install.
What is a banjo bolt and how it works
The banjo bolt is an essential part of the banjo fitting assembly. It is a specially designed bolt that passes through the center of the fitting and helps secure it to the hose or the equipment in the hydraulic system. The banjo bolt is crucial for:
Securing the fitting: The banjo bolt tightens the fitting into place, ensuring a secure connection between the hose and the equipment.
Allowing fluid flow: The bolt has a hole through its length, allowing hydraulic fluid to pass through it. This hole aligns with the central passage of the banjo fitting, enabling fluid transfer between the connected parts.
Creating a seal: When tightened, the bolt presses against the sealing surfaces of the fitting and the connected components, preventing fluid leaks.
How to Install a Hydraulic Hose Banjo Fitting
Preparing the hose and fitting for installation
Before beginning the installation of a hydraulic hose banjo fitting, it’s essential to properly prepare both the hose and the fitting to ensure a smooth and secure connection. Follow these steps:
Select the right hose: Ensure the hydraulic hose is the correct size, material, and pressure rating for the application. The hose should be compatible with both the fitting and the hydraulic system.
Cut the hose to the proper length: Measure and cut the hydraulic hose to the required length, ensuring it fits neatly between the components that will be connected.
Deburr the hose ends: After cutting the hose, use a deburring tool to smooth out any rough edges. This helps prevent damage to the fitting or seals during installation.
Inspect the fitting: Ensure the banjo fitting is clean, free from debris, and in good condition. Check for any cracks, wear, or signs of corrosion that could affect the connection’s integrity.
How to clean and inspect hydraulic components
Proper cleaning and inspection of hydraulic components, including the hose, fitting, and associated parts, are critical to prevent contamination and ensure the longevity of the hydraulic system. Here’s how to do it:
Clean the hose: Use a lint-free cloth and a solvent (approved for hydraulic systems) to clean the inside and outside of the hydraulic hose. Any dirt or debris left inside the hose can obstruct fluid flow and cause damage.
Inspect the fitting: Visually inspect the banjo fitting for any signs of damage, such as cracks, worn threads, or deformation. If the fitting is damaged or corroded, replace it before installation.
Check the sealing surfaces: Ensure that the sealing surfaces (such as the O-ring or washer) on both the fitting and the hose are intact. These surfaces need to be free from nicks, cuts, or debris to create a proper seal.
Inspect the banjo bolt: Check the banjo bolt for any damage, corrosion, or wear. A damaged bolt may not provide a secure connection or could lead to leaks.
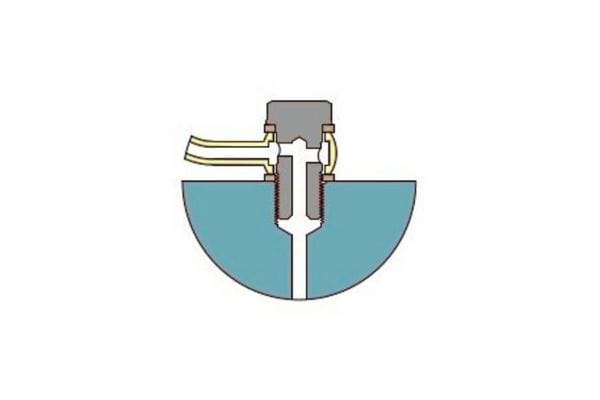
Attaching the banjo fitting to the hose assembly
Once you’ve prepared the hose and fitting, it’s time to attach the banjo fitting to the hose assembly. Follow these steps:
Align the fitting: Position the banjo fitting correctly over the hose end. Ensure that the sealing surfaces are properly aligned with the corresponding parts of the hose assembly. Be mindful of the fitting’s orientation to avoid twisting the hose during installation.
Insert the banjo bolt: Insert the banjo bolt through the center of the fitting and the hydraulic hose. The bolt should pass through the fitting and the hose end and align with the threaded hole on the connecting equipment or component.
Add sealing washers or O-rings: If your banjo fitting requires sealing washers or O-rings, place them on either side of the fitting to ensure a secure, leak-proof connection. Some banjo fittings use metal sealing washers, while others rely on rubber O-rings to form the seal.
Position the assembly: Gently position the entire assembly into place on the equipment or component you’re connecting to. Ensure that the fitting is aligned and properly seated to prevent stress on the hose and fitting.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Installing a Banjo Fitting
Installing a hydraulic hose banjo fitting might seem straightforward, but even small mistakes during the process can lead to system failure, leaks, or reduced performance. Here are some of the most common mistakes to avoid when installing a banjo fitting:
Over-tightening or Under-tightening the Banjo Bolt
One of the most critical steps in installing a banjo fitting is tightening the banjo bolt to the correct torque. Over-tightening or under-tightening the bolt can lead to serious issues.
Over-tightening: If you apply too much torque to the banjo bolt, it can damage the threads on the fitting or the bolt, strip the connection, or cause excessive pressure on the sealing surfaces. This may lead to cracks, leaks, or even breakage of the bolt. Additionally, over-tightening can distort the hose, leading to stress fractures and ultimately reducing its lifespan.
Under-tightening: On the other hand, not tightening the banjo bolt enough can result in a loose connection. This creates gaps between the sealing surfaces, which can lead to hydraulic fluid leaks, loss of pressure, and compromised performance of the hydraulic system. Under-tightening also increases the risk of the banjo bolt loosening over time due to vibrations or pressure changes.
Failing to Properly Align the Hose
Improper hose alignment is another common mistake during the installation of a banjo fitting. If the hose is not properly aligned, it can cause several issues:
Twisting the hose: If the hose is twisted when the fitting is installed, it can create internal stress within the hose, leading to premature wear, hose failure, or restricted fluid flow. Twisting the hose also increases the risk of leaks due to poor fitting alignment.
Incorrect fitting orientation: If the banjo fitting is not aligned correctly with the attached equipment or hose, it can cause excessive pressure on the connection, leading to leaks, component damage, or performance issues. The hose may also rub against other parts of the machine, causing abrasion and wear over time.
Kinks and bends: A poorly aligned hose can also result in sharp bends or kinks in the hose. These issues can restrict fluid flow and damage the hose, reducing system efficiency.
Ignoring Sealant and Sealing Techniques
Hydraulic systems rely heavily on sealing to maintain pressure and prevent leaks. Failing to use the correct sealant or ignoring sealing techniques can result in poor sealing, fluid leaks, or compromised system performance.
Using the wrong sealant: It’s essential to use the right sealant or gasket material to ensure a secure, leak-free connection. Some banjo fittings require O-rings, while others may use metal washers or gaskets. Using the wrong type of sealant can lead to improper sealing and leaks under high pressure.
Improper installation of seals: Even when the correct sealant is used, improper installation can lead to seal failure. If the O-ring, gasket, or washer is not seated properly or is damaged during installation, it won’t form a proper seal. This could result in leaks, reduced fluid pressure, or system failure.
Over-tightening seals: Some people believe that over-tightening the banjo fitting will improve the seal, but this can damage the sealant material. Too much pressure can distort or tear O-rings and washers, leading to leaks and compromising the fitting’s performance.
Additional Tips to Avoid Installation Mistakes:
Check for debris: Always ensure the hose and fitting are clean and free from dirt, debris, or metal shavings before installation. These contaminants can damage the sealing surfaces and cause leaks or performance issues.
Verify fitting compatibility: Double-check that the banjo fitting is the right size and material for your hydraulic system. Using the wrong fitting can lead to leaks, poor performance, or even damage to your hydraulic equipment.
How to Ensure a Leak-Free Hydraulic Hose Banjo Fitting
Hydraulic systems depend on the ability to maintain pressure and avoid fluid loss. Even small leaks can lead to system inefficiency, increased maintenance costs, and safety hazards. Ensuring a leak-free hydraulic hose banjo fitting is critical to achieving optimal system performance and reliability. Here’s how to make sure your installation is airtight.
The Importance of Sealing in Hydraulic Systems
Sealing plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of a hydraulic system. In a hydraulic circuit, the goal is to create a closed-loop where fluid is transmitted under pressure from one component to another. Any leak, no matter how small, can:
Reduce system pressure: Leaks can cause a drop in the operating pressure, which affects the performance of hydraulic machinery.
Waste hydraulic fluid: Hydraulic fluid is costly, and any leak wastes precious resources. A leak also contaminates the work environment, leading to additional cleanup costs.
Cause safety hazards: Leaking hydraulic fluid can pose serious safety risks, especially in high-pressure systems. It can create fire hazards, contaminate equipment, and damage the surrounding environment.
Damage components: When fluid leaks out of a connection, air may enter the system, which can lead to cavitation, erosion, or even complete failure of hydraulic components.
Proper sealing ensures that hydraulic fluid is contained under pressure, optimizing the system’s performance and lifespan. This is why achieving a tight, secure seal in the hydraulic hose banjo fitting is so essential.
Using the Right Sealing Materials for Banjo Fittings
Selecting the appropriate sealing materials is a key step in ensuring a leak-free connection. Different sealing materials are designed to handle various pressures, temperatures, and fluid types. Here’s what you need to consider:
O-rings: Many banjo fittings use O-rings to create a tight seal between the fitting and the connected component. O-rings are made from materials like rubber, elastomers, or synthetic compounds that provide flexibility and excellent sealing capabilities. However, it’s essential to use the right O-ring material for the hydraulic fluid in use, as some materials degrade when exposed to certain chemicals or temperatures.
Material selection: Nitrile rubber (NBR) is commonly used for petroleum-based fluids, while Viton is ideal for higher temperatures or aggressive fluids. Fluorocarbon O-rings are often used for extreme chemical compatibility.
Sealing Washers: Some banjo fittings require metal or composite sealing washers instead of O-rings. These washers create a metal-to-metal seal and are often used in high-pressure applications. Copper washers are common because they are malleable and conform to surfaces easily, providing a reliable seal.
Ensure proper washer size: Always use washers that match the size of the banjo fitting and the corresponding mating part. A washer that is too large or too small can cause improper sealing and lead to leaks.
Thread Sealant or PTFE Tape: In some instances, thread sealants or PTFE tape (Teflon tape) may be used to help seal the threads of the banjo bolt. However, this is typically not needed for banjo fittings with sealing washers or O-rings. Overuse of sealant can also make it harder to achieve the correct torque and may interfere with proper sealing.
Use sparingly: When using thread sealant, make sure to apply a small amount to the threads only. Avoid getting sealant on the sealing surfaces, as it could prevent a proper seal and lead to leaks.
Gaskets: Some applications may require gaskets in addition to or instead of washers and O-rings. Gaskets are used to create a larger sealing surface and are typically made from rubber, cork, or fiber material. Gaskets help distribute the load more evenly across the sealing surfaces, reducing the risk of leaks.

Banjo Fitting Torque Specs for Leak Prevention
Applying the correct torque to the banjo bolt is crucial for ensuring a leak-free connection. Both over-tightening and under-tightening the bolt can cause leaks. Here’s how to get it right:
Manufacturer’s Torque Specifications: Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications for the banjo bolt. The correct torque ensures the fitting is tight enough to prevent leaks but not so tight that it damages the fitting or sealing components. These specifications are usually provided in foot-pounds (ft-lbs) or Newton-meters (Nm).
Typical torque range: Banjo bolts are typically torqued in the range of 20-60 ft-lbs, but it is crucial to verify the exact specifications for your specific fitting and application.
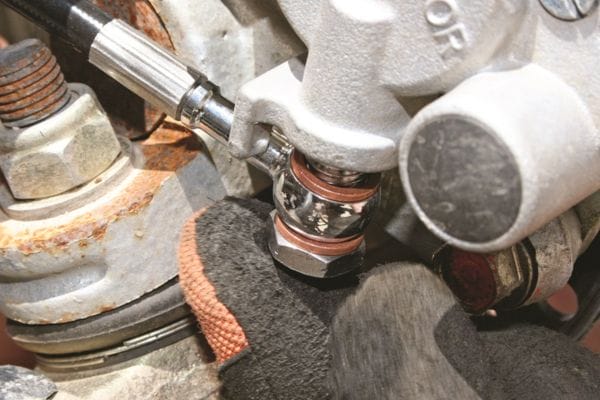
Use a Torque Wrench: To ensure that the correct torque is applied, always use a calibrated torque wrench. This tool allows you to apply the precise amount of force without over-tightening or under-tightening the bolt. It is the best way to achieve consistent, accurate torque across all connections.
Tighten in Steps: Rather than tightening the banjo bolt all at once, apply torque gradually in increments. Start by tightening the bolt slightly, then gradually increase the torque until it reaches the desired setting. This helps ensure that the sealant materials (such as O-rings or washers) seat properly without being over-compressed.
Check for Leaks After Installation: After tightening the bolt, always check for leaks. You can do this by applying a small amount of hydraulic fluid around the connection or using a leak detection fluid. If you notice any fluid seeping from the connection, stop and recheck the torque.
Re-torque if necessary: If the fitting leaks after initial tightening, it’s possible that the bolt wasn’t torqued enough or that the sealant material was not seated properly. Re-torque the bolt to the correct specification and check again.
Ensure Even Torque Distribution: When tightening the banjo bolt, make sure to apply pressure evenly. Uneven torque application can distort the fitting or damage the seals, increasing the likelihood of leaks.
Banjo Fitting Torque: Getting It Right for Optimal Performance
When it comes to hydraulic systems, banjo fitting torque is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and safety. Torque refers to the amount of rotational force applied to tighten the banjo bolt, which secures the fitting to the hydraulic hose and the corresponding equipment. Applying the correct amount of torque prevents leaks, maintains system pressure, and extends the life of the components.
Understanding the Correct Banjo Fitting Torque Specs
The correct torque specs for a banjo fitting depend on several factors, including the size and material of the fitting, the hose, and the hydraulic system. Each manufacturer will provide torque specifications tailored to their components, but here’s what you need to know to understand torque requirements:
Manufacturer Recommendations: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the specific banjo fitting you are using. These specifications will provide the exact torque range (usually in foot-pounds or Newton-meters) for the banjo bolt. For example, a typical torque spec might range from 20-60 ft-lbs, but it can vary depending on the application and fitting size.
Size of the Banjo Bolt: The torque specification often depends on the diameter and threading of the banjo bolt. Larger bolts typically require higher torque values, while smaller bolts require less force. Be sure to match the torque specification with the correct size of the bolt and fitting.
Material of the Fitting and Bolt: Banjo fittings and bolts come in various materials, such as stainless steel, brass, or carbon steel. Different materials require different torque values due to their varying strength and elasticity. For example, stainless steel fittings may require a lower torque setting compared to brass fittings to avoid over-stressing the components.
Operating Pressure: The operating pressure of the hydraulic system also plays a role in determining the correct torque. Systems that operate under higher pressure may require a tighter connection to prevent leaks or failure under load. Make sure to check if your system has specific requirements based on its operating pressure.
How to Use a Torque Wrench for Hydraulic Fittings
Using a torque wrench properly is key to achieving the correct torque when installing a banjo fitting. Here’s how you can ensure you apply the right amount of torque:
Choose the Right Torque Wrench: Select a calibrated torque wrench that’s designed for the torque range specified by the manufacturer. There are two main types of torque wrenches:
Click-type torque wrenches: These make a distinct “click” sound when the correct torque value is reached, alerting you that the desired force has been applied.
Beam-type torque wrenches: These are more basic and indicate the torque level using a dial or beam. However, they are less precise than click-type wrenches and may not be as reliable for critical applications.
Make sure the torque wrench is calibrated and in good working condition before use.
Set the Desired Torque: Adjust the torque wrench to the manufacturer’s recommended value. If you’re using a click-type torque wrench, simply turn the dial or knob to set the required torque in ft-lbs or Nm. If you’re using a beam-type wrench, ensure the beam is set to the correct reading before starting.
Tighten the Banjo Bolt: Place the torque wrench onto the banjo bolt and begin tightening. If you’re using a click-type wrench, keep turning until you hear the “click.” This sound means you have reached the correct torque. If using a beam-type wrench, carefully monitor the reading as you tighten and stop when you reach the recommended value.
Tighten Gradually in Steps: It’s best to tighten the banjo bolt in stages rather than all at once. Start by applying a small amount of torque, then increase it gradually in increments, tightening the bolt in a crisscross pattern if applicable. This ensures even pressure distribution across the sealing surfaces.
Avoid Over-Tightening: Be mindful not to exceed the recommended torque. Over-tightening can damage the fitting, bolt, or sealing materials, potentially leading to leaks or weakened connections.
Re-check the Torque: After you’ve torqued the banjo bolt to the specified value, it’s a good idea to double-check the torque, especially if the fitting has been subjected to any vibrations or stress after initial tightening. Reapply the torque wrench to ensure it’s still properly tightened.
Conclusion
Mastering the installation of a hydraulic hose banjo fitting will pay off by boosting your hydraulic system’s performance, reducing maintenance costs, and ensuring the safety of both equipment and personnel. By adhering to best practices and understanding the importance of proper installation, you’ll set yourself up for success in any hydraulic system application.
FAQ
What is a hydraulic hose banjo fitting?
A hydraulic hose banjo fitting is a type of connector used in hydraulic systems to link hoses to other components. It features a unique design with a banjo bolt and a hole in the fitting, allowing hydraulic fluid to flow through the connection while maintaining a tight seal.
Why is proper torque important for banjo fitting installation?
Proper torque ensures a leak-proof seal, prevents over-tightening or under-tightening, and helps maintain the integrity of the fitting and hose connection. Incorrect torque can lead to leaks, system inefficiency, or even component damage.
How do I know the correct torque for a banjo fitting?
The correct torque value for a banjo fitting is usually specified by the manufacturer. It can vary depending on the size, material, and application. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or product datasheets to find the exact torque specifications.
Can I use any sealant with banjo fittings?
It’s important to use the correct sealing material specified by the manufacturer, such as O-rings, washers, or gaskets. While some installations may require thread sealants, applying the wrong sealant can interfere with the fitting’s performance, so follow manufacturer recommendations.
What tools do I need to install a banjo fitting?
To install a banjo fitting, you’ll need basic tools such as a wrench for tightening the banjo bolt, a torque wrench to apply the correct torque, and cleaning supplies to ensure all components are free from debris before installation.
How can I check if the banjo fitting is properly installed?
After installation, check for leaks by applying a small amount of hydraulic fluid or using a leak detection solution around the connection. If you notice any leakage, recheck the torque and ensure that the fitting and sealing materials are properly aligned and seated.