Hydraulic Hose Fitting Types: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
Introduction
Hydraulic hose fittings act as the connectors that link hydraulic hoses to various system elements such as pumps, valves, cylinders, and other integral parts of a hydraulic circuit. Without these fittings, the transfer of hydraulic fluid would be inefficient, leading to potential system failures and decreased performance. Selecting the appropriate hydraulic hose fittings involves understanding various factors, including the type of threads, sealing methods, and compatibility with different fluids and environmental conditions.
Common Thread Types for Hydraulic Hose Fittings
NPT/NPTF (National Tapered Pipe/Fuel)
Appearance Characteristics
NPT (National Pipe Tapered) and NPTF (National Pipe Tapered Fuel) threads are characterized by their tapered design, which is a key visual feature. Unlike straight threads, the diameter of tapered threads decreases from the end of the fitting towards the beginning. This taper creates a wedging action as the male and female threads are tightened together. The taper typically follows a standard angle, making these fittings distinct and easily identifiable. When inspecting an NPT or NPTF fitting, you will notice that the thread peaks and valleys become progressively closer together towards the end of the fitting.
Sealing Method
The sealing method for NPT and NPTF threads relies primarily on thread deformation. As the tapered threads are screwed together, they deform slightly to fill the voids between the threads, creating a tight seal. This deformation is essential for achieving a leak-free connection. To further enhance the seal, it is common practice to use a thread sealant or tape, such as PTFE (Teflon) tape. The sealant fills in the microscopic gaps between the threads, preventing any fluid from escaping. This combination of mechanical deformation and sealant application makes NPT and NPTF threads highly effective in maintaining high-pressure hydraulic systems.
Country of Use
NPT and NPTF threads are predominantly used in the United States and Canada. They have become the standard for many industrial, commercial, and residential applications within these regions. This widespread adoption is due to their reliable performance in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and construction commonly utilize these fittings due to their robustness and ease of use. Moreover, the standards for NPT and NPTF threads are well-documented and widely accepted in North America.
NPT and NPTF threads are specified under various standards to ensure consistency and interchangeability. NPT threads are defined by the American National Standard Pipe Thread standards, often referred to as ANSI/ASME B1.20.1. On the other hand, NPTF threads are specified by the Dryseal Pipe Thread standards, which are designed to provide better sealing capabilities without the need for additional sealants. Despite these distinctions, both thread types share similar geometric characteristics, making them compatible in many applications. However, it is essential to select the correct type based on the specific requirements of the hydraulic system to ensure optimal performance and safety.
BSP (British Standard Pipe) Thread
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered)
External Characteristics: BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered) threads feature a tapered design similar to that of NPT threads. This taper means that the thread’s diameter decreases from the end of the fitting towards the beginning, creating a wedging action when the threads are tightened together. This tapering ensures a tighter fit as the threads are engaged, which is essential for forming a reliable seal. The taper angle for BSPT threads is 55 degrees, making it distinct from other thread types.
International Standard: The standard governing BSPT threads is ISO 7-1. This international standard ensures consistency and compatibility of BSPT fittings used across different regions and applications.
Sealing Method: BSPT threads seal primarily through thread deformation. As the tapered threads are screwed together, they deform slightly to fill any gaps between the threads, creating a tight and secure connection. This sealing method is effective in preventing leaks, especially in high-pressure applications. The wedging action produced by the tapering enhances the seal, making BSPT fittings reliable in various industrial and hydraulic systems.
Country of Use: BSPT fittings are used globally, with significant prevalence in Europe and Asia. They are a standard choice in many industries, including plumbing, hydraulic systems, and gas distribution.
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel)
External Characteristics: BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) threads differ from BSPT threads in that they maintain a consistent diameter along the length of the fitting. Unlike tapered threads, BSPP threads do not wedge together, which means they rely on additional sealing mechanisms to prevent leaks. The threads are parallel and feature a 55-degree flank angle, similar to BSPT threads but without the taper.
International Standard: BSPP threads are standardized under ISO 228-1. This standard ensures that BSPP fittings are compatible and can be used interchangeably in various applications worldwide.
Sealing Method: BSPP threads seal using a washer or an O-ring. The washer or O-ring sits between the mating faces of the fittings and is compressed to create a seal. This method is highly effective in preventing leaks and is preferred in applications where a reliable seal is critical. The use of a washer or O-ring also allows for easier disassembly and reassembly, which is beneficial in maintenance and repair operations.
Country of Use: BSPP fittings are used globally, especially in Europe and Asia. They are often preferred for their reliable sealing mechanism, which does not rely on thread deformation.
JIC (Joint Industry Committee) Thread
Appearance Characteristics
JIC (Joint Industry Committee) fittings are distinguished by their 37-degree flare seating surface. This flare is a critical design feature that ensures a secure and tight fit. The male fitting has a 37-degree flared end, which mates with a corresponding female fitting that has a matching 37-degree internal flare. This precise angle is crucial for the metal-to-metal sealing method that JIC fittings employ. When the male and female fittings are tightened together, the flared surfaces create a strong, leak-proof connection. The fittings are typically made of durable materials such as stainless steel or brass, which are chosen for their strength and corrosion resistance.
International Standard
The design and specifications of JIC fittings are standardized under SAE J514. This standard outlines the dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements for JIC fittings, ensuring compatibility and interchangeability across different manufacturers and applications.
Sealing Method
JIC fittings achieve their seal through metal-to-metal contact. The 37-degree flared surfaces of the male and female fittings form a seal when they are tightened together. This metal-to-metal sealing method is highly effective because it provides a large contact area, which distributes the pressure evenly and prevents leaks. The absence of additional sealing materials like O-rings or gaskets simplifies the design and reduces the risk of seal degradation over time.
Country of Use
JIC fittings are widely used in North America, where they have become a standard in many industries. Their reliability, ease of use, and ability to maintain a leak-free connection under high pressure make them a popular choice for various applications, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial hydraulic systems.
SAE Straight Thread
Appearance
SAE straight threads are characterized by their uniform diameter along the length of the fitting. Unlike tapered threads, SAE straight threads do not decrease in diameter and thus do not create a wedging action when tightened. Instead, they rely on a different sealing mechanism to ensure a leak-free connection. These fittings often include an O-ring, which plays a crucial role in the sealing process. The O-ring is typically seated in a groove on the male fitting, providing an additional layer of sealing integrity. The threads themselves provide mechanical strength, while the O-ring ensures the hydraulic fluid remains contained within the system.
International Standard
SAE straight threads are standardized under SAE J1926-1. This standard specifies the dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements for SAE straight thread fittings. Adhering to this standard ensures that fittings from different manufacturers are compatible and can be used interchangeably.
Sealing Method
The primary sealing method for SAE straight thread fittings involves an O-ring. The O-ring is positioned in a groove on the male fitting. When the male and female fittings are screwed together, the O-ring is compressed against the flat face of the female fitting. This compression creates a tight seal that prevents hydraulic fluid from leaking. The use of an O-ring is advantageous because it provides a reliable seal even under high pressure. Additionally, the O-ring can accommodate minor imperfections in the mating surfaces, ensuring a robust and leak-free connection.
ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) Thread
Appearance
ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal) fittings are distinctive due to their flat face design, which includes an O-ring situated in a groove on the face of the fitting. This flat face provides a large sealing surface area, which, when combined with the O-ring, ensures a reliable and robust seal.
International Standard
The specifications and dimensions for ORFS fittings are standardized under SAE J1453. This standard outlines the requirements for ORFS fittings, ensuring consistency and compatibility across different manufacturers. Adherence to this standard is crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of hydraulic systems that use these fittings. The SAE J1453 standard covers various aspects, including the material properties of the fittings and O-rings, dimensional tolerances, and performance under different pressures and temperatures.
Sealing Method
The primary sealing mechanism for ORFS fittings involves the compression of the O-ring. When the male and female fittings are joined, the O-ring on the flat face of the male fitting compresses against the flat surface of the female fitting. This compression creates a leak-free seal that can handle high pressures. The metal-to-metal contact between the flat faces provides structural support, while the O-ring ensures fluid containment. This sealing method is highly effective because it combines the strength of metal with the flexibility and sealing properties of the O-ring, making it suitable for both high-pressure and high-vibration environments.
Metric Thread
Appearance Characteristics
Metric threads often featuring either straight or tapered threads. The straight threads maintain a uniform diameter along the length of the fitting, while tapered threads gradually decrease in diameter, creating a wedging action when tightened. Metric threads are identified by their consistent pitch (the distance between threads) and diameter, which follow standardized measurements in millimeters.
International Standard
Metric fittings are standardized under several ISO norms to ensure consistency and interoperability. The key standards include:
ISO 6149: This standard covers metric threads for hydraulic fluid power systems and general use, specifying dimensions and performance requirements.
ISO 9974: This standard defines the specifications for metric adjustable and non-adjustable thread connectors.
DIN 2353: A German standard that specifies dimensions, design, and pressure ratings for metric thread fittings, widely adopted in Europe and other regions.
Adhering to these standards ensures that metric fittings from different manufacturers can be used interchangeably, providing flexibility and reliability in hydraulic systems.
Sealing Method
The sealing method for metric threads varies based on the type of thread and its application:
O-ring Seals: Many metric fittings use an O-ring seated in a groove on the male fitting, which compresses against the female fitting’s flat face. This method provides a reliable seal that can withstand high pressures and dynamic conditions.
Metal-to-Metal Contact: Some metric fittings rely on a metal-to-metal sealing method, where the threads themselves provide the seal through tight contact. This method is often used in applications where an O-ring might not be suitable, such as high-temperature environments or where there is a need for frequent disassembly and reassembly.
Classification
Metric threads are classified into three main series, each designed to handle different pressure capacities and usage scenarios:
Light Series (L): Suitable for lower-pressure applications, the light series fittings are used in less demanding environments.
Medium Series (M): These fittings are designed for medium-pressure applications and are commonly used in a wide range of hydraulic systems.
Heavy Series (S): Heavy series fittings are built to withstand high-pressure conditions and are used in the most demanding hydraulic applications, such as in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Country of Use
Metric fittings are predominantly used in Europe and Asia, where they are a standard choice for hydraulic systems and other applications. Their adoption in these regions is driven by the widespread use of the metric system and the standardized nature of the fittings, which ensures compatibility and ease of use.
Specialty Hose Fittings
Banjo Fitting
Banjo fittings feature a hollow, circular bolt that allows fluid to flow through it. The fitting typically consists of a hollow bolt with a spherical section and a mating socket. The bolt has an opening that aligns with a corresponding hole in the mating part, allowing fluid to pass through. This design not only enables 360-degree fluid transfer but also makes the fitting compact and ideal for tight spaces. The flat sealing surface on the bolt and the corresponding socket ensures a leak-free connection when tightened.
Barb Fittings
Exterior Features: Barb fittings have a distinctive barbed end designed to grip the inside of a hose. The barbs are ridged and tapered, allowing the hose to slide over them easily while providing a secure hold that prevents the hose from slipping off under pressure. These fittings are generally straightforward in design, featuring one or more barbs that increase in diameter away from the fitting base.
Material: Barb fittings are typically made from materials such as brass, stainless steel, or durable plastics. Brass and stainless steel are preferred for their resistance to corrosion and high strength, making them suitable for a variety of industrial applications. Plastic barb fittings, often made from materials like nylon or polyethylene, are used in less demanding, low-pressure applications due to their ease of installation and cost-effectiveness.
Bead Fittings
Bead fittings are identified by a prominent bead or raised ridge near the end of the fitting. This bead provides a positive stop for the hose when it is clamped in place, ensuring a secure connection. The body of the fitting is generally cylindrical, with the bead positioned strategically to prevent the hose from slipping off. This design makes bead fittings especially reliable for applications that involve high pressure or significant mechanical stress.
Additional Information
Specialty hose fittings are designed to meet the unique requirements of various applications, providing functionality and reliability where standard fittings may not suffice. Understanding the specific features and appropriate use cases for each type of specialty fitting is essential for optimizing the performance of hydraulic and fluid systems.
Banjo Fittings: These fittings are particularly useful in automotive and hydraulic systems where space is at a premium. Their ability to facilitate fluid flow in tight quarters makes them indispensable in fuel systems and brake lines.
Barb Fittings: Known for their ease of installation, barb fittings are commonly used in low-pressure applications such as irrigation systems, fuel lines, and air hoses. Their material versatility allows them to be used in a wide range of environments.
Bead Fittings: Bead fittings are designed for applications that require a highly secure connection, capable of withstanding high pressures and mechanical stresses. They are commonly used in HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and high-pressure hydraulic systems.
Identifying Hydraulic Hose Fittings
Measuring Techniques
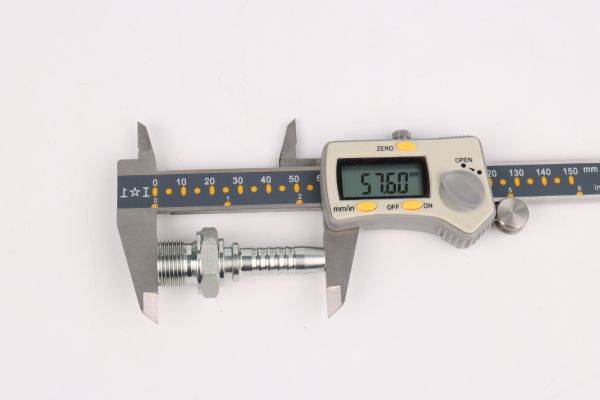

Thread Size: Measure the outside diameter of the thread using calipers. Place the caliper jaws on the outermost edges of the thread and read the measurement.
Diameter: Measure the inside diameter of the hose. Insert the caliper jaws inside the hose and expand until the jaws touch the inner walls. Record the measurement.
Pitch: Measure the distance between threads using a thread pitch gauge. Place the gauge teeth on the threads until they fit snugly with no gaps.
Tools Needed: Ensure you have calipers and thread pitch gauges to get accurate measurements.
Visual Recognition
Thread Shape: Observe the shape of the threads. Different types of fittings have unique thread patterns. For example, BSPT threads have a tapered profile, while BSPP threads are parallel.
O-rings: Check for the presence of O-rings, which are common in ORFS and some SAE fittings. The O-ring location and type can help identify the fitting.
Flare Angle: Look at the flare angle. JIC fittings have a 37° flare, while SAE fittings typically have a 45° flare. The flare angle can help distinguish between different fitting types.
Using Charts and Guides:
Manufacturer’s Charts: Utilize charts provided by manufacturers to match fitting specifications. These charts often include detailed diagrams and measurements that can help you identify the correct fitting.
Online Guides: Refer to online guides and resources. Many hydraulic fitting suppliers and manufacturers offer comprehensive guides that detail the specifications and identification techniques for various fittings.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of hydraulic hose fittings is essential to maintaining the efficiency and safety of hydraulic systems across multiple industries. By applying the knowledge gained in this guide, you can make informed decisions about hydraulic hose fittings to ensure optimal performance and safety of your hydraulic system. For more detailed information, be sure to contact Topa.
FAQ
What are the most common types of hydraulic hose fittings?
The most common types include NPT (National Pipe Tapered), BSP (British Standard Pipe), JIC (Joint Industry Council), SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) Straight Thread, ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal), and DIN Metric fittings.
How do I identify the correct hydraulic hose fitting?
Identification involves measuring the thread size (outside diameter), diameter (inside diameter of the hose), and pitch (distance between threads) using calipers and thread pitch gauges. Visual recognition, such as checking for unique features like thread shape and O-rings.
How do I prevent leaks in hydraulic hose fittings?
To prevent leaks, ensure that fittings are properly matched and correctly installed. Use the appropriate sealants, such as Teflon tape for tapered threads or O-rings for ORFS fittings. Regular maintenance checks to tighten loose fittings and replace worn seals can also help prevent leaks.
How do I properly install hydraulic hose fittings?
Proper installation involves ensuring that the fittings are clean and free from debris, using the correct tools, and following the manufacturer’s guidelines. It’s important to tighten fittings to the recommended torque to avoid leaks and damage.
What are the maintenance tips for hydraulic hose fittings?
Routine maintenance includes regularly inspecting fittings for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage, ensuring that all connections are secure, and replacing any worn or damaged components promptly.
What factors should I consider when selecting a hydraulic hose fitting?
Key factors include the pressure rating, fluid compatibility, environmental conditions (such as temperature and exposure to chemicals), and the specific application requirements.