The outer cover of a hydraulic hose is its first and most critical defense. This guide dissects the material science, compound engineering, and supplemental strategies that create a cover system capable of surviving the planet’s harshest environments.
The First Line of Defense: The Function of the Outer Cover
What looks like a simple black layer is actually the hose’s armor—a carefully engineered barrier that protects the inner reinforcement from mechanical damage and environmental attack. When the outer cover fails, it’s only a matter of time before the entire hose follows.

Protecting the Strength Members
Inside every hydraulic hose lies a network of steel wire or textile braid reinforcement, responsible for withstanding high internal pressure.
The outer cover’s first duty is to shield these strength members from moisture, oils, and chemicals.
Even a small cut or abrasion can expose the reinforcement to corrosion or degradation. Once rust begins, the hose’s ability to contain pressure declines rapidly, often leading to a dangerous burst or sudden hose failure.
A properly compounded and bonded cover acts as the first—and most vital—defense against this chain reaction.
A Sacrificial Barrier Against Abrasion
Hydraulic hoses often run along sharp edges, metal frames, or moving components. The outer cover is intentionally designed as a sacrificial layer, absorbing the friction, rubbing, and occasional impacts that occur during operation.
A high-quality cover doesn’t just resist wear; it wears predictably, providing visible signs of damage before deeper layers are affected.
This allows operators to identify abrasion issues early and replace the hose before internal damage occurs.
| Cover Type | Common Material | Abrasion Resistance | Typical Use Case |
| Standard Rubber (SBR/NBR) | Synthetic rubber blend | Moderate | General-purpose hydraulics |
| Tough Cover (TC) | Modified NBR compound | High | Mobile machinery, construction |
| Super Tough Cover (ST) | Special thermoplastic or advanced rubber | Very high | Extreme abrasion environments, mining, forestry |
Providing Environmental Resistance
Beyond mechanical wear, the outer cover serves as the hose’s environmental shield.
It protects against sunlight, ozone, heat, cold, and chemical exposure—all of which can prematurely age rubber and weaken the entire assembly.
A properly formulated outer cover:
- Resists UV and ozone to prevent surface cracking.
- Maintains flexibility in sub-zero temperatures.
- Withstands oil mist, coolants, and hydraulic fluid contact.
- Prevents swelling or hardening under heat.
This environmental durability ensures the hose continues performing safely across years of service, even in outdoor, marine, or industrial conditions where unprotected materials would fail quickly.
Material Science: Deconstructing the Cover Compound
Behind every durable hydraulic hose lies chemical engineering at the molecular level. The outer cover’s strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental stress come from a precisely formulated compound — a mix of base elastomer and specialized additives that work together to protect the hose from the elements.

The Base Elastomer Foundation
At its core, the cover is made from synthetic rubber, chosen according to the application’s environmental and chemical demands.
Each elastomer offers a distinct balance of oil resistance, temperature tolerance, and weather endurance.
| Base Elastomer | Key Properties | Typical Application |
| Neoprene (CR) | Excellent weathering, moderate oil resistance | General industrial use, outdoor equipment |
| Nitrile (NBR) | Outstanding oil and fuel resistance | Hydraulic systems with frequent oil exposure |
| EPDM | Superior heat, ozone, and chemical resistance | High-temperature, outdoor, or automotive systems |
| Chloroprene/Blend Systems | Balanced performance in mixed environments | Multi-purpose or general OEM hoses |
The chosen elastomer defines the core personality of the hose cover — determining how it reacts to sunlight, chemicals, and thermal stress over time.
The Critical Additive Package
The base rubber alone cannot survive the harsh reality of industrial work. To achieve durability, engineers blend it with a precise additive package, each component performing a specialized function:
- Antioxidants and Antiozonants: Delay degradation caused by oxygen and ozone exposure, extending service life.
- Carbon Black: Adds UV resistance, tensile strength, and improved thermal stability.
- Waxes and Surface Agents: Gradually migrate to the surface, forming a thin, self-renewing barrier that shields against ozone cracking.
- Plasticizers and Process Oils: Maintain flexibility and prevent hardening in cold or aging conditions.
Together, these ingredients turn a simple rubber compound into a high-performance shield capable of resisting sunlight, heat, oil, and abrasion all at once.
Engineering for Specific Threats
Not all environments attack hoses in the same way. Manufacturers fine-tune cover compounds for specific industries and hazards, creating proprietary blends optimized for targeted performance.
- Mining Applications: Formulated with ultra-high abrasion resistance and cut protection for contact with rocks and debris.
- Marine Environments: Enhanced UV stabilization and saltwater corrosion resistance for long-term outdoor exposure.
- Forestry and Construction: Reinforced to resist tearing and impact while maintaining flexibility under vibration.
- Industrial or Factory Use: Balanced compound with high oil resistance and moderate abrasion protection for cleaner environments.
This customization ensures each hose delivers the right balance of protection and longevity, even in the harshest conditions.
Resisting the Invisible Attack: Ozone and UV Radiation
Ozone and ultraviolet (UV) light are two of the most destructive, yet invisible, forces that a hydraulic hose will face. A superior cover compound is specifically engineered to neutralize these threats and prevent premature cracking and degradation.
The Ozone Challenge
Ozone gas in the atmosphere attacks the chemical bonds in rubber, causing the material to lose its elasticity and develop characteristic cracks, especially in areas under stress (like bends). Quality covers contain antiozonants that chemically intercept and neutralize ozone molecules.
Combating the UV Threat
Direct sunlight bombards the hose with UV radiation, which provides the energy to break down polymer chains, causing the cover to fade, become brittle, and crack. High-grade carbon black is a primary additive used to absorb and dissipate UV energy safely.
The Wax Bloom Phenomenon
Many advanced hose covers are designed with protective waxes blended into the compound. Over time, these waxes slowly migrate or “bloom” to the surface, creating a microscopic, self-renewing physical barrier that shields the rubber from both ozone and UV radiation.
| Cover Performance Metric | Standard Cover (e.g., EPDM-based) | Premium “Tough” Cover (e.g., Modified CR/NBR) | Specialty Cover (e.g., UHMW-PE Film) |
| Ozone Resistance | Good to Excellent. Meets basic industry requirements. | Excellent. Enhanced with advanced antiozonant packages for high-ozone environments. | Superior. The cover material is largely inert to ozone attack. |
| UV Resistance | Good. Relies on standard carbon black content. May fade or chalk over long-term exposure. | Excellent. Higher grade of carbon black and added UV stabilizers to prevent degradation and maintain flexibility. | Superior. Inherently resistant to UV degradation, maintaining both color and physical properties. |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate. Susceptible to certain aggressive oils and solvents. | Good. Often compounded for broader resistance to common industrial chemicals and oils. | Excellent. Resists a very wide spectrum of aggressive chemicals, acids, and bases. |
| Temperature Range | Typically -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F). | Often expanded, e.g., -40°C to 121°C (-40°F to 250°F), due to a more robust polymer base. | Can be application-specific, sometimes with a more limited temperature range than rubber. |
Winning the Physical War: Superior Abrasion Resistance
In most mobile applications, abrasion is the number one killer of hydraulic hoses. The cover’s ability to withstand rubbing, scraping, and friction is directly proportional to the hose’s potential service life.
Understanding Abrasion Mechanisms
Abrasion occurs when a hose rubs against another surface, such as the machine’s frame, another hose, or external objects. This friction grinds away the cover material, eventually exposing the fragile reinforcement wires to corrosion and further damage.

Standard vs. High-Abrasion Covers
While standard covers offer baseline protection, manufacturers have developed “tough” or “abrasion-resistant” covers using advanced compounds and polymer blends. These covers can offer hundreds of times the abrasion resistance of a standard rubber cover when tested to ISO 6945 standards.
The UHMW-PE Advantage
For the most extreme abrasion scenarios, some hoses feature an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW-PE) cover. This super-slick, ultra-tough plastic material offers an exceptional level of abrasion resistance, far surpassing even the toughest rubber compounds.
Matching the Cover to the Battlefield: Application-Specific Solutions
There is no “one-size-fits-all” solution for hose protection. Selecting the correct cover type is a critical engineering decision based on a thorough analysis of the equipment’s operational environment.
Case Study: Mining Operations
The environment in a mine is highly abrasive (rock, ore, slurry) and often corrosive. The ideal hose here features a premium “tough cover” or even a UHMW-PE cover to combat abrasion, combined with excellent MSHA-rated flame resistance for safety.
Case Study: Marine and Offshore
In a marine environment, the primary threats are constant UV exposure from the sun and corrosion from salt spray. A hose with a cover featuring an advanced UV stabilizer package and robust chemical resistance to salt is essential for longevity.

Case Study: Forestry and Agriculture
Forestry equipment operates in a dynamic environment with constant rubbing against trees, branches, and debris. This demands a cover with the highest possible abrasion resistance, coupled with excellent flexibility for routing through complex machine linkages.
| Operating Environment | Primary Threat(s) | Recommended Cover Type | Essential Cover Properties |
| General Construction | Moderate abrasion, UV exposure, dynamic flexing. | Standard or Premium “Tough” Cover. | Good abrasion resistance, flexibility, solid UV/ozone performance. |
| Mining (Surface & Underground) | Extreme abrasion, high pressure, potential for oil exposure, fire risk. | Premium “Tough” Cover or UHMW-PE Cover. | Maximum abrasion resistance (ISO 6945), MSHA flame resistance, good oil resistance. |
| Marine / Offshore | High UV exposure, saltwater corrosion, humidity. | Premium Cover with advanced UV package. | Superior UV stability, resistance to salt spray and chemical degradation, low water absorption. |
| Forestry / Logging | Severe abrasion from wood, high dynamic stress, wide temperature swings. | Premium “Tough” Cover with high tensile strength. | Exceptional abrasion and cut resistance, excellent cold-weather flexibility. |
| Cold Weather / Arctic | Extreme low temperatures, ice buildup. | Specialty Low-Temperature Cover. | Material must remain flexible and not become brittle at temperatures down to -57°C (-70°F). |
Beyond the Hose: Holistic Protection Strategies
Even the most advanced hose cover has limits. Real-world systems demand layered protection, where smart installation and external guarding complement the hose’s built-in defenses. This holistic approach extends service life, minimizes downtime, and ensures the hose assembly performs reliably under every condition.
The Power of Protective Sleeving
In applications where contact and movement are unavoidable, such as hose bundles or routing along machine frames, protective sleeves provide an additional sacrificial layer.
Woven nylon or polymer sleeves absorb friction and deflect cuts that would otherwise damage the hose cover. Some high-performance sleeves also offer flame resistance or burst containment, protecting both equipment and operators in the event of hose failure.
A sleeve’s role is simple but vital: it takes the abuse so the hose doesn’t have to—a small investment that delivers significant gains in longevity and safety.

Spring Guards and Armor
Where abrasion is extreme or where hoses risk impact and crushing, metallic protection systems come into play.
- Spring guards—coiled steel wires fitted over the hose—maintain flexibility while protecting against kinks and sharp bends.
- Interlocking armor or flat wire guards provide a tougher, semi-rigid shield for hoses operating in mining, forestry, or heavy construction environments.
These guards are especially effective near connection points, where bending stress and physical interference are most severe. When correctly installed, they allow the hose to move freely while preserving structural integrity.
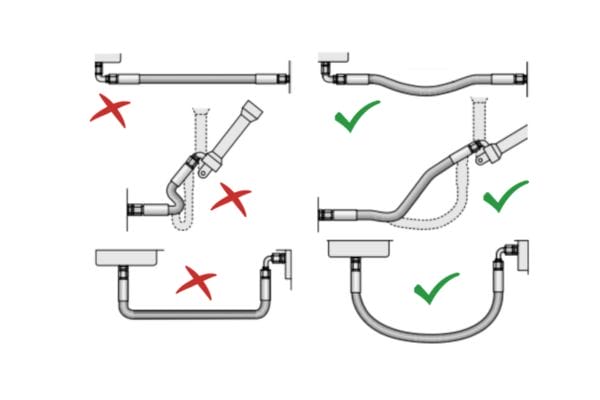
The Critical Role of Proper Routing
No amount of protection can compensate for poor installation. Proper routing remains the single most effective defense against premature hose failure.
Follow these core principles:
- Respect the hose’s minimum bend radius to avoid internal reinforcement fatigue.
- Use clamps and guides to prevent rubbing, twisting, or contact with moving parts.
- Keep hoses away from heat sources and areas with high vibration.
- Leave adequate slack for movement under pressure without tension or torsion.
A well-routed hose assembly doesn’t just look professional — it performs longer, safer, and more predictably.
FAQ
Does a faded or chalky hose cover mean the hose is bad?
It’s a clear sign of significant UV degradation. While the hose may still hold pressure, the cover has lost its flexibility and protective properties. It is brittle and can no longer effectively protect the reinforcement, so the hose should be scheduled for replacement.
What is the real difference between a “standard” and a “tough” cover?
The difference is in the compounding and testing. A “tough” cover has passed a rigorous abrasion test (ISO 6945) for a high number of cycles without failure, a test a standard cover would fail much earlier. They use more advanced, durable, and often more expensive rubber compounds.
Is it better to use a protective sleeve or just buy a hose with a better cover?
The best practice is to use a hose with a cover appropriate for the overall environment, and then use sleeving as a targeted solution for specific problem areas of extreme, localized rubbing. The sleeve acts as a secondary, low-cost sacrificial layer.
What does the MSHA rating on a hose cover mean?
MSHA (Mine Safety and Health Administration) approval means the hose cover has been tested and certified to be flame-resistant. It will not propagate a flame when exposed to an ignition source, a critical safety requirement for underground mining and other tunnel applications.
Why is my new high-abrasion hose showing scuff marks already?
Scuffing is not the same as abrasive wear. Tough covers are designed to resist material loss. Surface scuffs are cosmetic and indicate the cover is doing its job of protecting the hose from contact, without sacrificing its own structural integrity.
Can a hose cover be repaired if it’s damaged?
No. Once the cover is cut, gouged, or abraded down to the reinforcement wires, the hose’s integrity is compromised, and it must be replaced. There is no safe or reliable method for repairing the outer cover of a high-pressure hydraulic hose.